Today, ball games are one of the most popular leisure activities in the world, an important form of mass entertainment and big business.
But who invented balls, where and when? The oldest balls that are currently known about were made in Egypt about 4,500 years ago using linen. Central Americans have been playing ball games for at least 3,700 years, as evidenced through monumental ball courts made of stone and depictions of ball players.
Their oldest balls were made of rubber. Until now, it was believed that ball games in Europe and Asia followed much later: In Greece about 2,500 years ago and in China about 300 years after that.
Eurasia’s oldest known balls
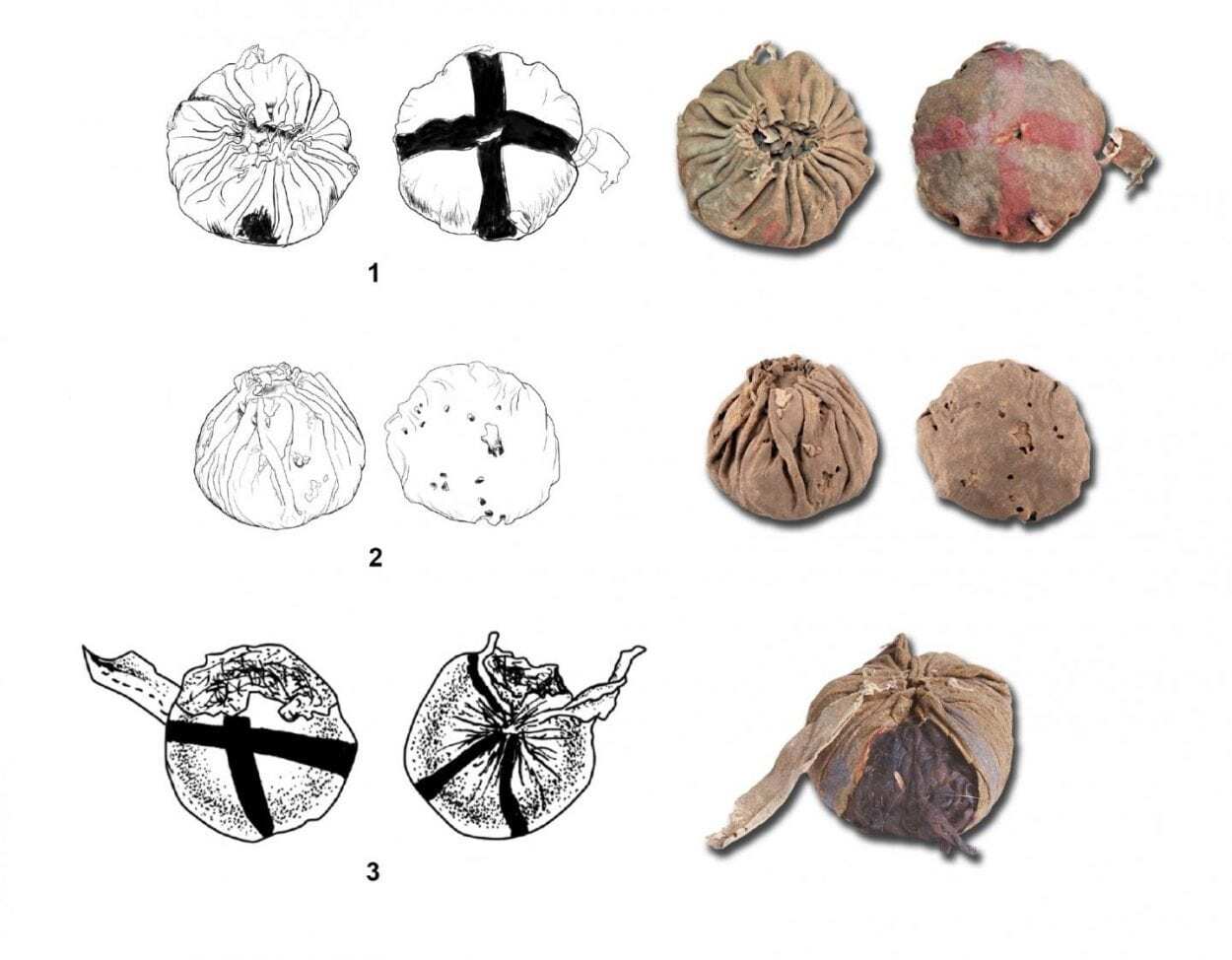
Researchers from the University of Zurich, together with German and Chinese researchers, have now examined in more detail three leather balls found in graves in the old Yanghai cemetery near the city of Turfan in northwest China. The balls, measuring between 7.4 and 9.2cm in diameter, have been dated at around 2,900 to 3,200 years old. “This makes these balls about five centuries older than the previously known ancient balls and depictions of ball games in Eurasia,” says first author Patrick Wertmann of the Institute of Asian and Oriental Studies of the University of Zurich. “Unfortunately, however, the associated archaeological information is not sufficient to answer the question of exactly how these balls were played.”
The earliest illustrations from Greece show ball players running, and depictions from China show riders using sticks. Comparable curved sticks were also found in Yanghai, but there was no apparent direct connection with the balls. Moreover, they are dated to a more recent period. “Therefore, the leather balls from Yanghai are not connected to early forms of field hockey or polo, even though two of the balls were found in the graves of horsemen,” says Wertmann.
New era of Central Asian equestrian warfare
In one of the riders’ graves, the preserved remains of a composite bow and a pair of trousers (1) were found, which were made in the region at that time and are among the oldest in the world. Both are signs of a new era of horse riding, equestrian warfare and fundamental societal transformations which accompanied increasing environmental changes and a rising mobility in eastern Central Asia.
The current study shows that balls and ball games were part of physical exercise and military training from the very beginning. In addition, just like today, sport also played a central role in society and was a widespread leisure activity. The study’s findings once again highlight that this region was a center of innovation within Eurasia several millennia ago.
Header Image Credit : UZH