New analysis of the fossilized skull of an Upper Paleolithic man suggests that he died a violent death, according to a study published by an international team from Greece, Romania and Germany led by the Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen, Germany
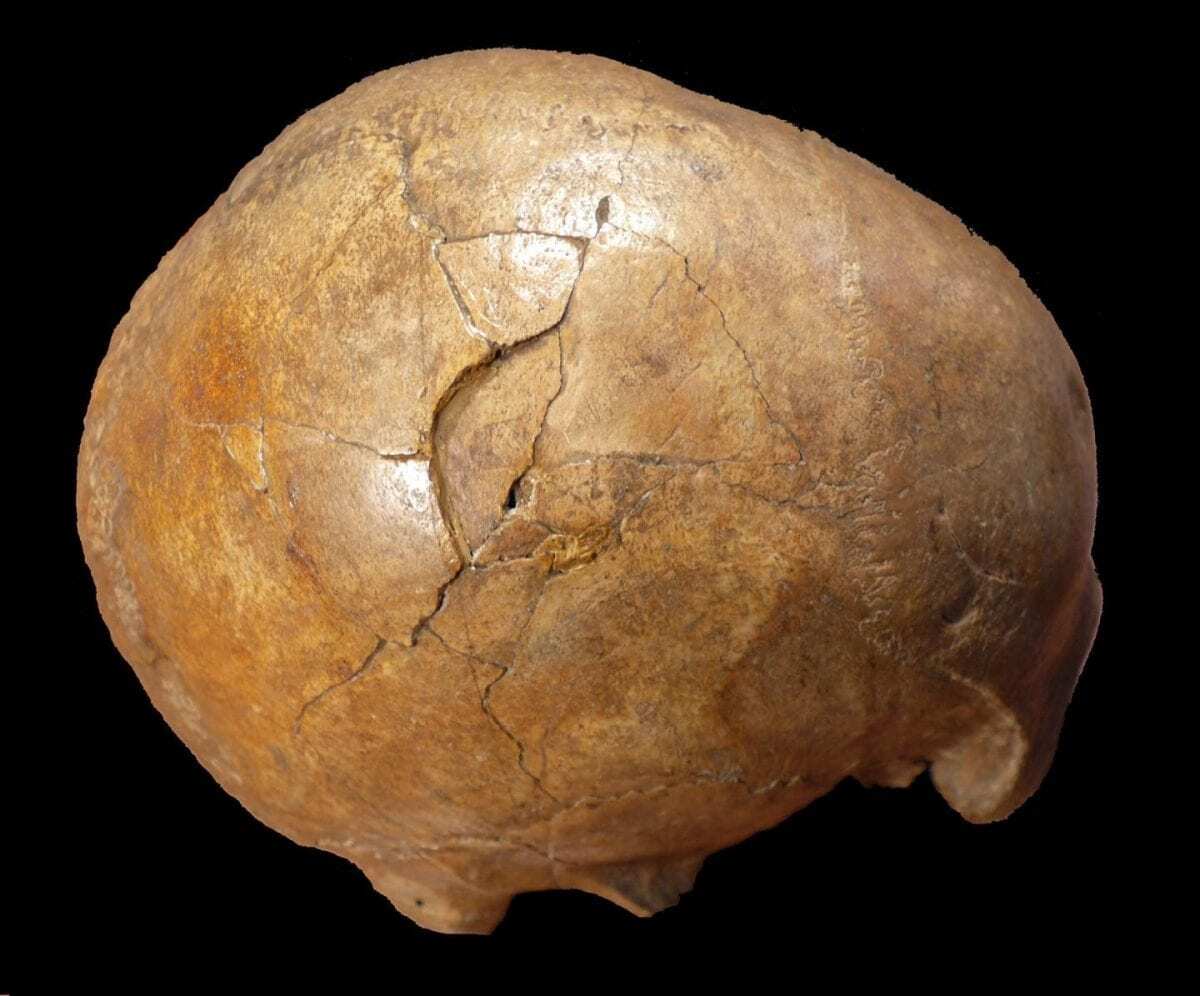
The fossilized skull of a Paleolithic adult man, known as the Cioclovina calvaria, was originally uncovered in a cave in South Transylvania and is thought to be around 33,000 years old. Since its discovery, this fossil has been extensively studied. Here, the authors reassessed trauma on the skull–specifically a large fracture on the right aspect of the cranium which has been disputed in the past–in order to evaluate whether this specific fracture occurred at the time of death or as a postmortem event.
The authors conducted experimental trauma simulations using twelve synthetic bone spheres, testing scenarios such as falls from various heights as well as single or double blows from rocks or bats. Along with these simulations, the authors inspected the fossil both visually and virtually using computed tomography technology.
The authors found there were actually two injuries at or near the time of death: a linear fracture at the base of the skull, followed by a depressed fracture on the right side of the cranial vault. The simulations showed that these fractures strongly resemble the pattern of injury resulting from consecutive blows with a bat-like object; the positioning suggests the blow resulting in the depressed fracture came from a face-to-face confrontation, possibly with the bat in the perpetrator’s left hand. The researchers’ analysis indicates that the two injuries were not the result of accidental injury, post-mortem damage, or a fall alone.
While the fractures would have been fatal, only the fossilized skull has been found so it’s possible that bodily injuries leading to death might also have been sustained. Regardless, the authors state that the forensic evidence described in this study points to an intentionally-caused violent death, suggesting that homicide was practiced by early humans during the Upper Paleolithic.
The authors add: “The Upper Paleolithic was a time of increasing cultural complexity and technological sophistication. Our work shows that violent interpersonal behaviour and murder was also part of the behavioural repertoire of these early modern Europeans.”
Header Image – Right lateral view of the Cioclovina calvaria exhibiting a large depressed fracture. Credit : Kranoti et al, 2019