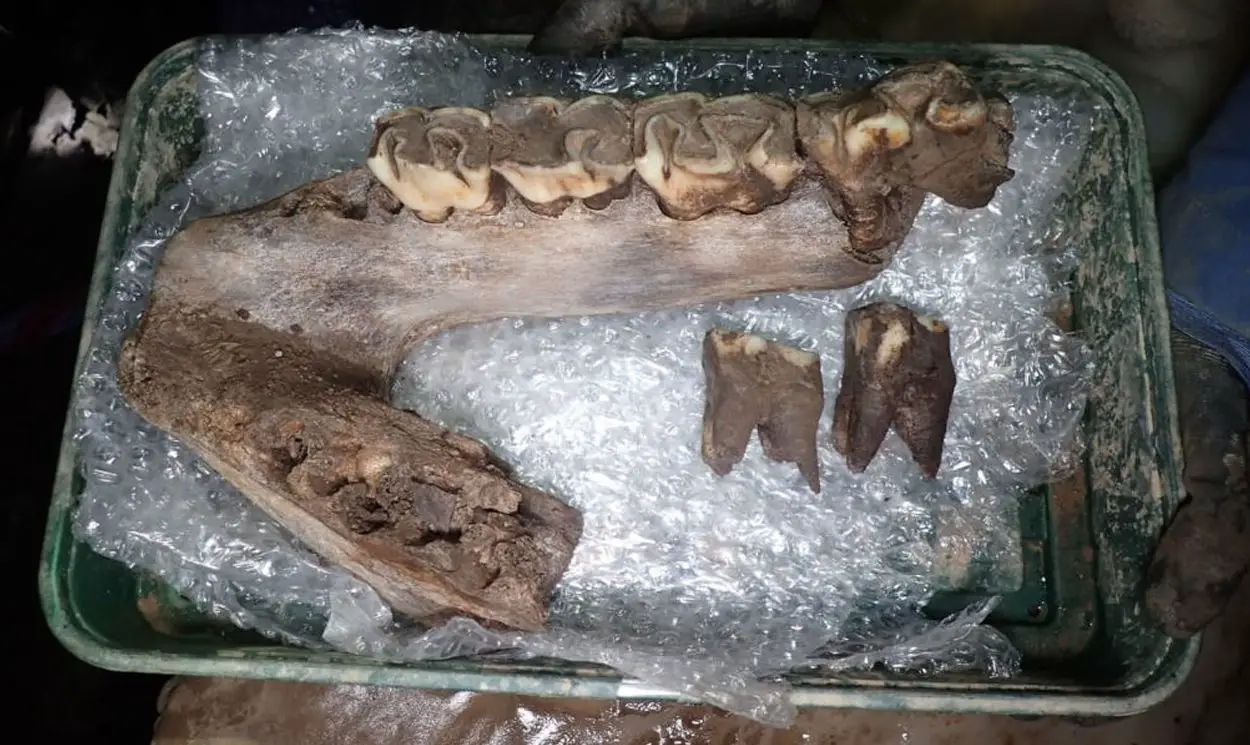
The bones of woolly mammoths and woolly rhinoceros are amongst the animal remains discovered in a cave near Plymouth, UK.
The cave was uncovered during the construction of a new housing estate in Sherford, Plymouth, offering a glimpse into an ancient ecosystem from between 60,000 and 30,000 years ago during the middle of the last Ice Age.
Excavations of the remains was conducted by Orion Heritage, Exeter-based AC Archaeology, and multiple expert academics, supported by the South West Science Advisor from Historic England.
The researchers unearthed a tusk, molar tooth and other bones from a woolly mammoth, an incomplete skull and lower jaw from a woolly rhinoceros and an almost complete wolf skeleton.
Partial remains uncovered include a hyena, horse, reindeer, mountain hare, bats, shrews and a red fox. It is anticipated that further bones of small mammals will be identified during post-excavation laboratory analysis.
Whether all of the creatures found in the cave coexisted in a similar time period, or existed at different points over a much longer time span is uncertain. One theory is that some of the creatures fell into a pit and were unable to escape, and carnivorous scavengers followed and met a similar fate – or the animals died elsewhere, and the bones washed into the area over a period of time.
Duncan Wilson, Chief Executive of Historic England, said: “This discovery is exceptional. To have found partial remains of such a range of species here in Devon gives us a brilliant insight into the animals which roamed around Ice Age Britain thousands of years ago, as well as a better understanding of the environment and climate at the time. We are delighted that this important part of our history will be preserved for future generations.”
Header Image Credit : The Sherford Consortium/AC Archaeology