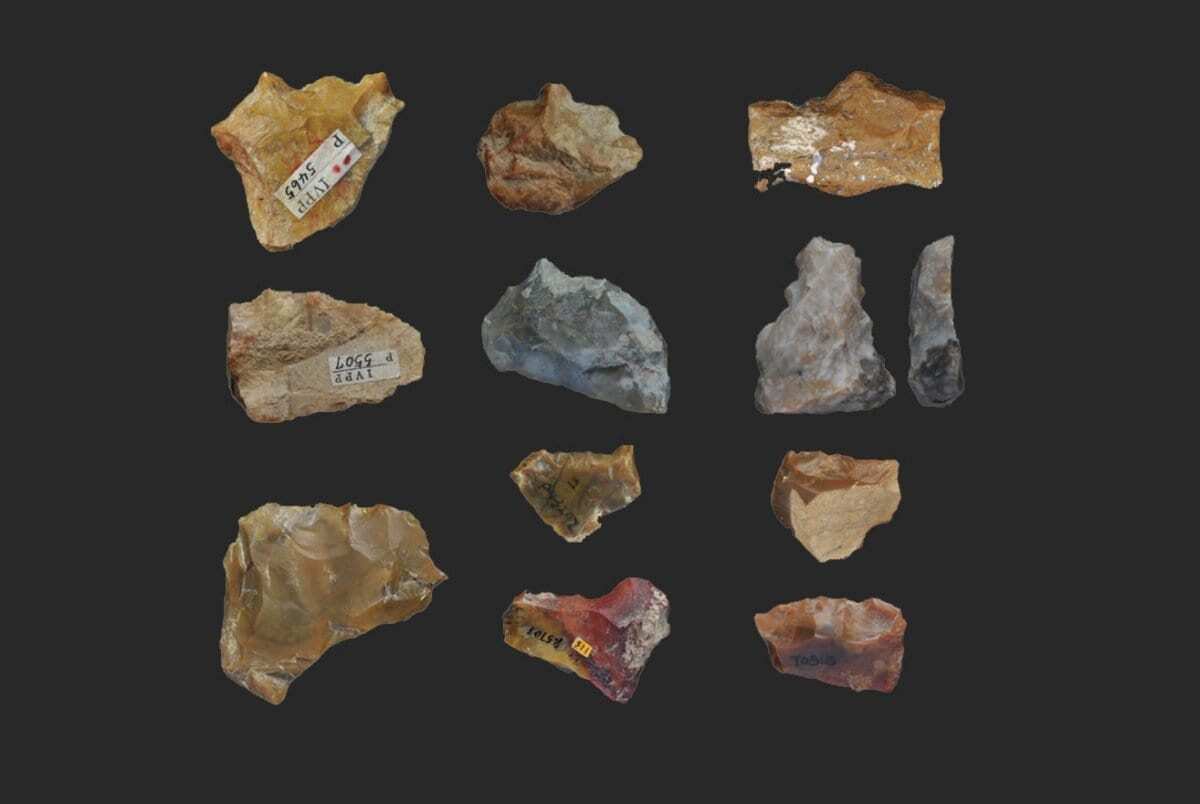
To assess the degree to which early stone tool-using hominins modified their tool manufacturing behaviours in Eastern Asia, archaeologists examined three well-known archaeological sites from the Nihewan Basin in North China.
Stone tool comparisons between the archaeological sites of Xiaochangliang, Cenjiawan and Donggutuo indicate that technological skills increase at ca. 1.1-1.0 million years ago.
The stone tools at Cenjiawan and Donggutuo show increasing levels of control in manufacturing procedures and some degree of planning in the tool-making process to produce desired end-products.
The technological innovations at ca. 1.1-1.0 million years ago in the Nihewan Basin correspond with a major climate transition that occurred between 1.2 million years ago to 700,000 years ago (called the Mid-Pleistocene Climate Transition).
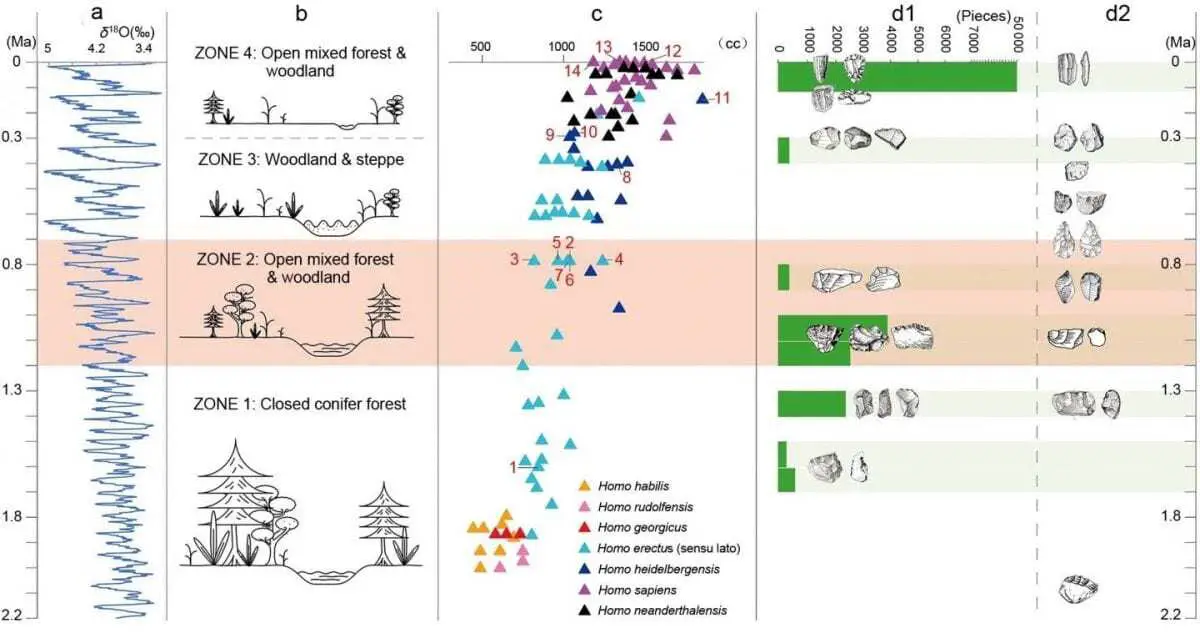
A series of global and regional palaeoclimatic and palaeoenvironmental changes occurred during this period, such as increases in aridity and monsoonal intensity and decreases in sea surface temperatures in the North Atlantic.
At 1.1 million years ago the early human inhabitants of the Nihewan Basin lived under a changeable and unstable environment, experiencing strengthened aridification. As climatic variability produced ecological changes, including landscape alterations and mammalian extinctions, novel technological innovations likely provided benefits to early hominin populations in the Nihewan Basin.
The unstable environmental conditions at the onset of this period provides a good example of the adaptive versatility of hominins in China, contrasting with the notion of long-lasting conservative behaviours described by other archaeologists. Yet, the increasingly harsh and oscillating climatic conditions of this period likely undermined sustained population in North China, illustrating that technological and cultural solutions did not always overcome environmental challenges.
Header Image Credit : Science China Press





