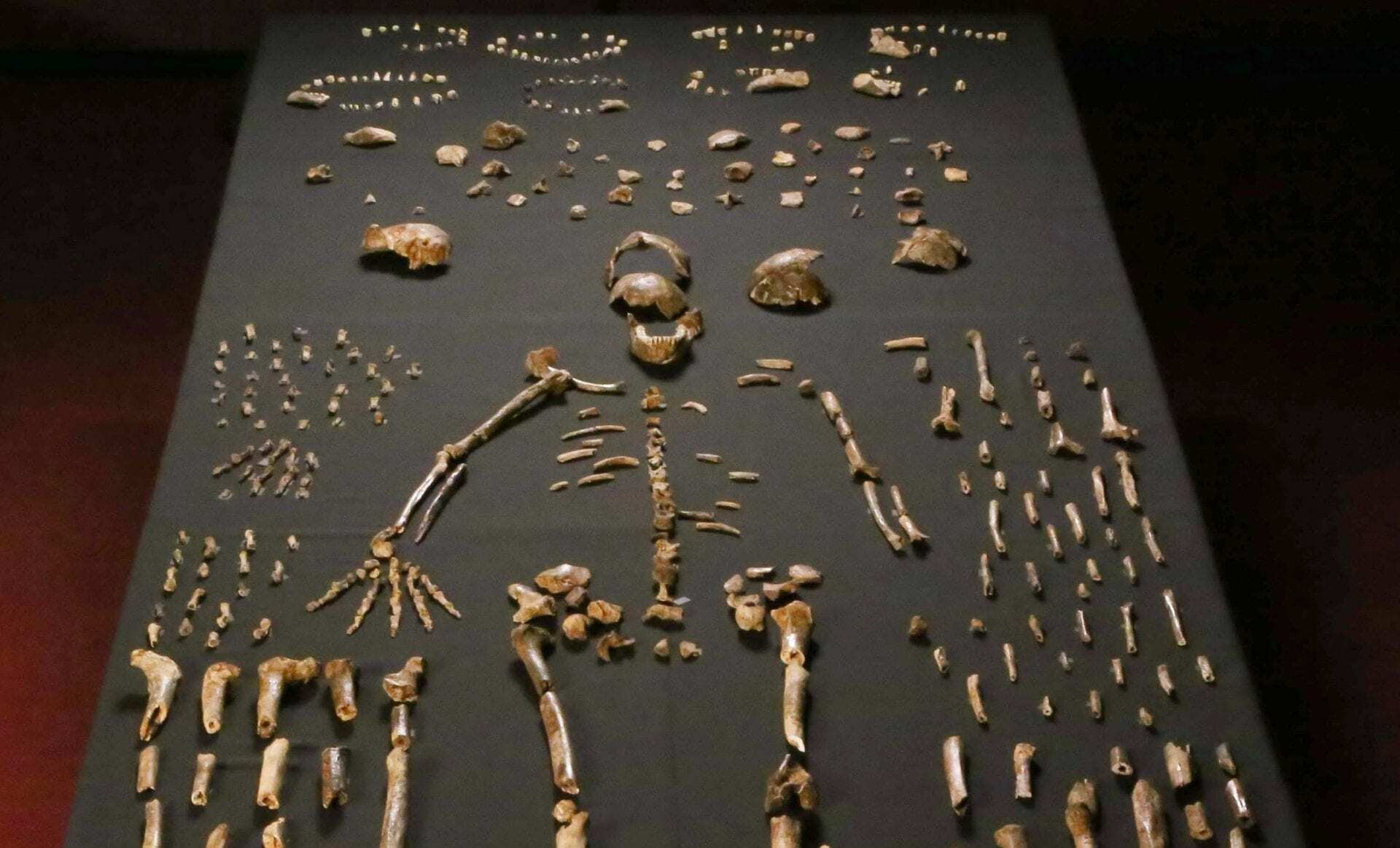
A partial skeleton of Homo naledi represents a rare case of an immature individual, shedding light on the evolution of growth and development in human ancestry, according to a study by Debra Bolter of Modesto Junior College in California and the University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, and colleagues.
Much research has gone into the evolution of ancient hominins – human relatives and ancestors – but little is known about their growth and development. Most hominin fossils represent adult individuals, and remains of developmentally young hominins are rare. This has left a gap in our understanding of how our ancient relatives grew from young into adults, and how modern human growth patterns evolved.
