Humans depend on fossil fuels as their primary energy source, especially in transportation. However, fossil fuels are both unsustainable and unsafe, serving as the largest source of greenhouse gas emissions and leading to adverse respiratory effects and devastation due to global warming.
A team of researchers at the Institute of Technological Sciences at Wuhan University has demonstrated a prototype device that uses microwave air plasmas for jet propulsion. They describe the engine in the journal AIP Advances, from AIP Publishing.
“The motivation of our work is to help solve the global warming problems owing to humans’ use of fossil fuel combustion engines to power machinery, such as cars and airplanes,” said author Jau Tang, a professor at Wuhan University. “There is no need for fossil fuel with our design, and therefore, there is no carbon emission to cause greenhouse effects and global warming.”
Beyond solid, liquid and gas, plasma is the fourth state of matter, consisting of an aggregate of charged ions. It exists naturally in places like the sun’s surface and Earth’s lightning, but it can also be generated. The researchers created a plasma jet by compressing air into high pressures and using a microwave to ionize the pressurized air stream.
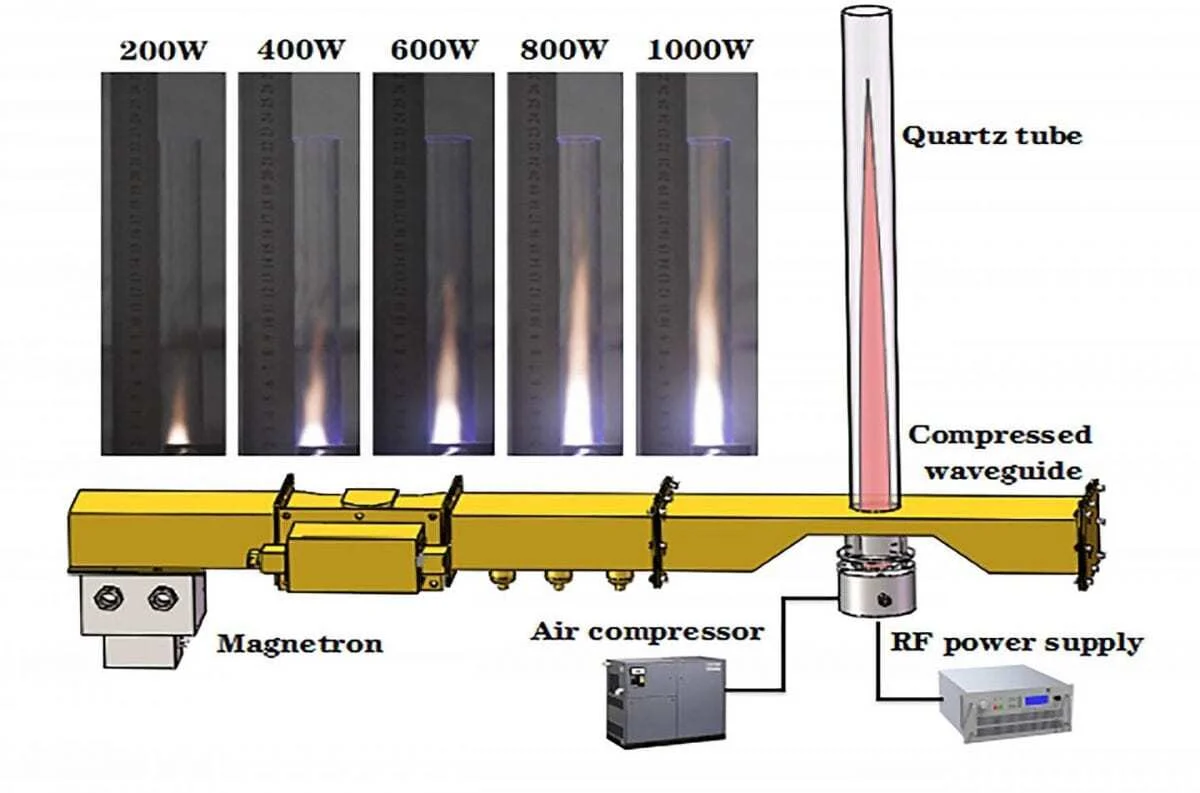
This method differs from previous attempts to create plasma jet thrusters in one key way. Other plasma jet thrusters, like NASA’s Dawn space probe, use xenon plasma, which cannot overcome the friction in Earth’s atmosphere, and are therefore not powerful enough for use in air transportation. Instead, the authors’ plasma jet thruster generates the high-temperature, high-pressure plasma in situ using only injected air and electricity.
The prototype plasma jet device can lift a 1-kilogram steel ball over a 24-millimeter diameter quartz tube, where the high-pressure air is converted into a plasma jet by passing through a microwave ionization chamber. To scale, the corresponding thrusting pressure is comparable to a commercial airplane jet engine.
By building a large array of these thrusters with high-power microwave sources, the prototype design can be scaled up to a full-sized jet. The authors are working on improving the efficiency of the device toward this goal.
“Our results demonstrated that such a jet engine based on microwave air plasma can be a potentially viable alternative to the conventional fossil fuel jet engine,” Tang said.
Header Image – Public Domain





