A project led by the University of Bradford, involving 15 universities and 63 heritage collections, will bring the prehistoric landscape of Doggerland back to life using advanced mapping techniques.
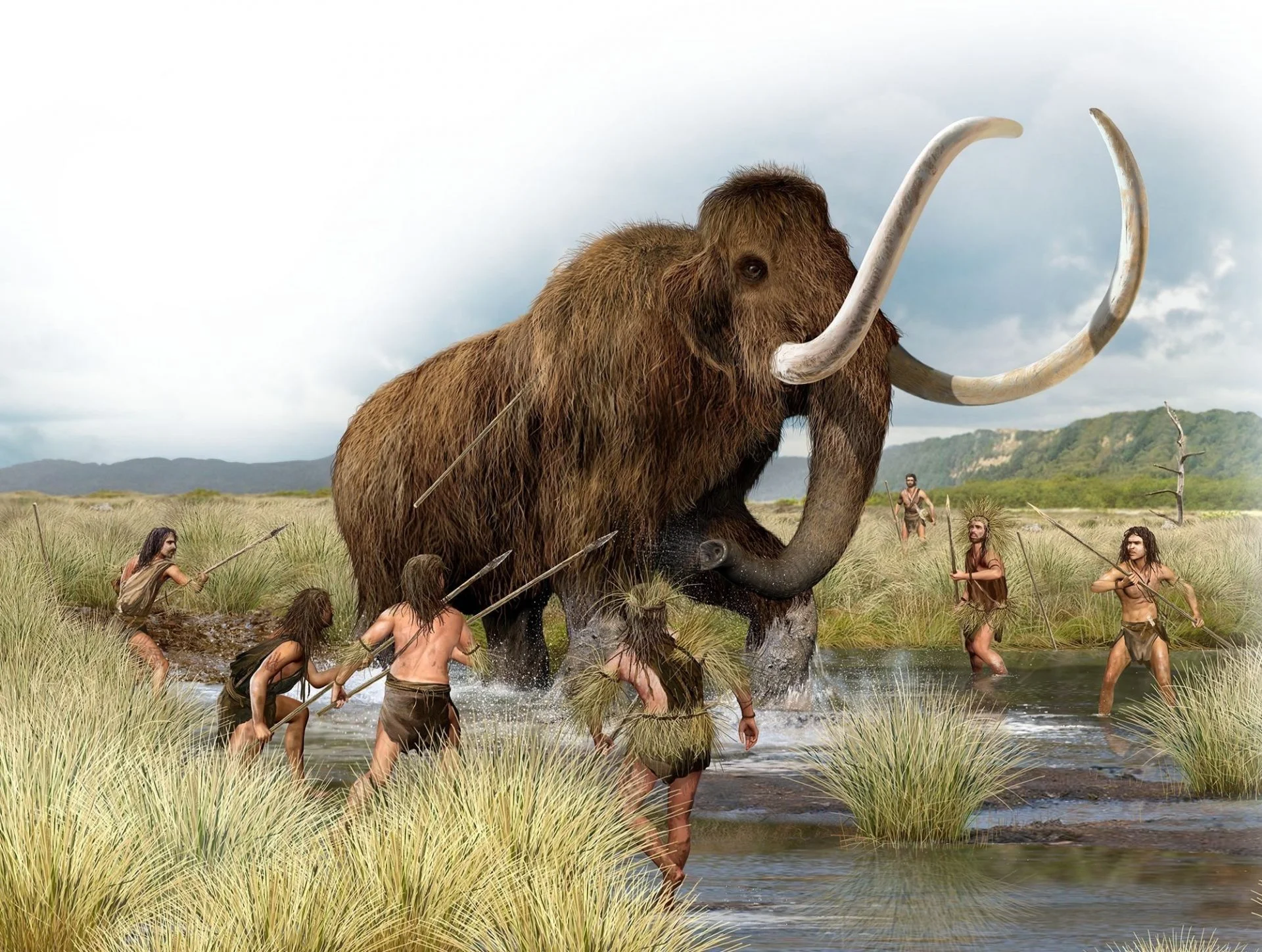
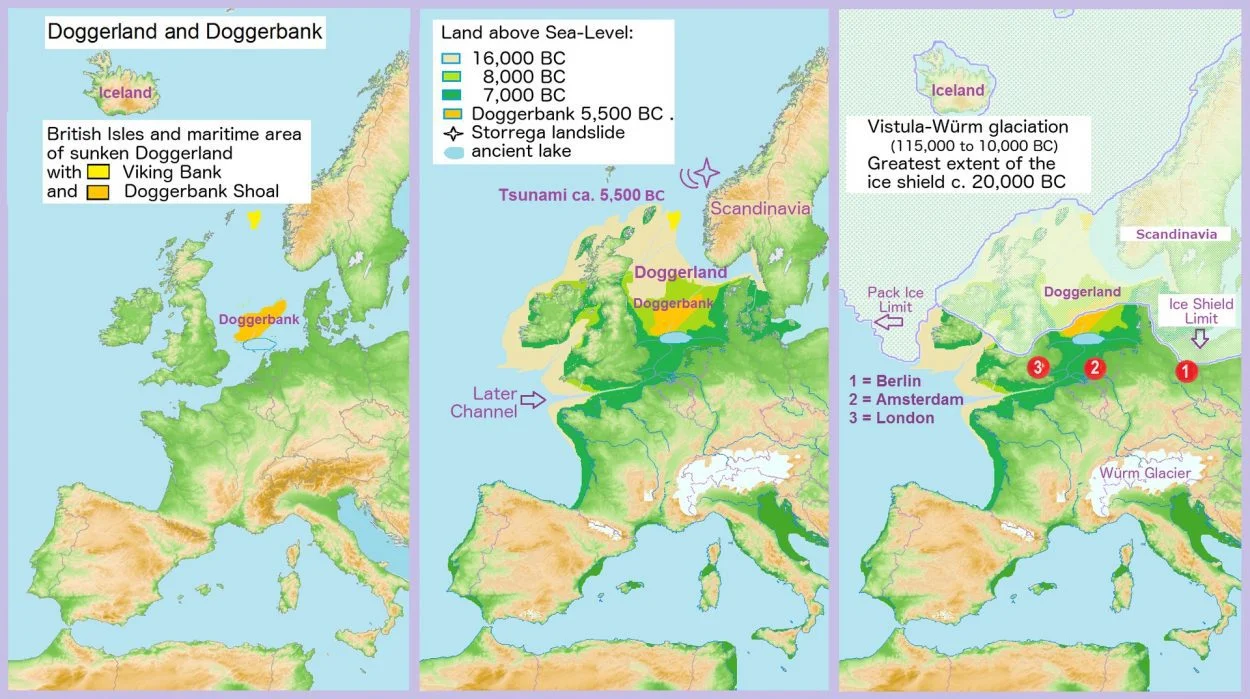
Doggerland is a submerged land mass beneath what is now the North Sea, that once connected Britain to continental Europe. The landscape was a diverse mix of gentle hills, marshes, wooded valleys, and swamps, inhabited by Mesolithic people who took advantage of the rich migrating wildlife and seasonal hunting grounds.
With the melting of ice at the end of the last glacial period, sea levels across the world rose, and the land began to tilt in an isostatic adjustment as the huge weight of ice lessened, submerging Doggerland beneath the sea.
As part of a £14.5m five-year initiative funded by the Arts and Humanities Research Council (AHRC), researchers are using machine learning and AI, to create cross-collection searching across dispersed historical data, archives, and maps, which aims to make the UK’s maritime heritage more accessible through an interactive mapping interface.
Professor Vince Gaffney said: “This is a massive project that will help preserve our national heritage archives and make them much more accessible. We are part of the group pulling together the marine archive. We will be looking at the underwater landscapes of the North Sea, which up until about 8,000 years ago was above water. People lived on this land. We know this because chance finds from the seabed have included stone tools, human remains and a variety of other man-made objects.”
Gaffney added “The team at Bradford has spent the last five years mapping the seafloor as part of a major European-funded project and we’re just at the stage now where we’re able to pinpoint where we believe settlements may have been.”
As well as providing information for developers on the North Sea to safeguard undiscovered underwater archaeological sites, the projects creation of a digital map will reveal what Doggerland’s landscape once looked like.
Prof Gaffney said: “The idea is to create an interactive map so people can explore the impact of climate change on the landscape since the last ice age. This will be online and accessible and will act as a springboard for new research.”
Header Image Credit : cloudinary.com – CC BY-SA 4.0





