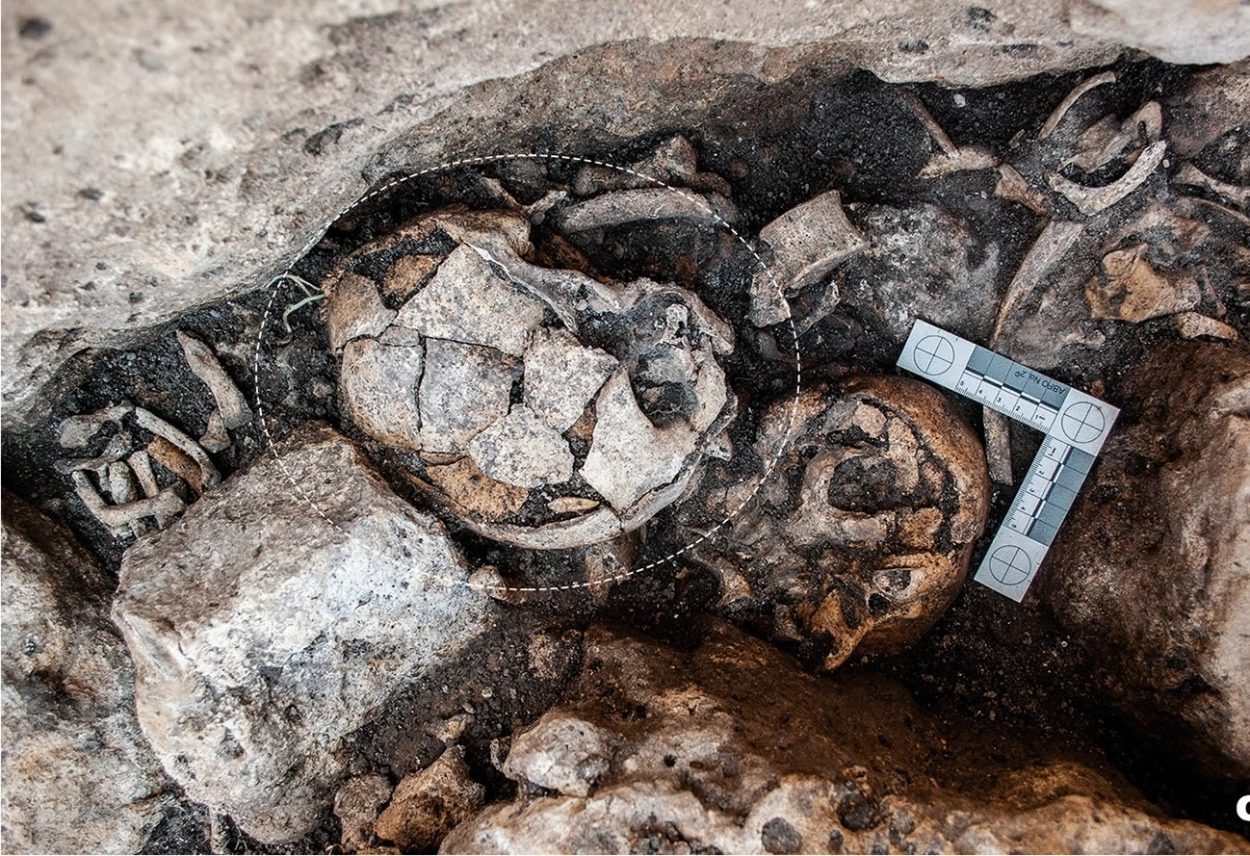
A team from the University of Valladolid have published in the journal ‘Scientific Reports’, evidence of the first successful ear surgery from excavations conducted at the ‘El Pendón’ dolmen located in Reinoso, Northern Spain.
The study of the megalithic monument from the 4th millennium BC was led by Manuel Rojo Guerra, where the researchers found an ossuary containing the remains of over a hundred individuals who suffered from diverse pathologies and injuries. Carbon 14 dating suggests that the dolmen was used for around 800 years between 3,800 and 3,000 BC for burial.
Amongst the remains was the skull of a woman with two bilateral perforations on both mastoid bones, suggesting that she had undergone surgery to eliminate infections of the middle ear.
