Recently discovered rock art from caves in Northern Spain represents an artistic cultural style common across ancient Europe, but previously unknown from the Iberian Peninsula, according to a study by Diego Garate of the Instituto Internacional de Investigaciones Prehistóricas de Cantabria, Spain, and colleagues.
The history of ancient human art includes various cultural complexes characterized by different artistic styles and conventions. In 2015, new instances of rock art were discovered in three caves in Aitzbitarte Hill in northern Spain, representing an artistic style previously unknown from the Iberian Peninsula. In this study, Garate and colleagues compare this artistic style to others from across Europe.
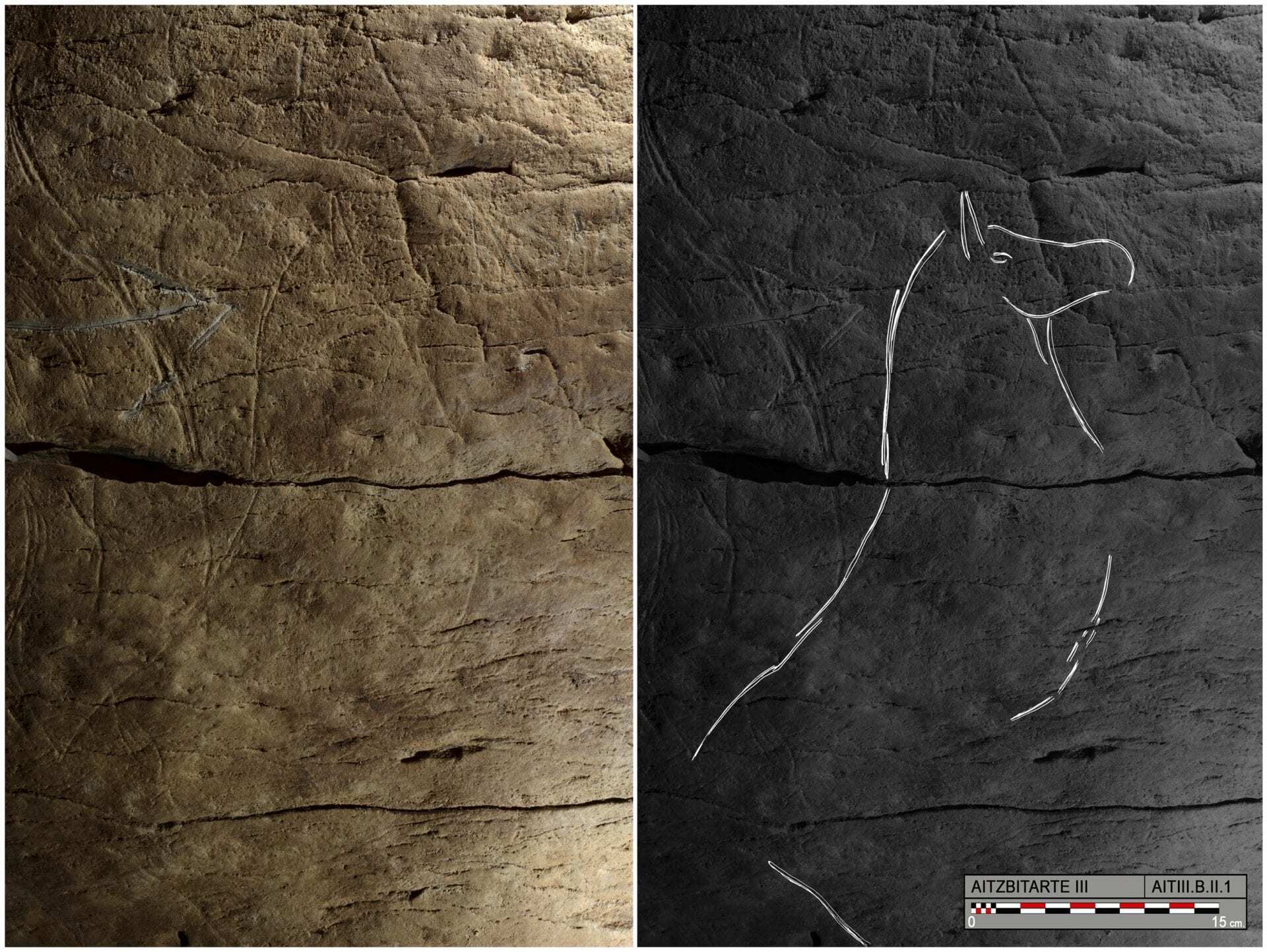
The artwork in the Aitzbitarte caves consists mostly of engravings of bison, complete with the animals’ characteristic horns and humps. The authors note the particular style in which the animals’ horns and legs are drawn, typically without proper perspective. Pairs of limbs are consistently depicted as a “double Y” with both legs visible, and the horns are similarly draw side-by-side with a series of lines in between.
This is consistent with the artistic style of the Gravettian cultural complex, characterized by specific customs in art, tools, and burial practices between about 34,000 and 24,000 years ago. This culture is known from across Europe but has not been seen before on the Iberian Peninsula. The authors combine this new discovery with data from around Europe to show that the Gravettian culture was more widespread and varied than previously appreciated.
The authors add: “The study analyses the particularities of Palaeolithic animal engravings found in the Aitzbitarte Caves (Basque Country, Spain) in 2016. These prehistoric images, mainly depicting bison, were drawn in a way that has never before been seen in northern Spain; in a kind of fashion in the way of drawing the engravings that is more characteristic of southern France and some parts of the Mediterranean. The study has shown the close regional relationships in Western Europe cave art since very early times, at least, 25,000 years ago.”
Header Image Credit : Garate et al, 2020 (PLOS ONE, CC BY)