A fetus previously identified in a mummified Egyptian woman has remained preserved for more than 2,000 years due to an unusual decomposition process.
In April 2021, the Warsaw Mummy Project published an article that revealed the first known case of a pregnant Ancient Egyptian mummy.
The mummy, which is housed in the National Museum in Warsaw was previously thought to be the remains of the priest Hor-Djehuti, until it was discovered in 2016 to be an embalmed woman.
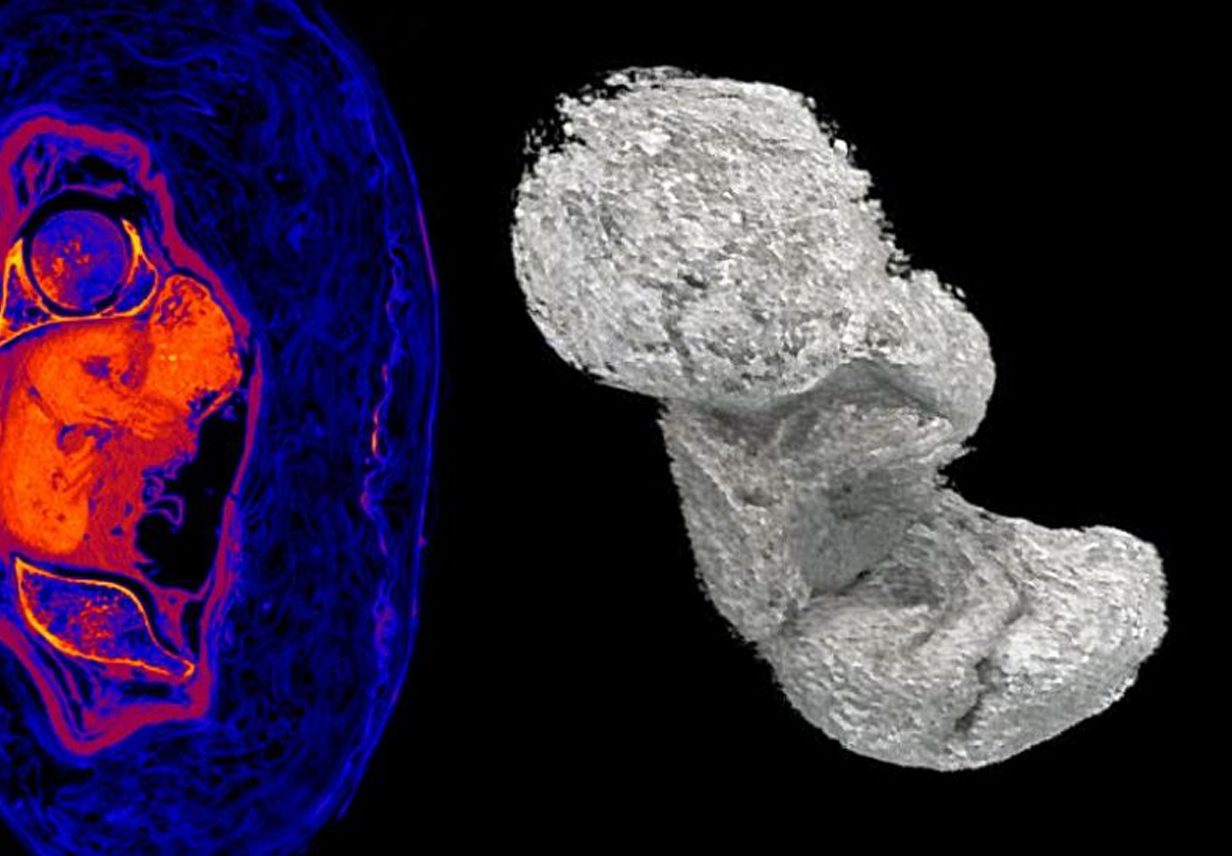
A closer examination using tomographic imaging revealed that the woman was between 20-30 years old when she died and was in her 26th to 30th week of her pregnancy.
In a new study published in the “Journal of Archaeological Science”, Ożarek-Szilke, co-director of the Warsaw Mummy Project explained that the deceased was covered with natron to dry the body.
Natron is a naturally occurring mixture of sodium carbonate decahydrate (Na2CO3·10H2O, a kind of soda ash) and around 17% sodium bicarbonate (also called baking soda, NaHCO3) along with small quantities of sodium chloride and sodium sulfate.
During this process, the fetus was still in the uterus and essentially began too “pickle” in an acidic environment. Formic acid and other compounds (formed after death in the uterus because of various chemical processes related to decomposition) changed the Ph inside the woman’s body.
The change from alkaline to an acidic environment caused the leaching of minerals from the fetal bones, which began to dry out and mineralise. According to the researchers, the process of Egyptian mummification from a chemical point of view is the process of mineralisation of tissues that can survive for a millennia.
Ożarek-Szilke said: “These two processes explain to us why you hardly see the bones of the fetus in CT scans. You can see, for example, hands or a foot, but these are not bones, but dried tissues. The skull, which develops the fastest and is the most mineralised has been partially preserved.” Find out more
Header Image Credit : M. Ożarek-Szilka / Affidea