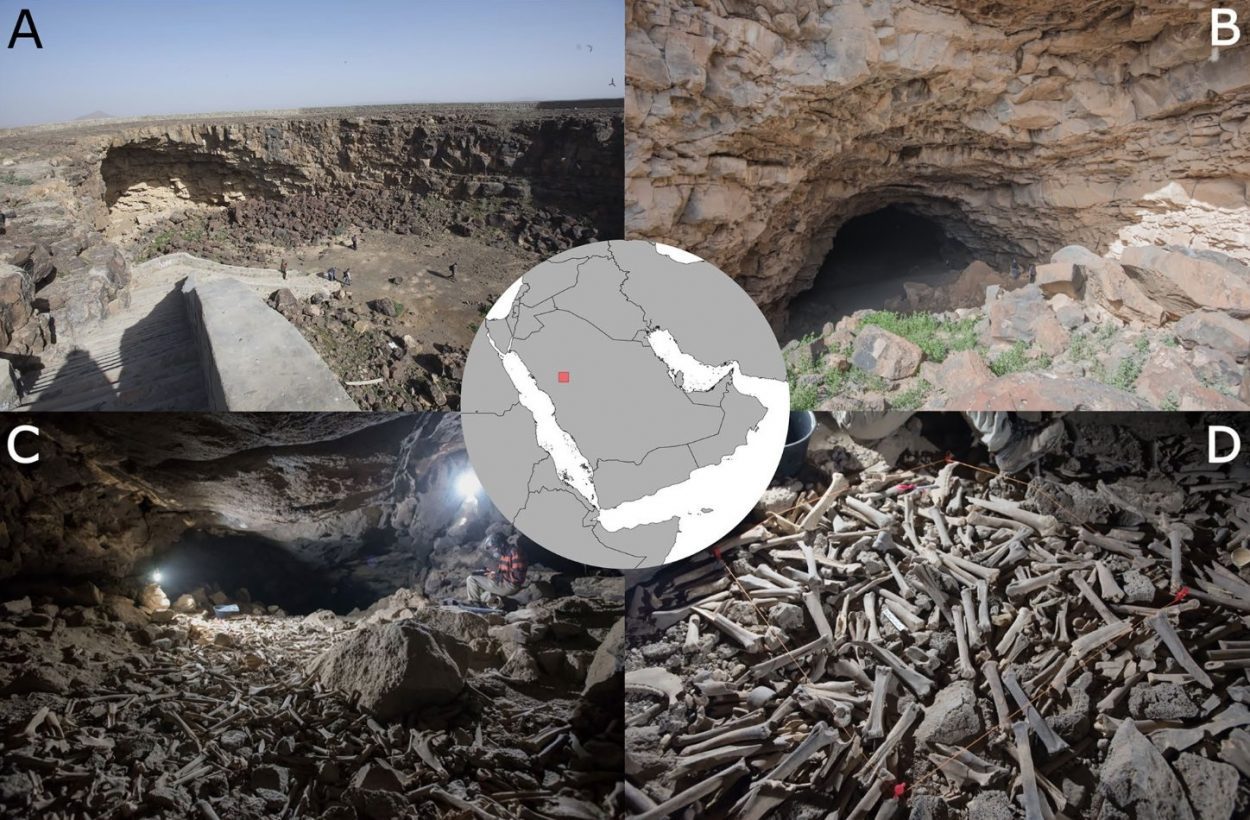
Archaeologists conducting research in Arabia’s longest lava tube system, has found thousands of bones deposited by hyenas.
