The diets of ancient foxes were influenced by humans, and these small carnivores might be tracers of human activity over time, according to a study by Chris Baumann of the University of Tübingen, Germany and colleagues.
Foxes love leftovers. In the wild, foxes regularly feed on scraps left behind by larger predators like bears and wolves, but the closer foxes live to human civilization, the more of their diet is made up of foods that humans leave behind. In this study, Baumann and colleagues hypothesized that if this commensal relationship goes back to ancient times, then foxes might be useful indicators of human impact in the past.
The authors compared ratios of Carbon and Nitrogen isotopes between the remains of various herbivores, large carnivores, and red and Arctic foxes from several archaeological sites in southwest Germany dating to the Middle and Upper Palaeolithic.
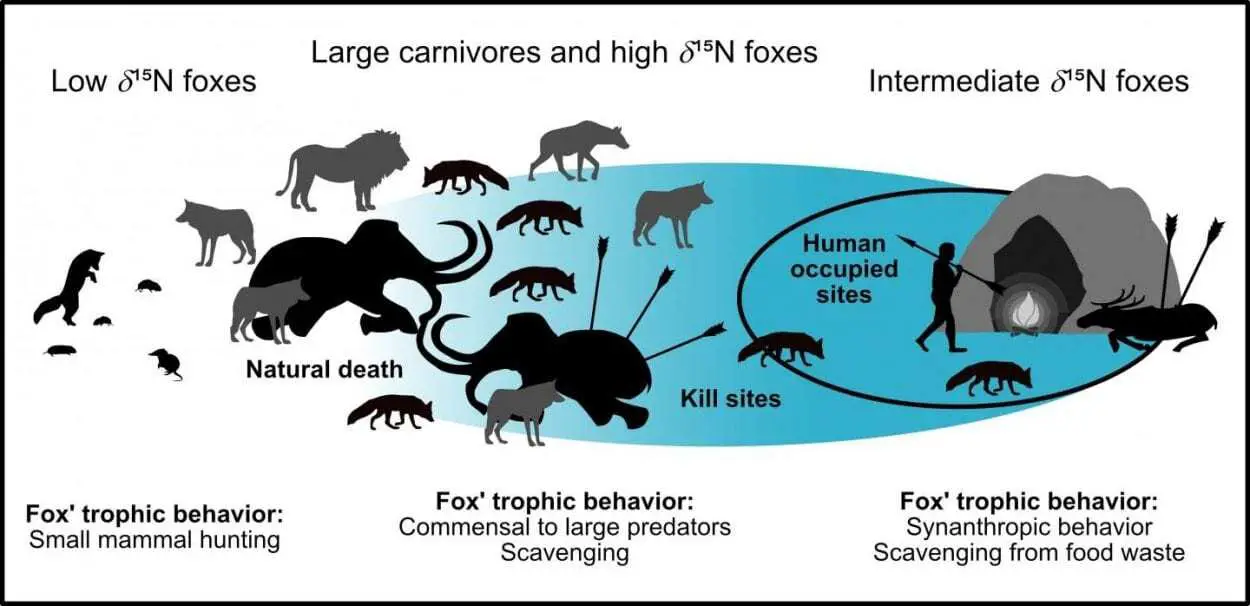
At sites older than 42,000 years, when Neanderthals sparsely occupied the region, fox diets were similar to their local large carnivores. But in the younger sites, as Homo sapiens became common in the area, foxes developed a more unique diet consisting largely of reindeer, which are too big for foxes to hunt but which are known to have been important game for ancient humans of the time.
These results suggest that during the Upper Palaeolithic, these foxes made a shift from feeding on scraps left by local large predators to eating food left behind by humans. This indicates that foxes’ reliance on human food goes back a good 42,000 years. The authors propose that, with further studies investigating this fox-human relationship, ancient fox diets may be useful indicators of human impact on ecosystems over time.
The authors add: “Dietary reconstructions of ice-age foxes have shown that early modern humans had an influence on the local ecosystem as early as 40,000 years ago. The more humans populated a particular region, the more the foxes adapted to them.”
Header Image Credit : Public Domain





