Scientists led by the University of the Witwatersrand in South Africa, has been able to reconstruct the skulls of some of the world’s oldest known dinosaur embryos in 3D, using powerful and non-destructive synchrotron techniques at the ESRF, the European Synchrotron in France.
They found that the skulls develop in the same order as those of today’s crocodiles, chickens, turtles and lizards. The findings are published today in Scientific Reports.
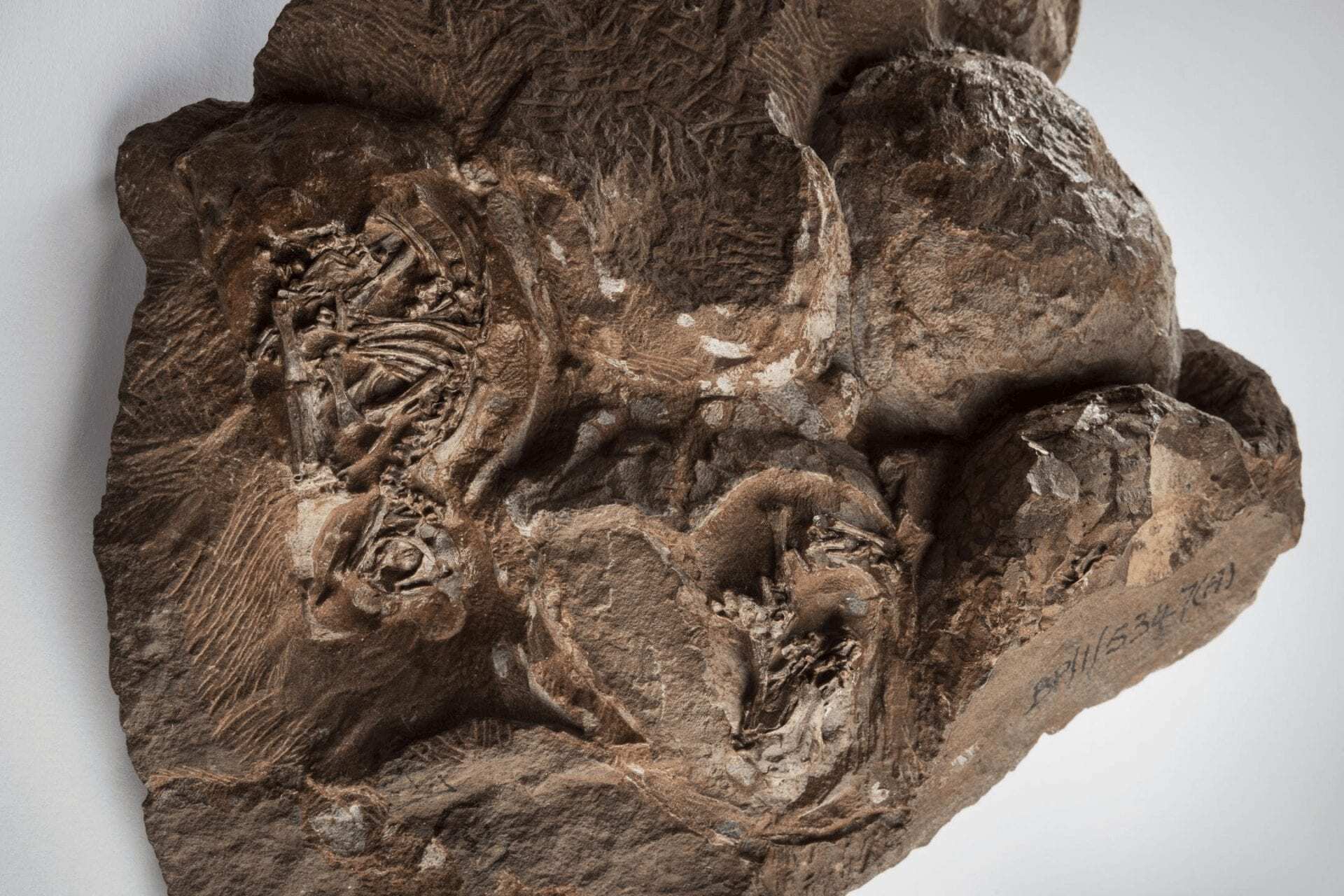
University of the Witwatersrand scientists publish 3D reconstructions of the ~2cm-long skulls of some of the world’s oldest dinosaur embryos in an article in Scientific Reports. The embryos, found in 1976 in Golden Gate Highlands National Park (Free State Province, South Africa) belong to South Africa’s iconic dinosaur Massospondylus carinatus, a 5-meter long herbivore that nested in the Free State region 200 million years ago.

