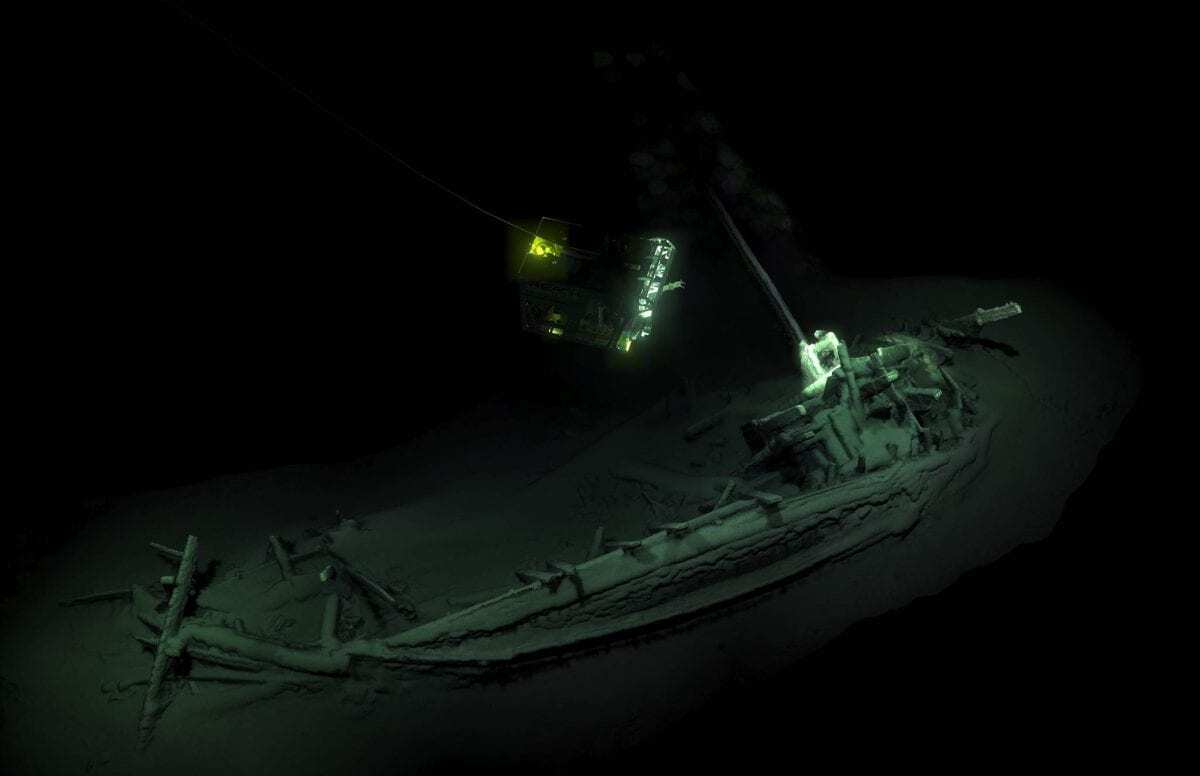
A Greek merchant ship dating back more than 2,400 years has been found off the Bulgarian coast in the Black Sea.
Using the latest technology, previously only typically made available to oil, gas and renewable energy companies, The Black Sea Maritime Archaeology Project (Black Sea MAP) surveyed over 2000 sqkm of seabed.
During the life of the project over 60 shipwrecks, varying in age from a 17th century Cossack raiding fleet, through Roman trading vessels complete with amphorae to a complete ship from the Classical period, were found.
It was during the most recent phase in late 2017 that the team discovered what has been confirmed as the world’s ‘oldest intact shipwreck’ – a Greek trading vessel design previously only seen on the side of ancient Greek pottery such as the ‘Siren Vase’ in the British Museum.
The ship lies in over 2km of water deep in the Black Sea where the water is anoxic (oxygen free), which can preserve organic material for thousands of years. A small piece of the vessel has been carbon dated and has now been confirmed as the oldest intact shipwreck known to mankind.
“A ship, surviving intact, from the Classical world, lying in over 2km of water, is something I would never have believed possible,” said University of Southampton Professor Jon Adams, the Black Sea MAP’s principal investigator. “This will change our understanding of shipbuilding and seafaring in the ancient world.”
The Black Sea MAP team is under the leadership of the University of Southampton and Professor Jon Adams, Professor Lyudmil Vagalinsky of the National Institute of Archaeology with Museum of the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences and Dr. Kalin Dimitrov of the Center of Underwater Archaeology in Sozopol, Bulgaria.
In 2015, the Black Sea MAP set out to investigate the changes in the ancient environment of the region off the coast of Bulgaria, including the impact of sea-level change following the last glacial cycle. Field studies were conducted over three seasons – concluding in September 2017, with the team of world-renowned maritime scientists returning from their final trip with knowledge of some astonishing finds and a collection of amphorae and other fascinating artefacts.
In addition to the discovery of the shipwrecks, the scientists excavated the remains of an early Bronze Age settlement at Ropotamo in Bulgaria, near what was the ancient shoreline when the sea level was much lower than today. As the waters rose, the settlement was abandoned and now the remains of house timbers, hearths and ceramics lie 2.5 metres below the seabed.
The valley in which the village had lain became a sheltered bay visited by Greek colonists of the Archaic period, then a harbour for early Byzantine seafarers and finally an anchorage used by the Ottomans.
Also onboard the vessels during the expedition were A level students specially chosen from disadvantaged schools, who had previously shown an interest in the STEM subjects, Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths.
The Black Sea MAP project was conceived by Hans K Rausing who established the Expedition and Education Foundation to commission the project. The Foundation’s work is funded by The Julia and Hans Rausing Trust, a charitable fund.