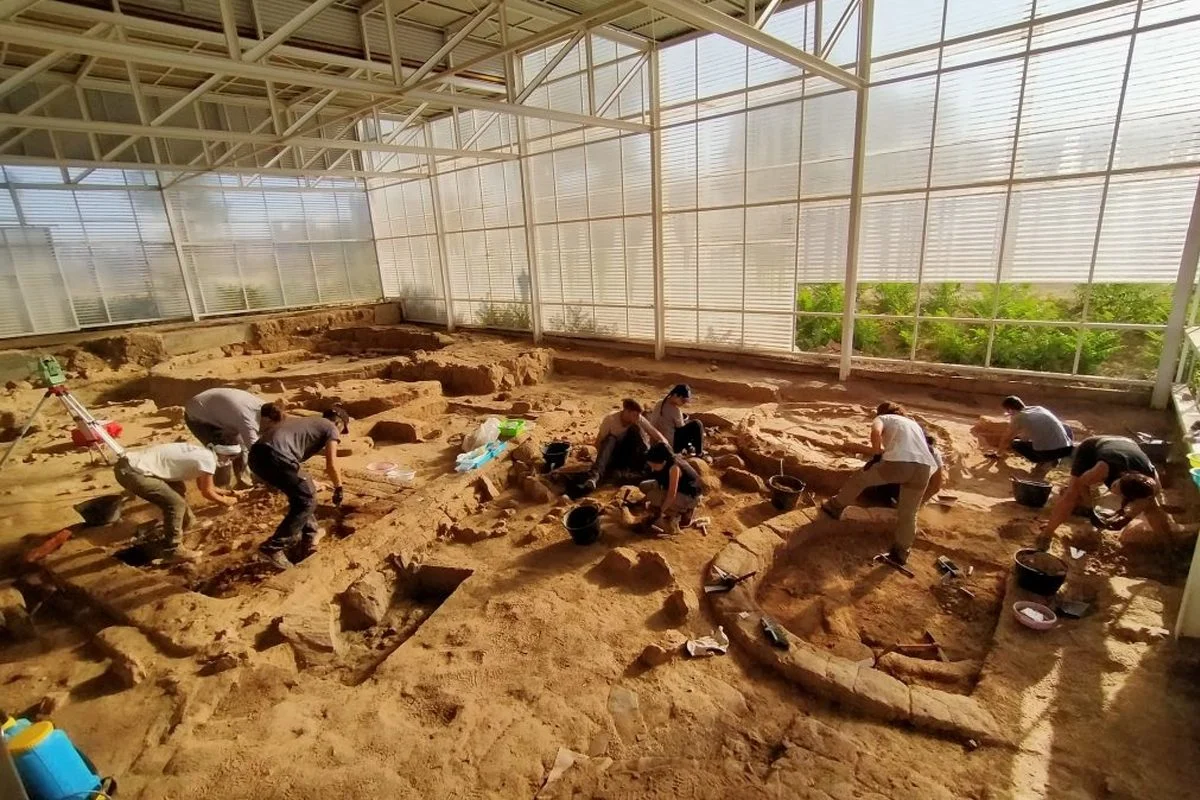
Archaeologists excavating a 2,700-year-old Iron Age settlement in Salamanca, Spain, have uncovered a fragment of an Ancient Egyptian goddess.
The team were excavating on the Cerro de San Vicente, one of three hills in Salamanca, where a walled Iron Age settlement was first uncovered in 1990. The settlement covers an area of 3.2 acres, of which archaeologists have so far explored 1000 square metres over the past three decades.
In the latest excavation, led by Antonio Blanco and Juan Jesús Padilla from the University of Salamanca, the team uncovered amulets and painted ceramics, featuring motifs of Egyptian or other eastern Mediterranean origins.
The ceramics are part of a glazed ceramic inlay with gold leaf, depicting the goddess Hathor who was worshiped as the consort of the sky god Horus and the sun god Ra, both of whom were connected with kingship, and thus she was the symbolic mother of their earthly representatives, the pharaohs. The pieces form a fragment that is around five centimetres in length, showing the bottom section of the goddess’s hair with her curls plainly visible.
