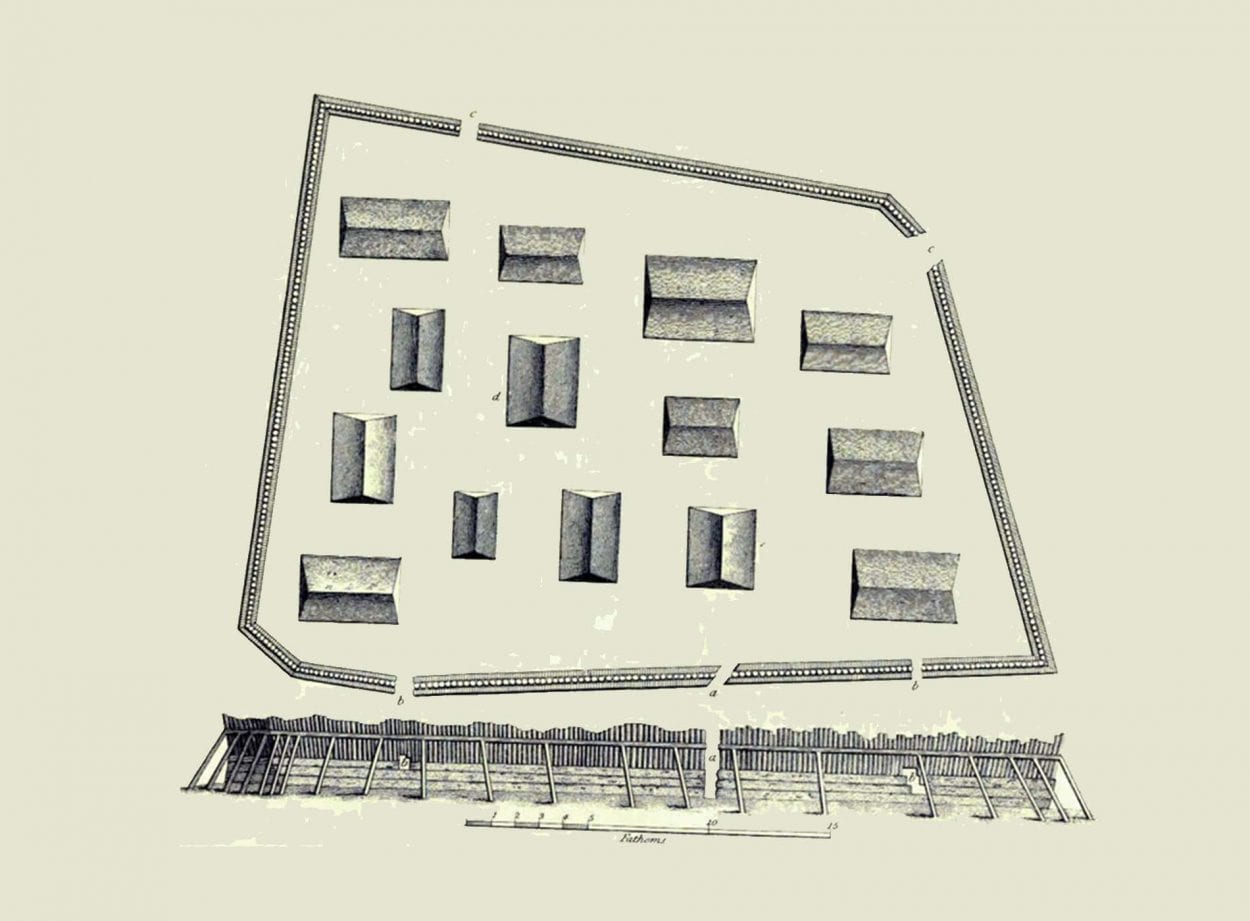
Researchers from Cornell University and the National Park Service have discovered the remnants of a wooden fort in Alaska – the Tlingit people’s last physical bulwark against Russian colonisation forces in 1804.
The Tlingit built what they called Shiskinoow – the “sapling fort” – on a peninsula in modern-day Sitka, Alaska, where the mouth of Kasda Heen (Indian River) meets Sitka Sound at the Sitka National Historical Park. The fort was the last physical barrier to fall before Russia’s six-decade occupation of Alaska, which ended when the United States purchased Alaska in 1867 for $7 million.
Thomas Urban, researcher at Cornell University said: .“The fort’s definitive physical location had eluded investigators for a century. Previous archaeological digs had found some suggestive clues, but they never really found conclusive evidence that tied these clues together.”
The researchers discovered the site using geophysical imaging techniques and ground-penetrating radar (a non-intrusive method that uses radar pulses to image the subsurface). To find Shiskinoow, Urban created a grid to see if the electromagnetic induction methods could spot the potential outline of the fort and then created a small grid for dragging the ground penetrating radar.

“We believe this survey has yielded the only convincing, multi-method evidence to date for the location of the sapling fort, which is a significant locus in New World colonial history and an important cultural symbol of Tlingit resistance to colonization,” Urban said. In 1799, Russia sent a small army to take over Alaska in order to develop the fur trade, but the Tlingit successfully expelled them in 1802. Expecting the Russians to return, the Tlingit built a wooden fort over two years – the trapezoidal-shaped Shiskinoow.
The Tlingit armed it with guns, cannons and gunpowder obtained from British American traders. When the Russians returned in 1804, the Tlingit held them off for five days, but suffered a setback when a gunpowder supply being carried to the fort from storage across Sitka Sound blew up in a canoe.
The Tlingit clans escaped Shiskinoow by night across Shee (Baranov Island) to Cháatl Ḵáa Noow (Halibut Man Fort) and the Russians then established a trading post at what is now Sitka. “A large-scale survey was necessary to convincingly rule out alternative locations for this historically and culturally significant structure,” said co-author Brinnen Carter of the National Parks Service.