Doggerland, dubbed “Britain’s Atlantis” is a submerged landmass beneath what is now the North Sea, that once connected Britain to continental Europe.
The landscape was a diverse mix of gentle hills, marshes, wooded valleys, and swamps, inhabited by Mesolithic people who took advantage of the rich migrating wildlife and seasonal hunting grounds.
Fishing trawlers operating in the area have recovered a rich fauna of mammoths, lions, and other animals, and several prehistoric tools and weapons. Doggerland was named in the 1990s, after the Dogger Bank, which in turn was named after the 17th-century Dutch fishing boats called “doggers”.
Around 8,000 years ago, the North Sea coast of Britain and Doggerland was struck by a massive tsunami caused by the Storegga Slides, a series of underwater landslips (the largest known from the Holocene) at the edge of Norway’s continental shelf in the Norwegian Sea.
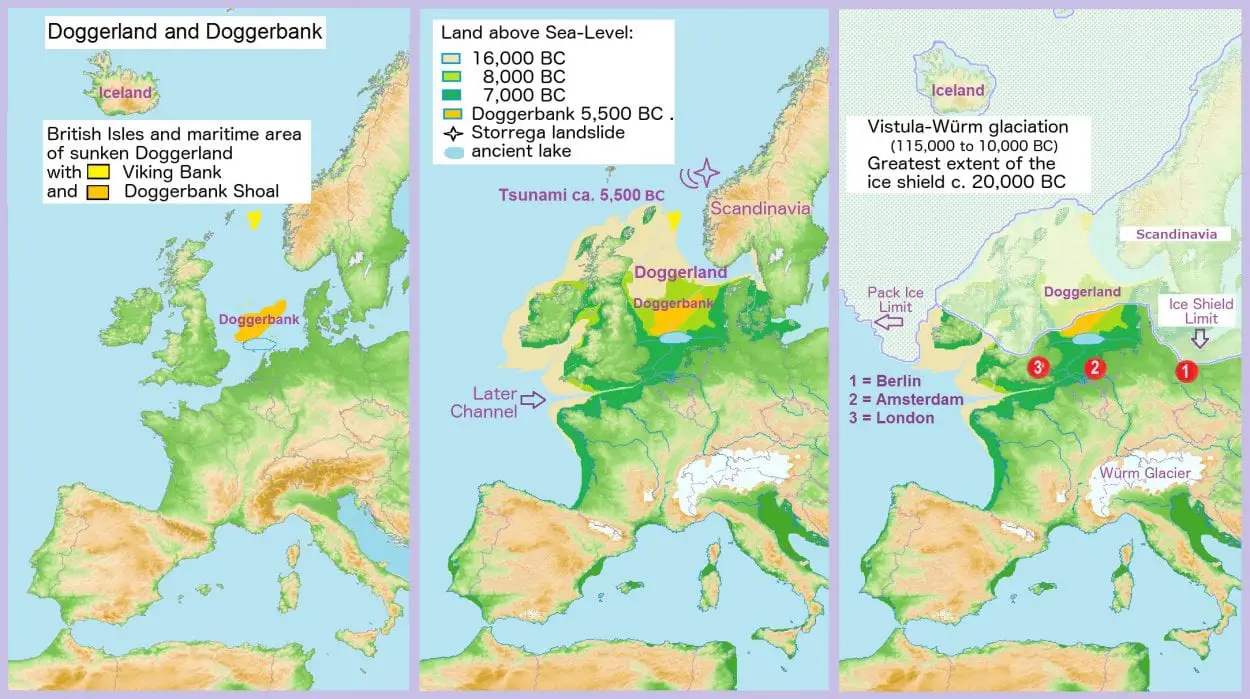
The tsunami devasted vast areas of land, with academics proposing that the tsunami finally submerged Doggerland (which was already partially flooded by rising sea levels from the last ice age).
Researchers from Europe’s Lost Frontiers project, comprised of scientists from the UK and Estonia have been studying plant remains, isotopes, and sediments from core samples extracted from Doggerland’s southern region, combined with an analysis of the region’s topography and a study of modern tsunamis to gain a topographic picture of the Storegga tsunami event.
The study has revealed that the tsunami reached over 40km inland, but the dense forests and the uplands (known as Dogger bank), most likely dissipated the wave’s intensity, allowing Doggerland to survive as a small archipelago for many centuries that followed.
The researchers propose that these surviving islands may have played a key part in prehistory; such as providing a staging point for the spread of farming into the rest of Britain. The data also obtained also supports modern tsunami research, anticipating similar future events in an increasingly developed North Sea.
Europe’s Lost Frontiers
Europe’s Lost Frontiers is an ERC-funded Advanced Grant project to explore Doggerland, the impact of climate change on the settlement of the submerged landscapes of the North Sea basin using ancient DNA, seismic mapping, and complex systems modelling. Find out more
Header Image Credit : cloudinary