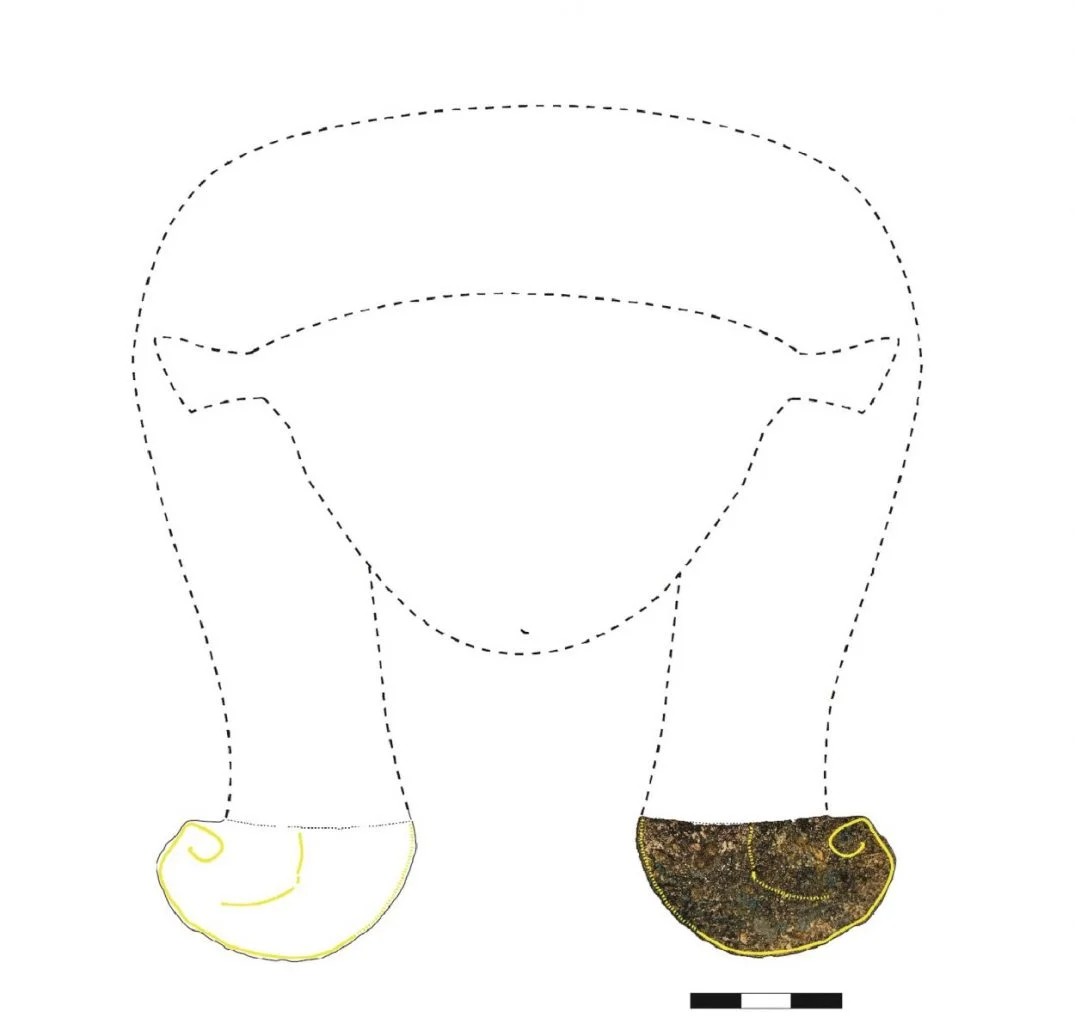
Speaking to El Pais, Padilla said: “Each piece was shaped to fit perfectly into its support base. Then, with a kind of resin or adhesive, they were glued into place. We are currently analysing the piece in our laboratory to see if there are any traces of this glue still on the inner surface, to determine what kind of resin was used.”
Archaeologists found the ceramics deliberately placed within the walls of a large rectangular hall (megaron). They were positioned among the adobe blocks and mud grout, along with a shark’s tooth, necklace beads, and a piece of an amphora which is decorated with floral motifs painted in Egyptian blue.
How a depiction of Hathor found its way to an Iron Age site in Spain is an enigma. The team suggest that a Phoenician delegation may have brought the artefact as a gift or to trade, however, there is also the possibility that the inhabitants of the settlements had adopted the rites and iconography of far reaching eastern Mediterranean cultures. Both theories are supported by previous excavations, where in 2021 the team also uncovered a blue amulet that also depicts Hathor.
Header Image Credit : University of Salamanca





