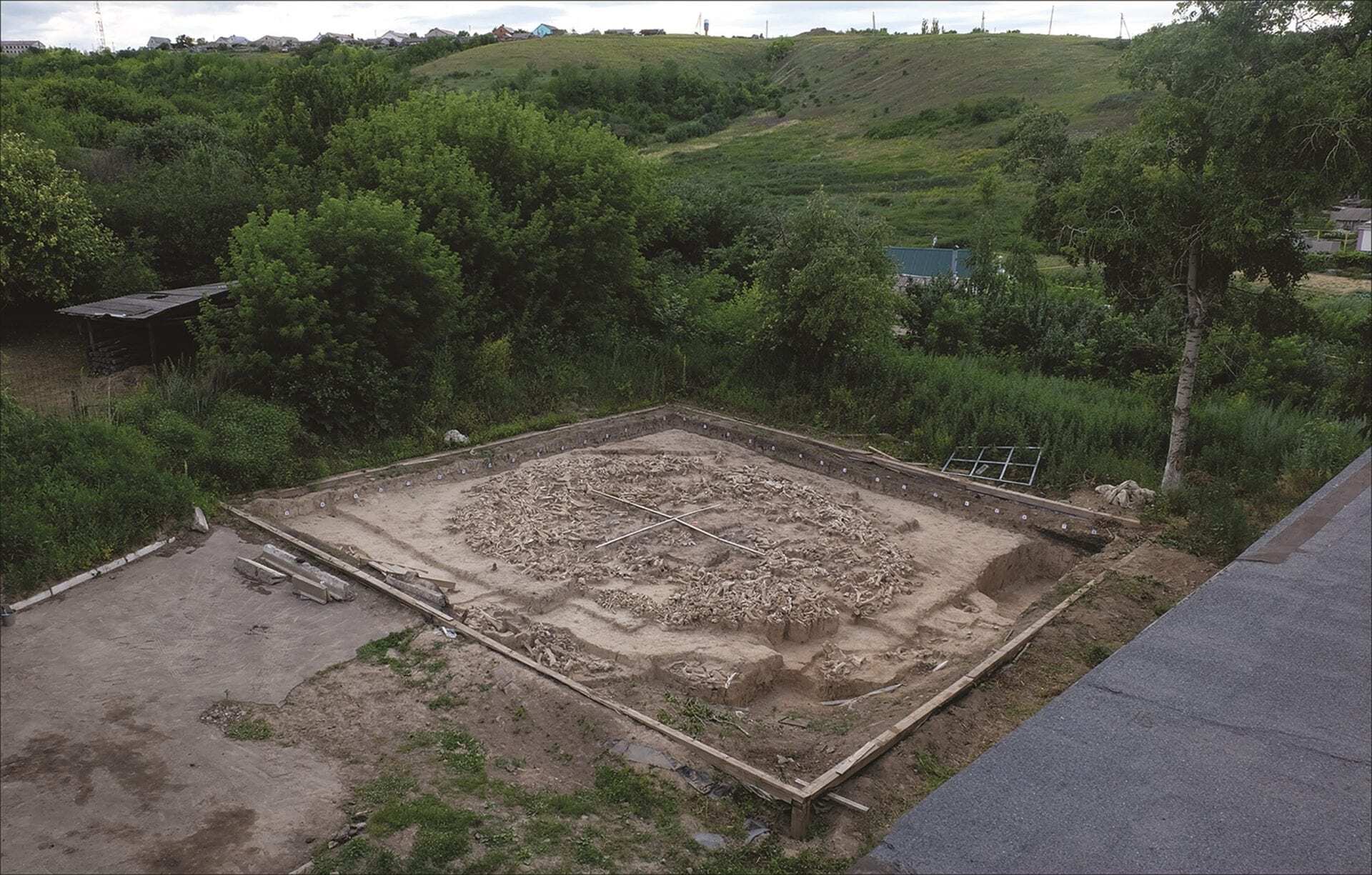
Archaeologists have announced the discovery of a giant Ice Age structure built from the remains of at least 60 mammoths at the Kostenki-Borshevo archaeological complex.
The Kostenki-Borshevo site complex on the Don river is one of the most important Upper Palaeolithic site-complexes of Europe.
Previous excavations in the region almost 40 years ago unearthed similar structures, but this new discovery offers archaeologists the opportunity to study how these dwellings were constructed using modern scientific techniques.
The giant circular structure has a diameter of 12.5 metres and was built around 25,000 years ago during the peak of the last Ice Age (called the last glacial maximum), when communities were mainly mobile hunter-gatherers. This would make it one of the oldest known mammoth bone buildings, compared to similar structures that date from 22,000 years ago.
A total of 51 lower jaws and 64 individual mammoth skulls were used to construct the walls of the 30ft by 30ft structure and scattered across its interior. Small numbers of reindeer, horse, bear, wolf, red fox and arctic fox bones were also found.
Dr Alexander Pryor from the University of Exeter stated, “Mammoth bones are very heavy and building the circular structure represents a huge investment of time and energy by the humans that built this.”
Previously archaeologists have assumed that the circular mammoth bone structures were used as dwellings, occupied for many months at a time. The new study suggests this may not always have been the case as the intensity of activity at Kostenki 11 appears less than would be expected from a long term base campsite.
Other finds include more than 300 tiny stone and flint chips just a few millimetres in size, debris left behind the site’s inhabitants as they knapped stone nodules into sharp tools with distinctive shapes used for tasks such as butchering animals and scraping hides.

Flotation techniques has been applied to the site using water and sieves to study the material from the soil. Dr Pryor added “We found pieces of soft plant tissue, typically found in edible roots or tubers, hinting at a plant food component in people’s diet.
These finds are important because they illustrate how our human ancestors adapted to survive the harsh environments of the last ice age by making use of the resources they found around them”.

Header Image Credit : Antiquity Journal





