Earth’s molten core may be leaking iron, according to researchers who analyzed how iron behaves inside our planet.
The boundary between the liquid iron core and the rocky mantle is located some 1,800 miles (2,900 km) below Earth’s surface. At this transition, the temperature drops by more than a thousand degrees from the hotter core to the cooler mantle.
The new study suggests heavier iron isotopes migrate toward lower temperatures — and into the mantle — while lighter iron isotopes circulate back down into the core. (Isotopes of the same element have different numbers of neutrons, giving them slightly different masses.) This effect could cause core material infiltrating the lowermost mantle to be enriched in heavy iron isotopes.
“If correct, this stands to improve our understanding of core-mantle interaction,” said Charles Lesher, lead author, professor emeritus of geology at UC Davis and professor of earth system petrology at Aarhus University in Denmark.
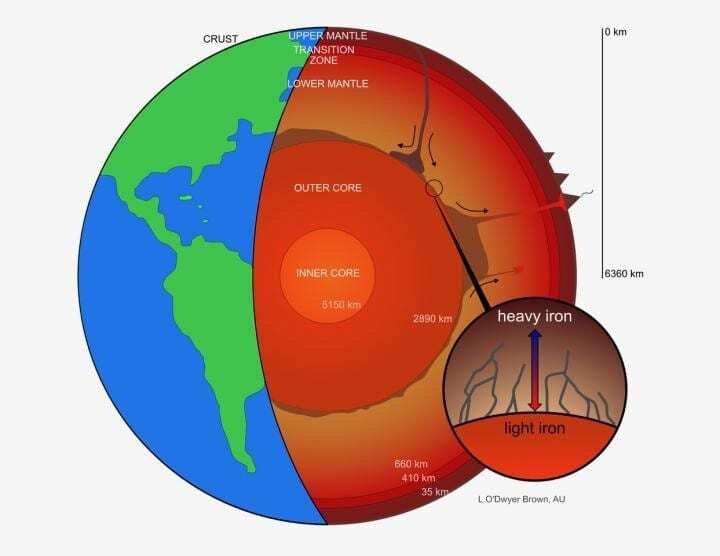
Understanding the physical processes operating at the core-mantle boundary is important for interpreting seismic images of the deep mantle, as well as modeling the extent of chemical and thermal transfer between the deep Earth and surface of our planet, Lesher said.
Lesher and his colleagues analyzed how iron isotopes move between areas of different temperatures during experiments conducted under high temperature and pressure. Their findings can explain why there are more heavy iron isotopes in mantle rocks than in chondrite meteorites, the primordial material from the early solar system, Lesher said.
“If true, the results suggest iron from the core has been leaking into the mantle for billions of years,” he said.
Computer simulations performed by the research team show this core material can even reach the surface, mixed with and transported by hot, upwelling mantle plumes. Some lavas erupted at oceanic hot spots such as Samoa and Hawaii are enriched in heavy iron isotopes, which Lesher and the team propose could be a signature of a leaky core.
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA – DAVIS
Header Image – Public Domain





