Scientists have found that increasing oxygen levels are linked to the rise of North American dinosaurs around 215 M years ago.
A new technique for measuring oxygen levels in ancient rocks shows that oxygen levels in North American rocks leapt by nearly a third in just a couple of million years, possibly setting the scene for a dinosaur expansion into the tropics of North America and elsewhere. This is presented in a Keynote talk at the Goldschmidt Geochemistry conference, in Barcelona.
The US-based scientists have developed a new technique for releasing tiny amounts of gas trapped inside ancient carbonate minerals. The gases are then channelled directly into a mass spectrometer, which measures their composition.
Lead researcher, Professor Morgan Schaller (Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, New York) said: “We tested rocks from the Colorado Plateau and the Newark Basin that formed at the same time about 1000 km apart on the supercontinent of Pangea. Our results show that over a period of around 3 million years – which is very rapid in geological terms – the oxygen levels in the atmosphere jumped from around 15% to around 19%. For comparison, there is 21% oxygen in today’s atmosphere. We really don’t know what might have caused this increase, but we also see a drop in CO2 levels at that time.”
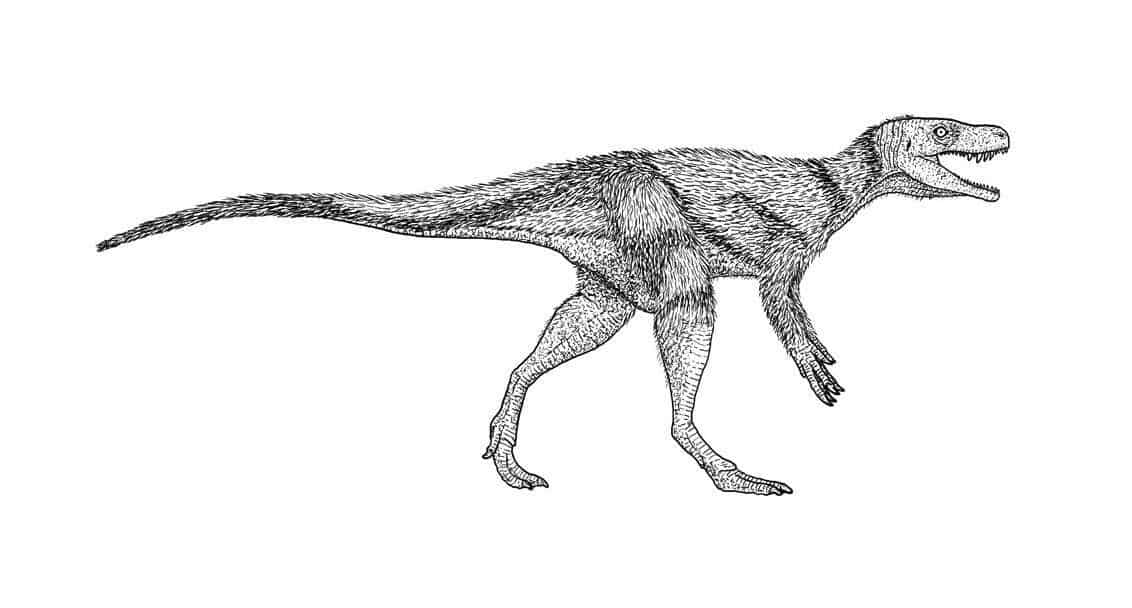
“We expect that this change in oxygen concentration would have been global change, and in fact we found the change in samples which were 1000km apart. What is remarkable is that right at the oxygen peak we see the first dinosaurs appearing in the North American tropics, the Chindesaurus. The Sauropods followed soon afterwards. Again, we can’t yet say if this was a global development, and the dinosaurs don’t rise to ecological dominance in the tropics until after the End-Triassic extinction. What we can say is that this shows that the changing environment 215 M years ago was right for their evolutionary diversification, but of course oxygen levels may not have been the only factor”.
Chindesaurus was an upright carnivorous dinosaur (around 2m long and nearly 1m high). Found extensively in North America, with origins in the North American Tropics, it was a characteristic late Triassic Dinosaur of the American Southwest. It was originally discovered in the Petrified Forest National Park. The Sauropods, which appeared soon after Chindesaurus, were the largest animals ever to live on land.
Commenting, Professor Mike Benton (University of Bristol) said: ‘The first dinosaurs were quite small, but higher oxygen levels in the atmosphere are often associated with a trend to larger size. This new result is interesting as the timing of oxygen rise and dinosaur appearance is good, although dinosaurs had become abundant in South America rather earlier, about 232 million years ago.’ Professor Benton was not involved in this work; this is an independent comment.
At the time the gases were trapped, the Colorado Plateau and the Newark Basin were part of the giant supercontinent, Pangea. Both were located near the equator. The rocks containing the oxygen and carbon dioxide were dated by measuring the radioactive decay of Uranium which was found in the samples.
Header Image Credit : Jeff Martz