A surface histological analyses confirmed that the woman survived the procedure, making the operation the first documented successful otological surgery in history performed around 5,300 years ago. The hypothesis of surgical intervention is also supported by the presence of cut marks at the anterior edge of the trepanation made in the left ear.
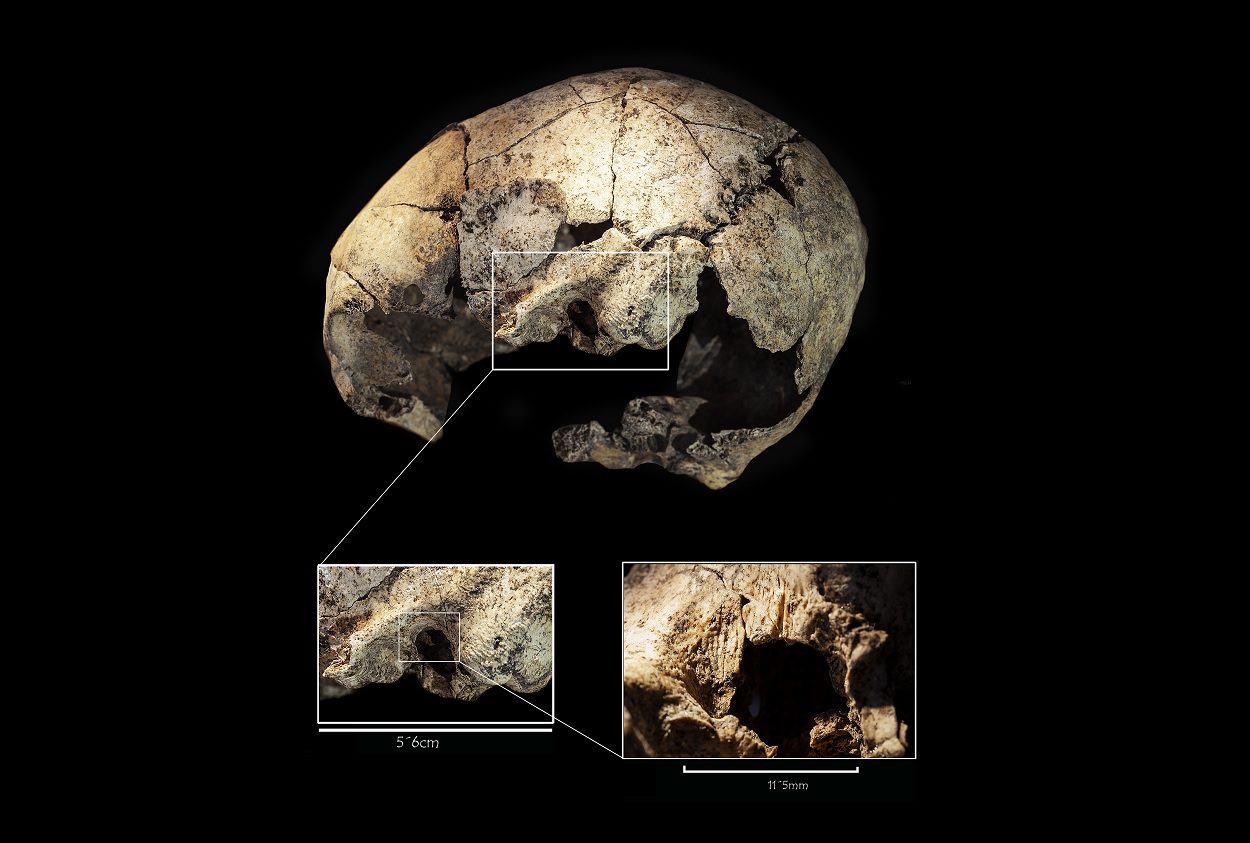
Rojo Guerra told DICYT that this type of intervention “must have been carried out by specialists or individuals with certain anatomical knowledge and accumulated therapeutic experiences.”
The study notes, that given the pre-metallurgical chronology of the site, this surgical intervention had to be performed with a lithic instrument. Several tools made of flint were deposited at the site as grave goods or ritual offerings, consisting of simple and retouched blades of different sizes, geometric microliths and arrowheads of different shapes. Find out more
Header Image Credit : ÑFotógrafos Photography Stud





