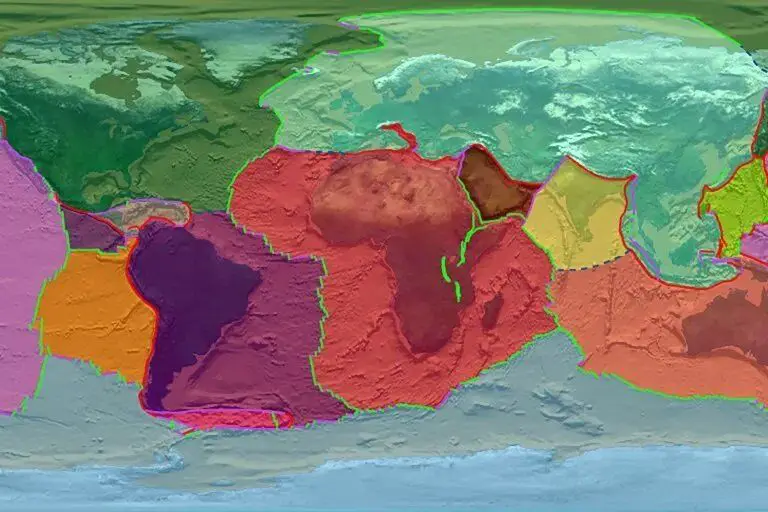
A new study suggests that plate tectonics–a scientific theory that divides the earth into large chunks of crust that move slowly over hot viscous mantle rock–could have been active from the planet’s very beginning.
The new findings defy previous beliefs that tectonic plates were developed over the course of billions of years.
The paper, published in Earth and Planetary Science Letters, has important implications in the fields of geochemistry and geophysics. For example, a better understanding of plate tectonics could help predict whether planets beyond our solar system could be hospitable to life.
“Plate tectonics set up the conditions for life,” said Nick Dygert, assistant professor of petrology and geochemistry in UT’s Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences and coauthor of the study. “The more we know about ancient plate tectonics, the better we can understand how Earth got to be the way it is now.”
For the research, Dygert and his team looked into the distribution of two very specific noble gas isotopes: Helium-3 and Neon-22. Noble gases are those that don’t react to any other chemical element.
Previous models have explained the Earth’s current Helium-3/Neon-22 ratio by arguing that a series of large-scale impacts (like the one that produced our moon) resulted in massive magma oceans, which degassed and incrementally increased the ratio of the Earth each time.
However, Dygert believes the scenario is unlikely.
“While there is no conclusive evidence that this didn’t happen,” he said, “it could have only raised the Earth’s Helium-3/Neon-22 ratio under very specific conditions.”
Instead, Dygert and his team believe the Helium-3/Neon-22 ratio raised in a different way.
As the Earth’s crust is continuously formed, the ratio of helium to neon in the mantle beneath the crust increases. By calculating this ratio in the mantle beneath the crust, and considering how this process would affect the bulk Earth over long periods of time, a rough timeline of Earth’s tectonic plate cycling can be established.
“Helium-3 and Neon-22 were produced during the formation of the solar system and not by other means,” Dygert said. “As such, they provide valuable insight into Earth’s earliest conditions and subsequent geologic activity.”
UNIVERSITY OF TENNESSEE AT KNOXVILLE
Header Image – A combined image of Earth’s plates and their boundaries. NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center Scientific Visualization Studio