Some 3,500 years ago, there was already a brisk trade in fish on the shores of the southeastern Mediterranean Sea.
This conclusion follows from the analysis of 100 fish teeth that were found at various archeological sites in what is now Israel. The saltwater fish from which these teeth originated is the gilthead sea bream, which is also known as the dorade. It was caught in the Bardawil lagoon on the northern Sinai coast and then transported from Egypt to sites in the southern Levant.
This fish transport persisted for about 2,000 years, beginning in the Late Bronze Age and continuing into the early Byzantine Period, roughly 300 to 600 AD. “Our examination of the teeth revealed that the sea bream must have come from a very saline waterbody, containing much more salt than the water in the Mediterranean Sea,” said Professor Thomas Tütken of Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU). The geoscientist participated in the study together with colleagues from Israel and Göttingen. The Bardawil lagoon formed 4,000 years ago, when the sea level finally stabilized after the end of the last Ice Age. The lagoon was fished intensively and was the point of origin of an extensive fish trade.
As demonstrated by archeological finds, fishing was an important economic factor for many ancient cultures. In the southern Levant, the gilthead sea bream with the scientific name of Sparus aurata was already being fished by local costal fishermen 50,000 years ago. More exotic fish, such as the Nile perch, were already being traded between Egypt and Canaan over 5,000 years ago. However, the current study shows the extent to which the trade between the neighbors increased in the Late Bronze Age and continued for 2,000 years into the Byzantine Period. “The Bardawil lagoon was apparently a major source of fish and the starting point for the fish deliveries to Canaan, today’s Israel, even though the sea bream could have been caught there locally,” stated co-author Professor Andreas Pack from the University of Göttingen.
Fish teeth document over 2,000 years of trade
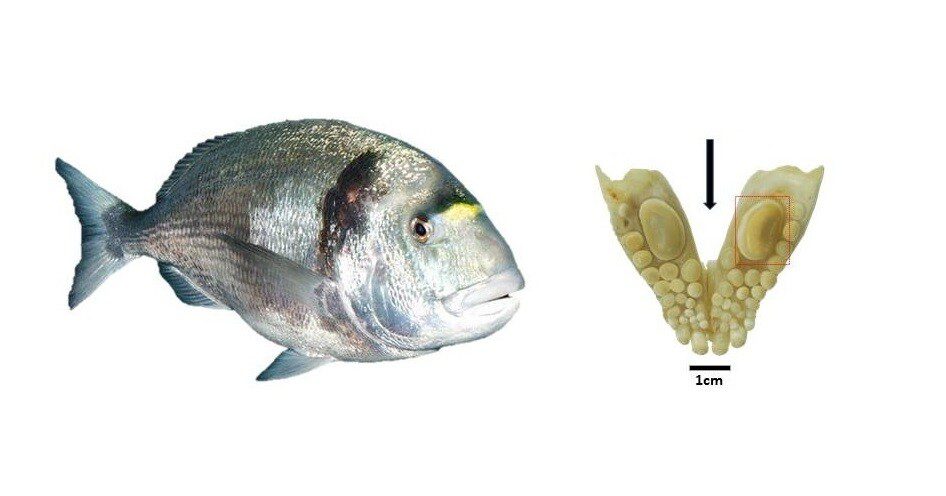
Gilthead sea bream are a food fish that primarily feed on crabs and mussels. They have a durophagous dentition with button-shaped teeth that enable them to crush the shells to get at the flesh. For the purposes of the study, 100 large shell-cracking teeth of gilthead sea bream were examined. The teeth originate from 12 archeological sites in the southern Levant, some of which lie inland, some on the coast, and cover a time period from the Neolithic to the Byzantine Period. One approach of the researchers was to analyze the content of the oxygen isotopes ^18O and ^16O in the tooth enamel of the sea bream. The ratio of ^18O to ^16O provides information on the evaporation rate and thus on the salt content of the surrounding water in which the fish lived. In addition, the researchers were able to estimate the body size of the fish on the basis of the size of the shell-cracking teeth.
The analyses showed that some of the gilthead sea bream originated from the southeastern Mediterranean but that roughly three out of every four must have lived in a very saline body of water. The only water that comes into question in the locality is that of the Bardawil lagoon, the hypersaline water of which has a salt content of 3.9 to 7.4 percent, providing the perfect environment for the growth of sea bream. The Bardawil lagoon on the Sinai coast is approximately 30 kilometers long, 14 kilometers wide, and has a maximum depth of 3 meters. It is separated from the Mediterranean by a narrow sand bar.
“There was a mainland route from there to Canaan, but the fish were probably first dried and then transported by sea,” added Tütken. Even back then, sea bream were probably a very popular food fish, although it is impossible to estimate actual quantities consumed. However, it became apparent that the fish traded from the period of the Late Bronze Age were significantly smaller than in the previous era.
According to the researchers, this reduction in body size is a sign of an increase in the intensity of fishing that led to a depletion of stocks, which is to be witnessed also in modern times. “It would seem that fishing and the trade of fish expanded significantly, in fact to such a degree that the fish did not have the chance to grow as large,” continued Tütken, pointing out that this was an early form of the systematic commercial exploitation of fish, a type of proto-aquaculture, which persisted for some 2,000 years.
JOHANNES GUTENBERG UNIVERSITAET MAINZ
Header Image – Jaw with a durophagous dentition consisting of teeth with thick enamel of the gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata): The large molariform tooth was used for oxygen isotope analysis and to estimate the size of the fish. Credit : photo/©: Guy Sisma-Ventura, Israel