In this study, Bolter and colleagues examined fossils from the Dinaledi Chamber of the Rising Star Cave System in South Africa. This site is famous for providing abundant remains of the hominin Homo naledi, including individuals ranging from infants to adult. These fossils date to the late Middle Pleistocene, between 335,000 and 226,000 years ago, possibly overlapping in time with the earliest members of our own species. The team identified a collection of arm and leg bones and a partial jaw as the remains of a single young individual designated DH7.
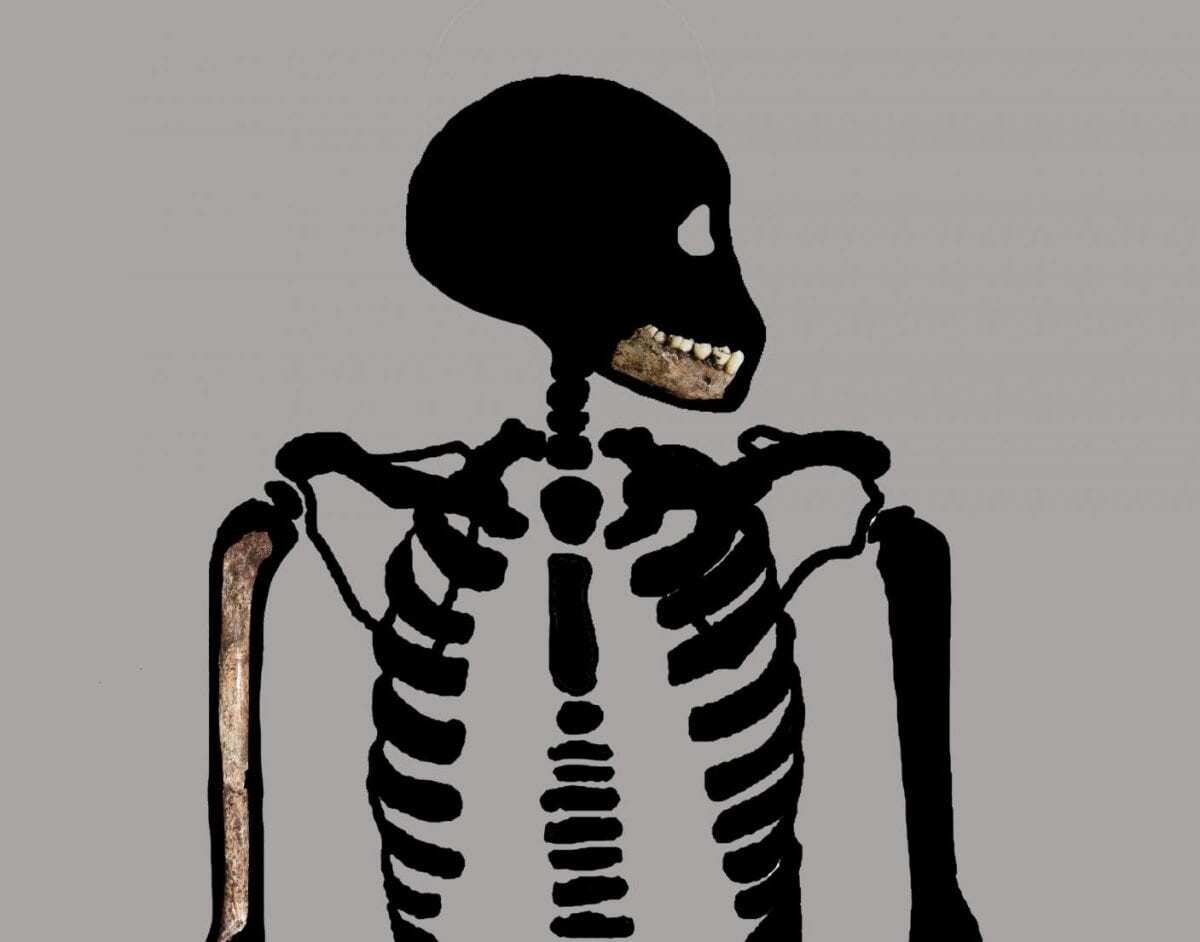
The bones and teeth of DH7 were not fully developed and display a mixture of maturity patterns seen in modern humans and earlier hominins. DH7 is estimated to be similar in its developmental stage to immature specimens of other fossil hominins between 8-11 years old at death. The authors note, however, that if Homo naledi had a slower growth rate like modern humans, DH7 might have been as old as 15. Further study is needed to assess how Homo naledi grew and where it fits into the evolution of human growth and development.
Bolter adds: The rare juvenile Homo naledi partial skeleton will shed light on whether this extinct species is more human-like in its development, or more primitive. The findings help reconstruct the selective pressures that shaped extended maturity in our own species. Read full article
Header Image Credit : Lee Roger Berger