A large fossil discovered in Antarctica by Chilean researchers in 2011 has been found to be a giant, soft-shell egg from 66 million years ago.
The egg had remained unstudied in the collection of the National Museum of Natural History in Chile, until an analysis by a team from the University of Texas at Austin.
The egg measures 11.7 inches, called “the thing” it is the largest specimen of a soft-shell egg discovered, and the second-largest egg from any known species.
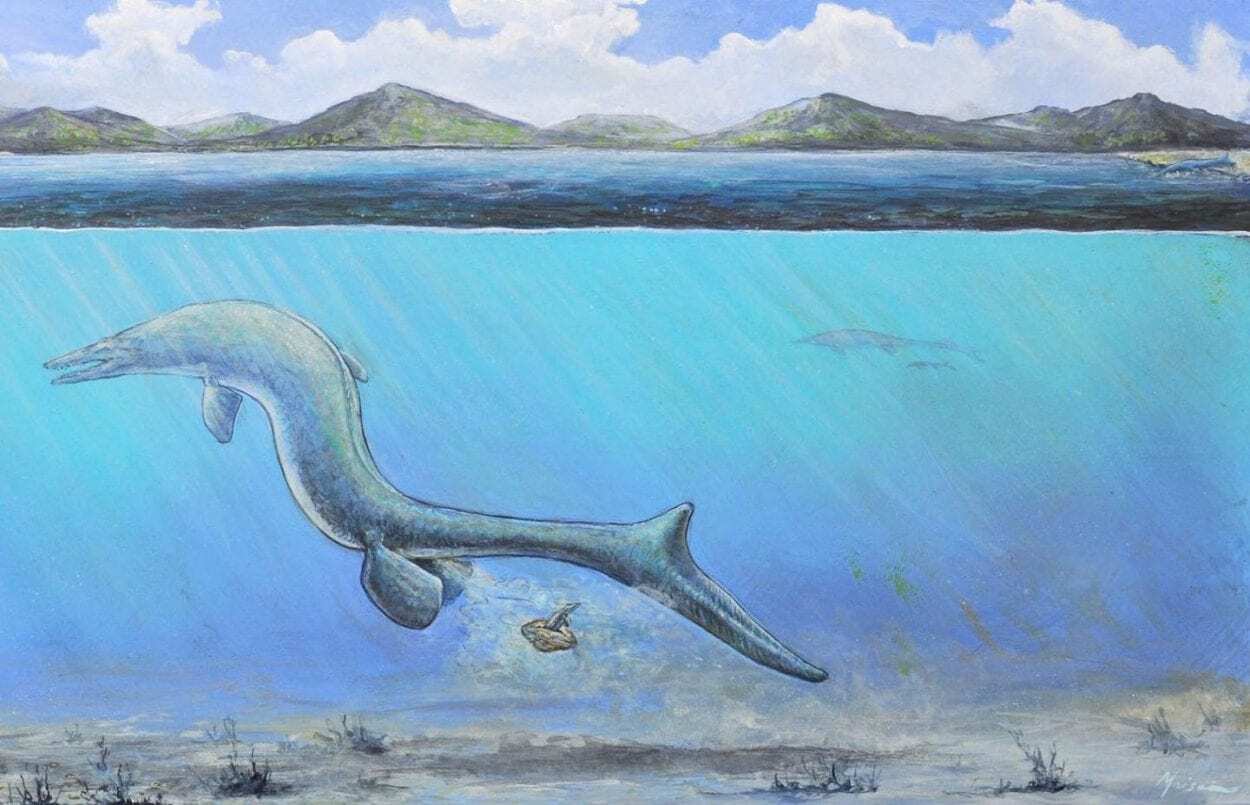
Palaeontologists believe that the egg was laid by an extinct marine reptile such as a mosasaur as the rock formation where the egg was discovered also hosts fossils from baby mosasaurs and plesiosaurs, along with adult specimens.
“It is from an animal the size of a large dinosaur, but it is completely unlike a dinosaur egg,” said lead author Lucas Legendre, a postdoctoral researcher at UT Austin’s Jackson School of Geosciences. “It is most similar to the eggs of lizards and snakes, but it is from a truly giant relative of these animals.”
