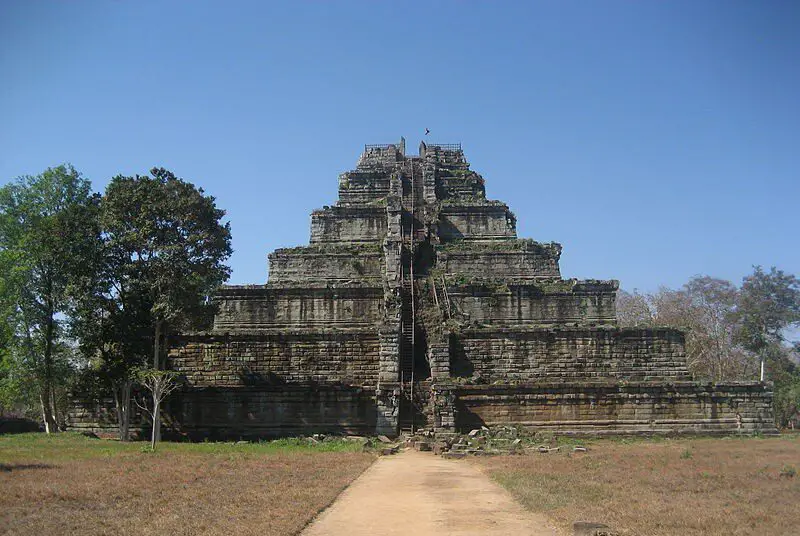
The classic account of the ancient city of Koh Ker is one of a briefly-occupied and abruptly-abandoned region, but in reality, the area may have been occupied for several centuries beyond what is traditionally acknowledged.
Koh Ker was part of the Khmer kingdom during the Angkor period in what is now Cambodia. For a mere two decades in the tenth century CE, the city served as royal capital, and it has long been proposed that after the royal seat moved back to Angkor, the city and its surroundings were abandoned.
In this study, Hall and colleagues tested this theory by analyzing charcoal and pollen remains in sediment cores spanning several centuries in three Koh Ker localities, including the moat of the main central temple. From these data, they inferred a long history of fluctuations in fire regimes and vegetation which are highly indicative of patterns of human occupation and land use over time.
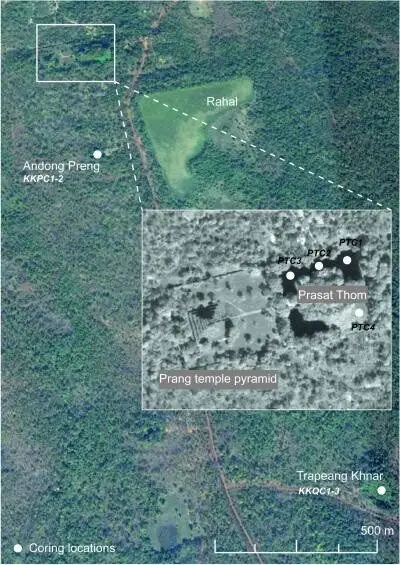
Hall et al., 2018
The newly-painted picture is of a region that was occupied well before the Angkor period, at least as far back as the late 7th century CE, and continuing seven centuries or more after the royal seat’s departure. The authors suggest that the mobility of royal houses may have had less of an impact on regional populations in the Khmer kingdom than previously thought. This study also highlights the utility of palaeoecological tools to reconstruct the occupational history of ancient urban settlements.
Hall adds: “When the environmental record is analyzed, it becomes clear that Koh Ker was much more than a temporary 10th century capital of the Khmer kingdom. The settlement history of the site is extensive and complex, beginning in the pre-Angkor period and lasting for centuries beyond the decline of Angkor.”
Header Image Credit : Arian Zwegers





