A study of the pigments used in wall paintings in the Cueva Ardales caves in southern Spain originated from Neanderthals.
The cave was discovered in 1821, when an earthquake exposed the cave entrance. In 1918, the famous prehistorian Henri Breuil visited the cave and discovered the first Palaeolithic paintings and engravings.
The research, “The symbolic role of the underground world among Middle Palaeolithic Neanderthals” published in PNAS (Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America) was conducted by Àfrica Pitarch Martí and her colleagues from Collaborative Research Center 806 “Our Way to Europe”, where they performed a geoscientific analyses on red pigments from a massive stalagmitic pillar in the cave system.
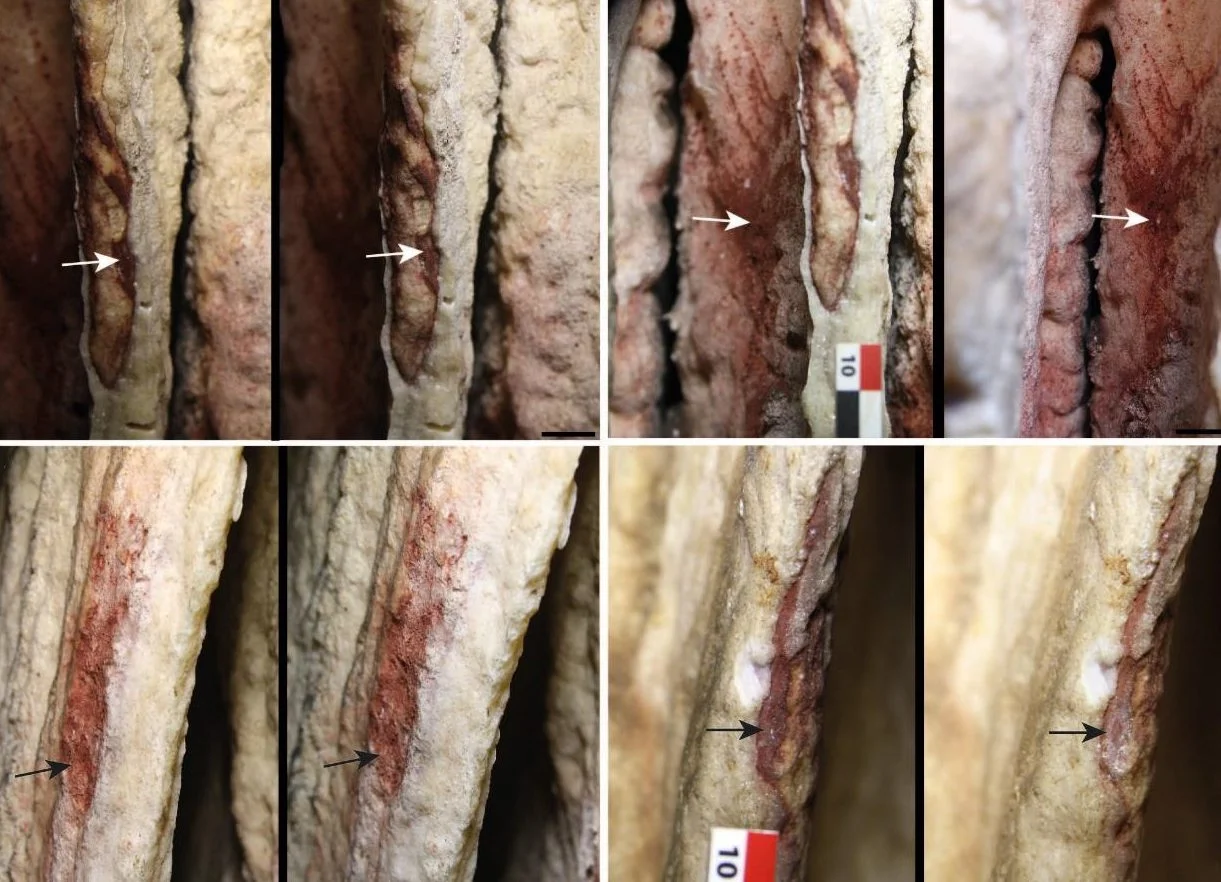
The edges of the pillar show an entire series of narrow sinter plumes. In these sinter curtain alone, red paint spots, dots, and lines were applied in 45 places.
The objective was to characterise the composition and possible origin of the pigments. The results showed that the composition and arrangement of the pigments cannot be attributed to natural processes, but that they were applied by spraying and in some places by blowing.
The researchers found that the nature of the pigments does not match natural samples taken from the floor and walls of the cave, suggesting that the pigments were brought into the cave from outside.
Dating of the pigment suggests that they were applied on two separate occasions, the first being more than 65,000 years ago, whilst the other has been dated to 45,300 and 48,700 years ago during the period of Neanderthal occupation.
According to the authors, these are not art in the strict sense, but rather markings of selected areas of the cave whose symbolic meaning is unknown.
Header Image Credit : Africa Pitarch Martí