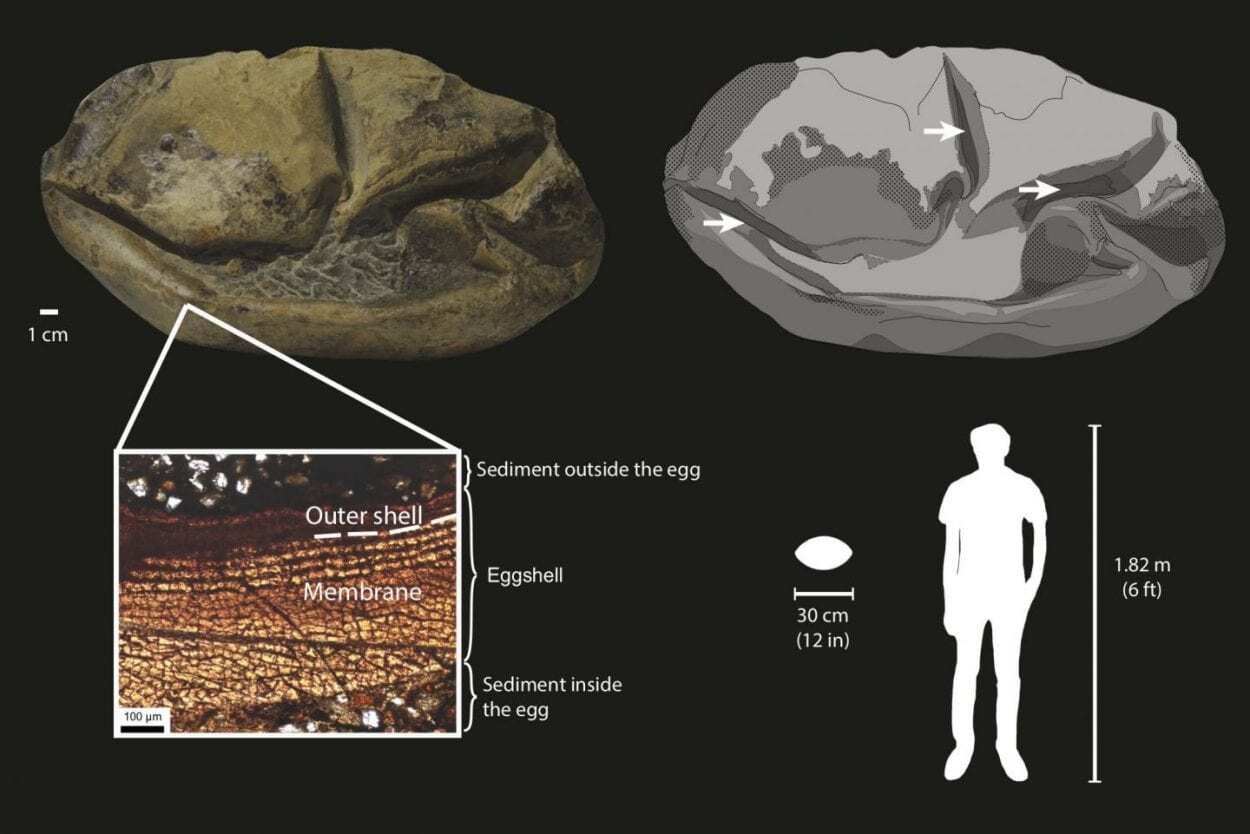
Using a suite of microscopes to study samples, Legendre found several layers of membrane that confirmed that the fossil was indeed an egg. The structure is very similar to transparent, quick-hatching eggs laid by some snakes and lizards today, he said. However, because the fossil egg is hatched and contains no skeleton, Legendre had to use other means to zero in on the type of reptile that laid it.
He compiled a data set to compare the body size of 259 living reptiles to the size of their eggs, and he found that the reptile that laid the egg would have been more than 20 feet long from the tip of its snout to the end of its body, not counting a tail.
Header Image – An artist’s interpretation of a baby mosasaur emerging from an egg just moments after it was laid. The scene is set in the shallow waters of Late Cretaceous Antarctica. In the background, mountains are covered in vegetation due to a warm climate. In the upper right, an alternative hypothesis for egg laying is depicted, with the mosasaur laying an egg on the beach.
UNIVERSITY OF TEXAS AT AUSTIN
Image Credit : John Maisano/The University of Texas at Austin Jackson School of Geosciences