The scientific usefulness of the embryos was previously limited by their extremely fragile nature and tiny size. In 2015, scientists Kimi Chapelle and Jonah Choiniere, from the University of Witwatersrand, brought them to the European Synchrotron (ESRF) in Grenoble, France for scanning. At the ESRF, an 844 metre-ring of electrons travelling at the speed of light emits high-powered X-ray beams that can be used to non-destructively scan matter, including fossils. The embryos were scanned at an unprecedented level of detail – at the resolution of an individual bone cell.
With these data in hand, and after nearly 3 years of data processing at Wits’ laboratory, the team was able to reconstruct a 3D model of the baby dinosaur skull. “No lab CT scanner in the world can generate these kinds of data,” said Vincent Fernandez, one of the co-authors and scientist at the Natural History Museum in London (UK). “Only with a huge facility like the ESRF can we unlock the hidden potential of our most exciting fossils. This research is a great example of a global collaboration between Europe and the South African National Research Foundation”, he adds.
Up until now, it was believed that the embryos in those eggs had died just before hatching. However, during the study, lead author Chapelle noticed similarities with the developing embryos of living dinosaur relatives (crocodiles, chickens, turtles, and lizards). By comparing which bones of the skull were present at different stages of their embryonic development, Chapelle and co-authors can now show that the Massospondylus embryos were actually much younger than previously thought and were only at 60% through their incubation period.
The team also found that each embryo had two types of teeth preserved in its developing jaws. One set was made up of very simple triangular teeth that would have been resorbed or shed before hatching, just like geckos and crocodiles today. The second set were very similar to those of adults, and would be the ones that the embryos hatched with. “I was really surprised to find that these embryos not only had teeth, but had two types of teeth. The teeth are so tiny; they range from 0.4 to 0.7mm wide. That’s smaller than the tip of a toothpick!”, explains Chapelle.
The conclusion of this research is that dinosaurs developed in the egg just like their reptilian relatives, whose embryonic developmental pattern hasn’t changed in 200 million years. “It’s incredible that in more than 250 million years of reptile evolution, the way the skull develops in the egg remains more or less the same. Goes to show – you don’t mess with a good thing!”, concludes Jonah Choiniere, professor at the University of Witwatersrand and also co-author of the study.
The team hopes to apply their method to other dinosaur embryos to estimate their level of development. They will be looking at the rest of the skeleton of the Massospondylus embryos to see if it also shares similarities in development with today’s dinosaur relatives. The arms and legs of the Massospondylus embryos have already been used to show that hatchlings likely walked on two legs (see doi: 10.1111/pala.12451).
Main findings:
1) High powered X-rays were used to reconstruct the skulls of some of the world’s oldest known dinosaur embryos.
2) The skull could be seen in 3D at an unprecedented level of detail.
3) Dinosaur embryo skulls appear to develop in the same order as those of today’s crocodiles, chickens, turtles and lizards.
4) These dinosaur embryos appear to have been fossilised at approximately 60% through their incubation period. This is much earlier than previously thought.
5) The dinosaur embryos have two types of teeth that range in size from 0.4 to 0.7mm wide. One of these sets would have been shed or resorbed before hatching.
EUROPEAN SYNCHROTRON RADIATION FACILITY
Header Image – Some of the world’s oldest known dinosaur eggs and embryos. The clutch of Massospondylus carinatus eggs discovered in 1976 in Golden Gate Highland National Park, South Africa. Credit : Brett Eloff