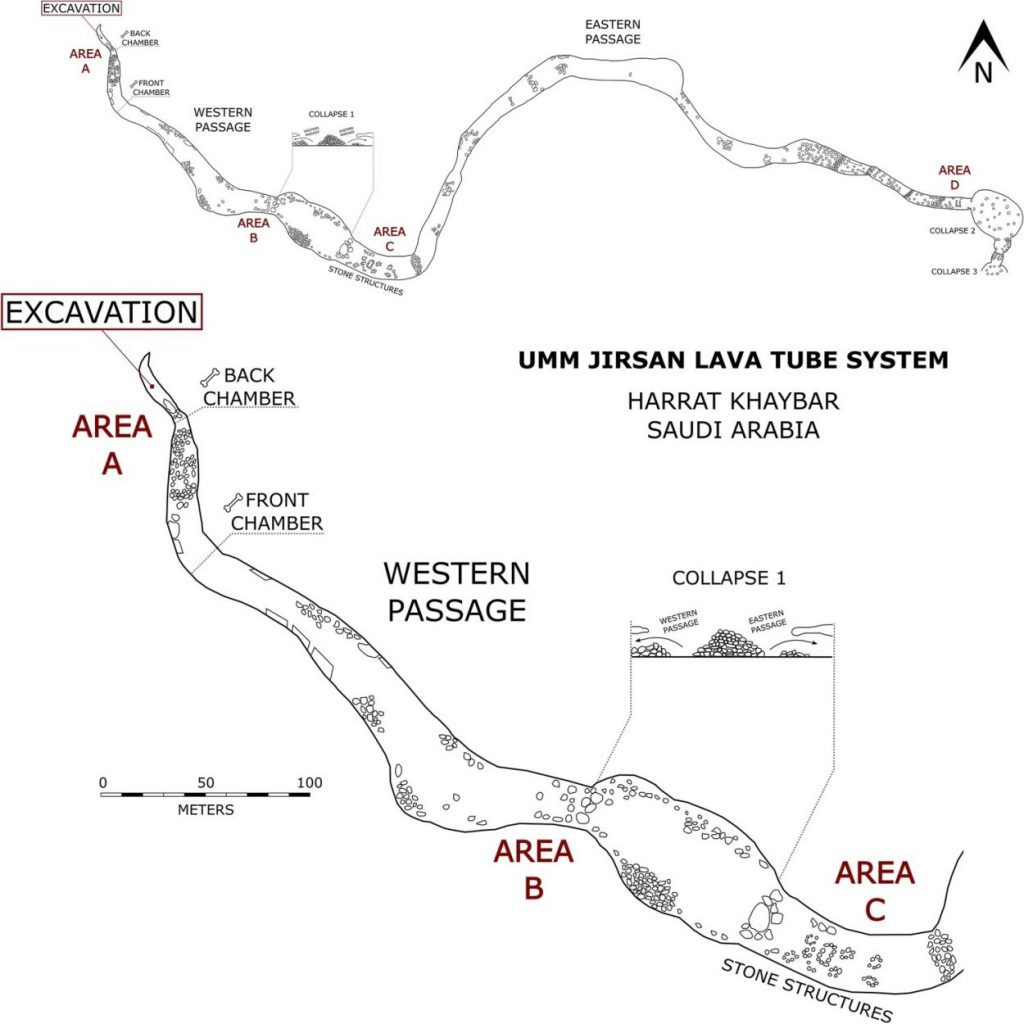
The Umm Jirsan lava tube system is located in the Harrat Khaybar Lava Field, 130 km north of Medina in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
Taphonomic studies of fossil bone accumulations as part of the ‘Palaeodeserts Project’ to track human and animal migration across the Arabian Peninsula, has identified hundreds of thousands of bone accumulations consisting of over 40 different species, including horses, asses, cattle, camels, rodents, caprids, and even humans.
Although the lava-tube was discovered in the mid-2000s, only recently did researchers venture deeper into the tube system, where the bone accumulations were found.
Experts believe that the bone accumulation was deposited by hyenas using the lava system as a den, where carcasses and carcass parts were transported to and fed on over a period spanning 7,000 years.
The presence of hyena skeletal remains and coprolites, suggest that the assemblage was primarily accumulated by striped hyena (Hyaena hyaena).
The researchers said: The material dates back as far as ~ 7000 years, highlighting the exceptional preservation within the lava tube, and the potential for future research at Umm Jirsan and other nearby lava tubes.
These findings highlight the need for continued neo-taphonomic studies for capturing the full variation of carnivore bone-accumulating and modifying behaviour. Such sites have the potential to inform on the paleoecology and prehistory of this understudied region.”
Header Image Credit : Stewart et al. / Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences, 2021





