A new study, published in the Journal of the British Archaeological Association, reveals the story of how England’s ‘White Queen’, Elizabeth Woodville, once worshipped at the Chapel of St Erasmus.
Erasmus of Formia, also known as Saint Elmo, was a Christian saint and martyr, who died when the Western Roman Emperor Maximian, had him placed in a barrel full of protruding spikes and rolled down a hill.
He is venerated as the patron saint of sailors, child wellbeing, abdominal pain, and is also one of the Fourteen Holy Helpers, saintly figures of Christian tradition who are venerated especially as intercessors.
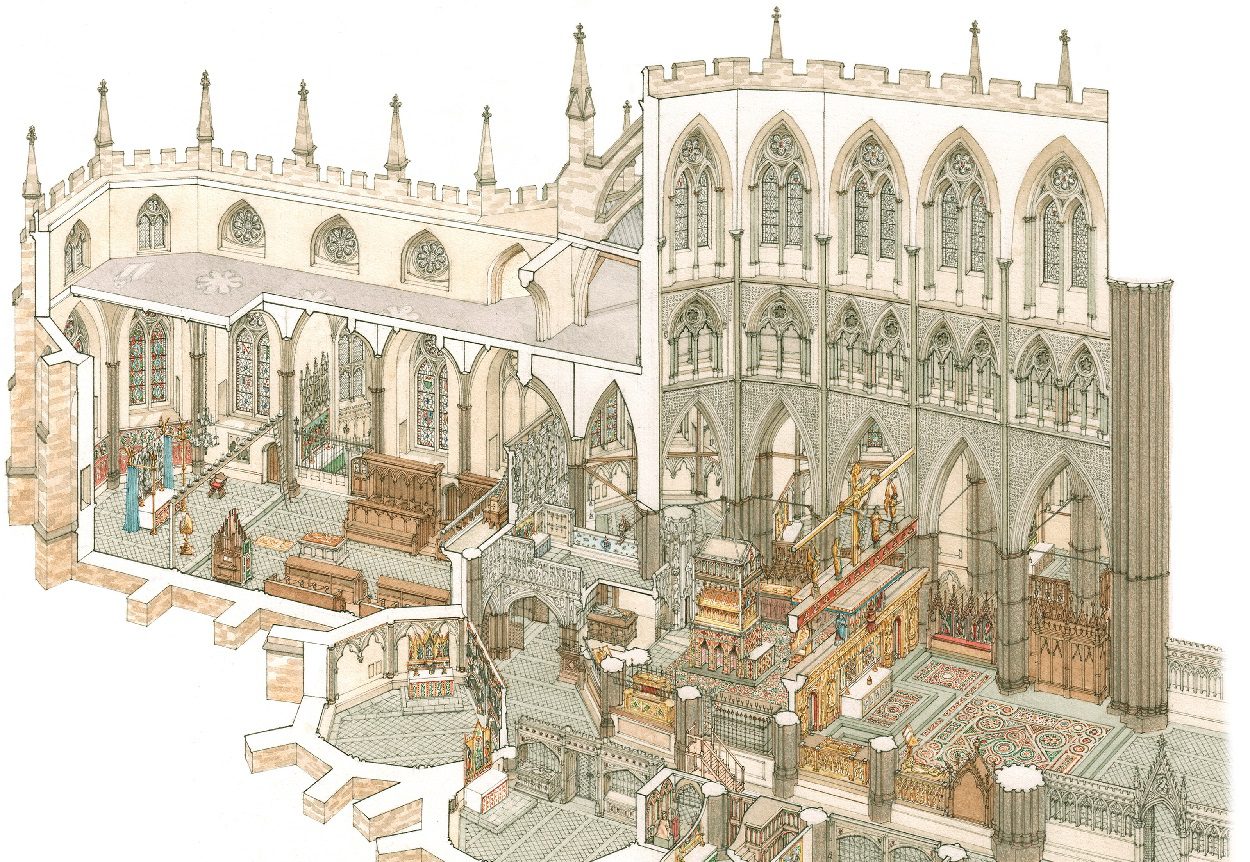
Up until now, very little was known about the chapel, which was demolished in 1502, leaving only an intricate stone frame surviving. However, an extensive study can now reconstruct what the chapel looked like, located at the east end of the Abbey church.
The chapel was constructed on the south side of the Gothic Lady Chapel in the late 1470s on space formerly allotted to a garden, and is traditionally ascribed to the generosity of Elizabeth Woodville, Edward IV’s queen, in gratitude for her periods of sanctuary at the abbey in 1470–71, and for the health of her children.
The chapel likely contained gruesome images of the saint’s death, as well as one of his teeth, among other relics that were stored there.
Commenting on the prominence of the chapel, the Abbey’s archivist Matthew Payne, said: “The White Queen wished to worship there and it appears, also, to be buried there as the grant declares prayers should be sung ‘around the tomb of our consort (Elizabeth Woodville).
The reconstruction was created by Stephen Conlin, based on all available knowledge about the interior and fittings prior to the chapel’s construction, and previously unrecognised fragments surviving in the roof space of the antechapel. Some of the reconstruction is also derived from St George’s, Windsor, and the colouring of the interior draws on the recently identified colour copy of the mortuary roll of Abbot Islip drawn up in 1532.
The study presents further evidence that the reredos was created by an outsider to the Abbey’s design tradition. Architect Robert Stowell, the Abbey’s master mason, probably designed the chapel itself and may have helped salvage the chapel’s most ornate pieces when it was knocked down after less than 25 years.
https://doi.org/10.1080/00681288.2022.2101237
Header Image Credit : Stephen Conlin