Archaeologists studying the Israeli site of Ohalo II, a previously submerged fisher-hunter-gatherer camp on the shores of the Sea of Galilee from 23,500-22,500 years ago, suggest that the ancient inhabitants thrived at the end of the last Ice Age.
During the Last Glacial Maximum, ice sheets profoundly affected the Earth’s climate by causing drought, desertification, and a large drop in sea levels. Ironically enough, Ohalo II was discovered in 1989 following drought conditions that lowered the water level of the Sea of Galilee by several meters.
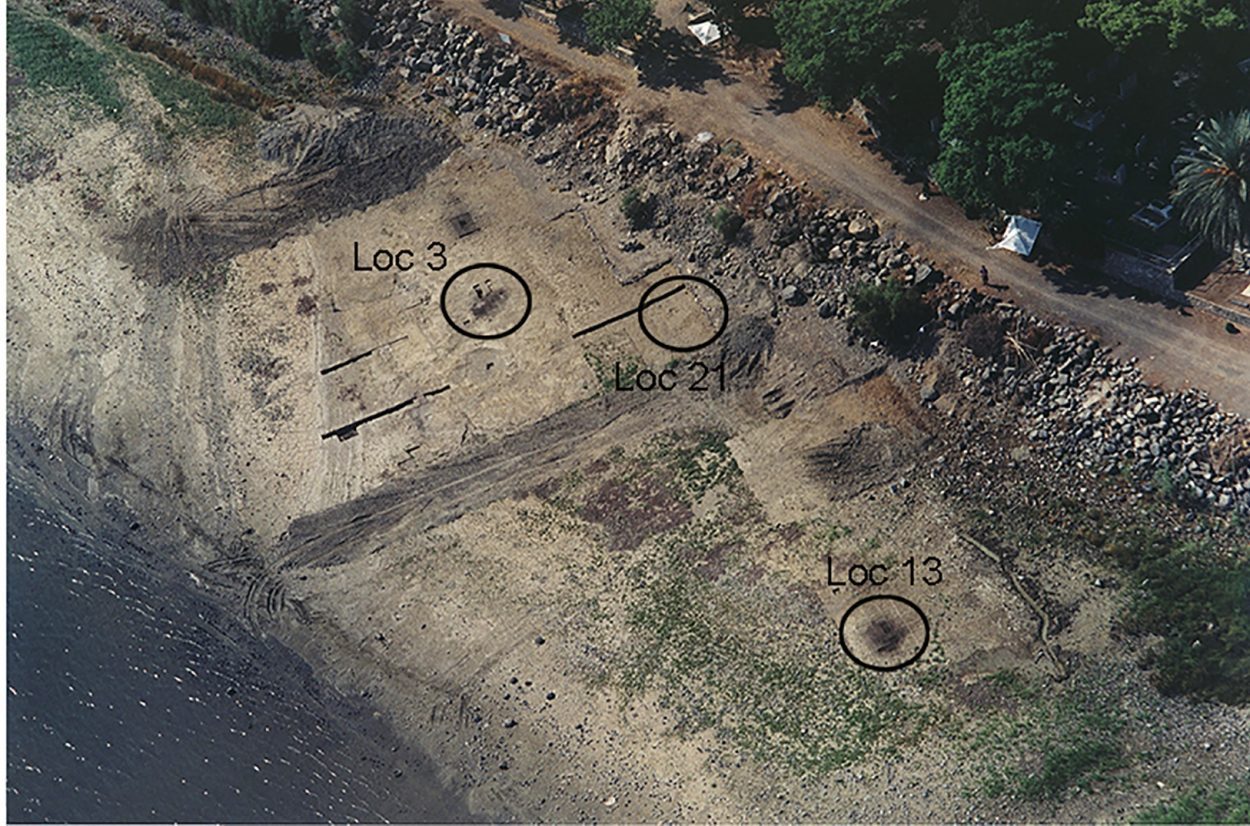
Excavations were carried out between 1989-1991, and again between 1998-2001. The site covers 2000 meters and contains the remains of six oval-shaped brush huts, open-air hearths, the grave of an adult male, as well as various installations and refuse heaps.
In a new study published in PLOS ONE by the Hebrew University of Jerusalem (HU)’s Institute of Archaeology team, the researchers examined the diet and extensive use of animal parts to determine the welfare and lifestyle of these ancient inhabitants.
Through a close analysis of the abundance, variety and through use of animal remains, the team concluded that people living at Ohalo II had survived the latest Ice Age and thrived, whereas most other contemporaries across the continents had nearly starved due to the extreme weather conditions.
From a close analysis of 22,000 animal bones found at the site, including gazelles, deer, hares, and foxes, as well previous documentation regarding the number of charred plant remains, flint tools, cereal grains found there which signify a robust diet and lifestyle, the team concluded that Ohalo II presents a different picture of subsistence than most other early Epipaleolithic sites.
The researchers believe that the findings from the site do not indicate a decline in the availability of food during this period but rather a rich diversity of food sources. In this way, Ohalo II is a wonderful example of a true broad-spectrum economy during the latest Ice Age, at the very beginning of the Epipaleolithic period.