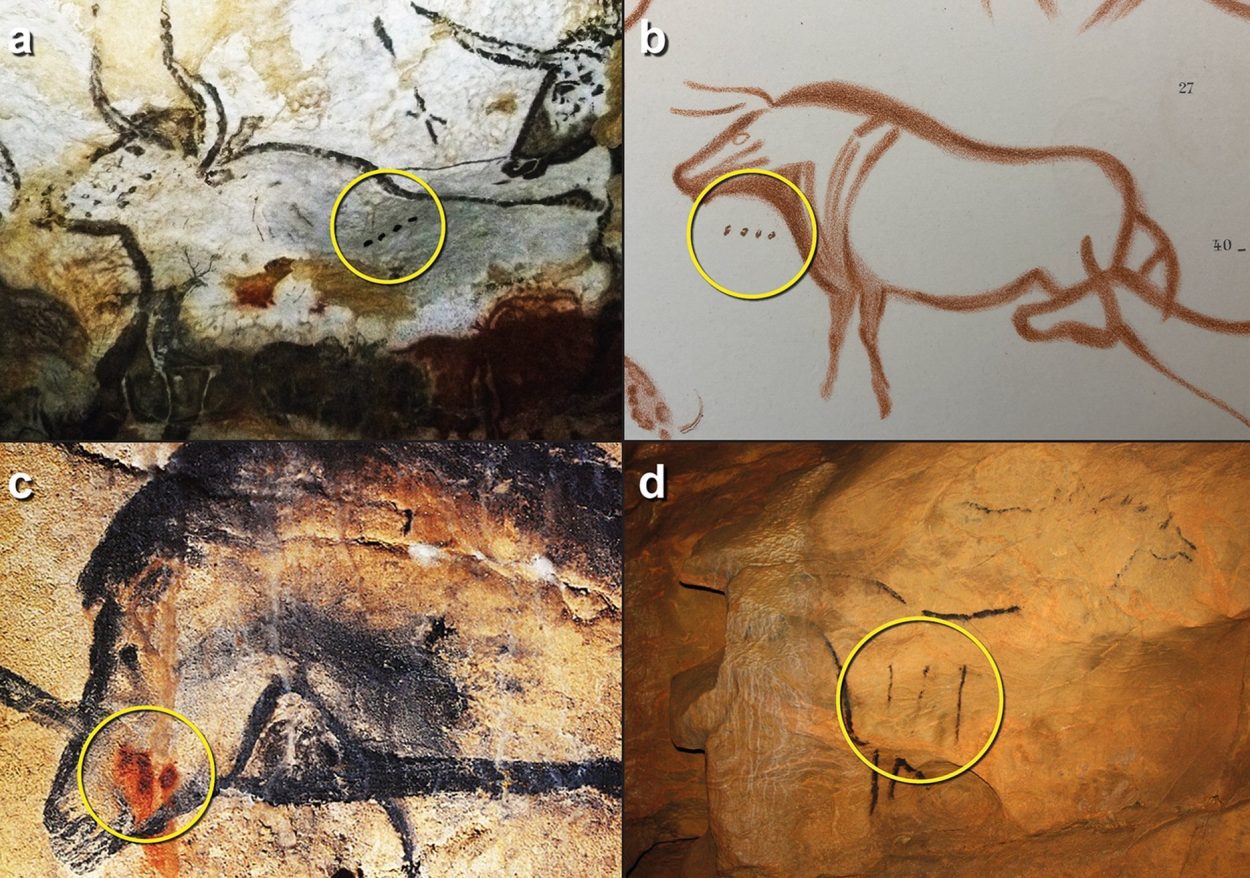
Researchers from Durham University have decoded the meaning of markings found in Ice Age drawings, providing evidence of early writing at least 20,000 years ago.
The team were studying cave art, found in at least 400 European caves such as Lascaux, Chauvet and Altamira, which contains a series of lines and dots found alongside drawings of animals.
The study, published in the Cambridge Archaeological Journal, was led by an independent researcher, Ben Bacon, and involved a small team including Durham Professors Paul Pettitt (Department of Archaeology), and Robert Kentridge (Department of Psychology).
The team has revealed that the lines and dots indicate the mating and birthing seasons of animals. A “Y” sign formed by adding a diverging line to another has also been determined to mean “giving birth”.
By using the birth cycles of equivalent animals today as a reference point, the researchers were able to work out that the number of marks associated with Ice Age animals were a phenological record by lunar month of when they were mating, as well as functioned as units of communication.
The study refers to the writing as a proto-writing system, pre-dating other token-based systems that are thought to have emerged during the Near Eastern Neolithic by at least 10,000 years.
The researchers state in their paper: “This synthesis of image, mathematical syntax (the ordinal/linear sequences) and signs functioning as words formed an efficient means of recording and communicating information that has at its heart the core intellectual achievement of abstraction.
The ability to assign abstract signs to phenomena in the world—animals, numbers, parturition, cyclical phases of the moon—and subsequently to use these signs as representations of external reality in a material form that could be used to record past events and predict future events was a profound intellectual achievement.”
Having demonstrated that they can crack the meaning of at least some of these symbols, the team is hoping to continue their work and attempt to understand more of the symbols, their cognitive bases and what information Ice Age hunter-gatherers valued.
Header Image Credit : Durham University