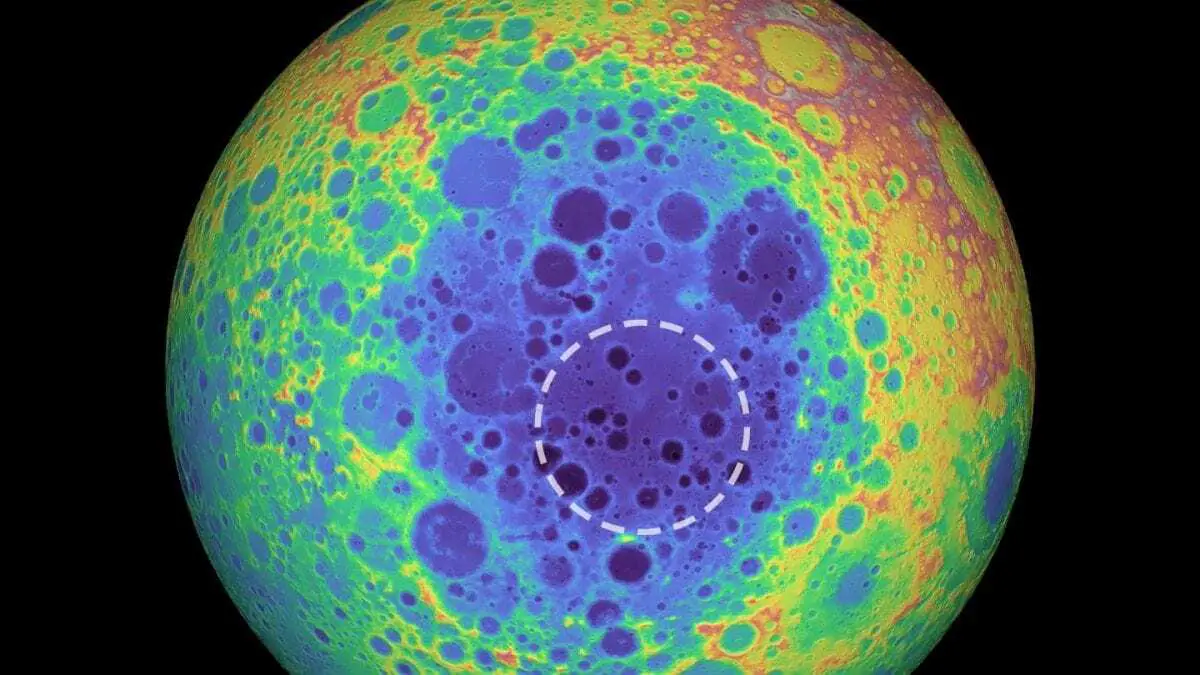
A mysterious large mass of material has been discovered beneath the largest crater in our solar system — the Moon’s South Pole-Aitken basin — and may contain metal from the asteroid that crashed into the Moon and formed the crater, according to a Baylor University study.
“Imagine taking a pile of metal five times larger than the Big Island of Hawaii and burying it underground. That’s roughly how much unexpected mass we detected,” said lead author Peter B. James,
Ph.D., assistant professor of planetary geophysics in Baylor’s College of Arts & Sciences. The crater itself is oval-shaped, as wide as 2,000 kilometers — roughly the distance between Waco, Texas, and Washington, D.C. — and several miles deep. Despite its size, it cannot be seen from Earth because it is on the far side of the Moon.
The study — “Deep Structure of the Lunar South Pole-Aitken Basin” — is published in the journal Geophysical Research Letters.
To measure subtle changes in the strength of gravity around the Moon, researchers analyzed data from spacecrafts used for the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory (GRAIL) mission.
“When we combined that with lunar topography data from the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, we discovered the unexpectedly large amount of mass hundreds of miles underneath the South Pole-Aitken basin,” James said. “One of the explanations of this extra mass is that the metal from the asteroid that formed this crater is still embedded in the Moon’s mantle.”
The dense mass — “whatever it is, wherever it came from” — is weighing the basin floor downward by more than half a mile, he said. Computer simulations of large asteroid impacts suggest that, under the right conditions, an iron-nickel core of an asteroid may be dispersed into the upper mantle (the layer between the Moon’s crust and core) during an impact.
“We did the math and showed that a sufficiently dispersed core of the asteroid that made the impact could remain suspended in the Moon’s mantle until the present day, rather than sinking to the Moon’s core,” James said.
Another possibility is that the large mass might be a concentration of dense oxides associated with the last stage of lunar magma ocean solidification.
James said that the South Pole-Aitken basin — thought to have been created about 4 billion years ago — is the largest preserved crater in the solar system. While larger impacts may have occurred throughout the solar system, including on Earth, most traces of those have been lost.
James called the basin “one of the best natural laboratories for studying catastrophic impact events, an ancient process that shaped all of the rocky planets and moons we see today.”
Header Image – This false-color graphic shows the topography of the far side of the Moon. The warmer colors indicate high topography and the bluer colors indicate low topography. The South Pole-Aitken (SPA) basin is shown by the shades of blue. The dashed circle shows the location of the mass anomaly under the basin. Credit : NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center/University of Arizona