Scientists from Norway and the UK have shown that, 20.000 years ago, Arctic sea ice in the winter covered more than twice the area than it does today.
Yet, there was a small ice-free oasis between ice covered continents and the frozen ocean. There, marine life prevailed.
“When we were looking for evidence of biological life in sediments at the bottom of the ocean, we found that between the sea ice covered oceans, and the ice sheets on land, there must have been a narrow ice-free corridor that extended over hundreds of kilometres into the Arctic. Such ice-free regions are often called “polynyas” – a Russian expression for an area of open water that is surrounded by sea ice and/or ice sheets”, says research scientist Jochen Knies from Centre for Arctic Gas Hydrate, Environment and Climate at UiT The Arctic University of Norway, and Geological Survey of Norway.
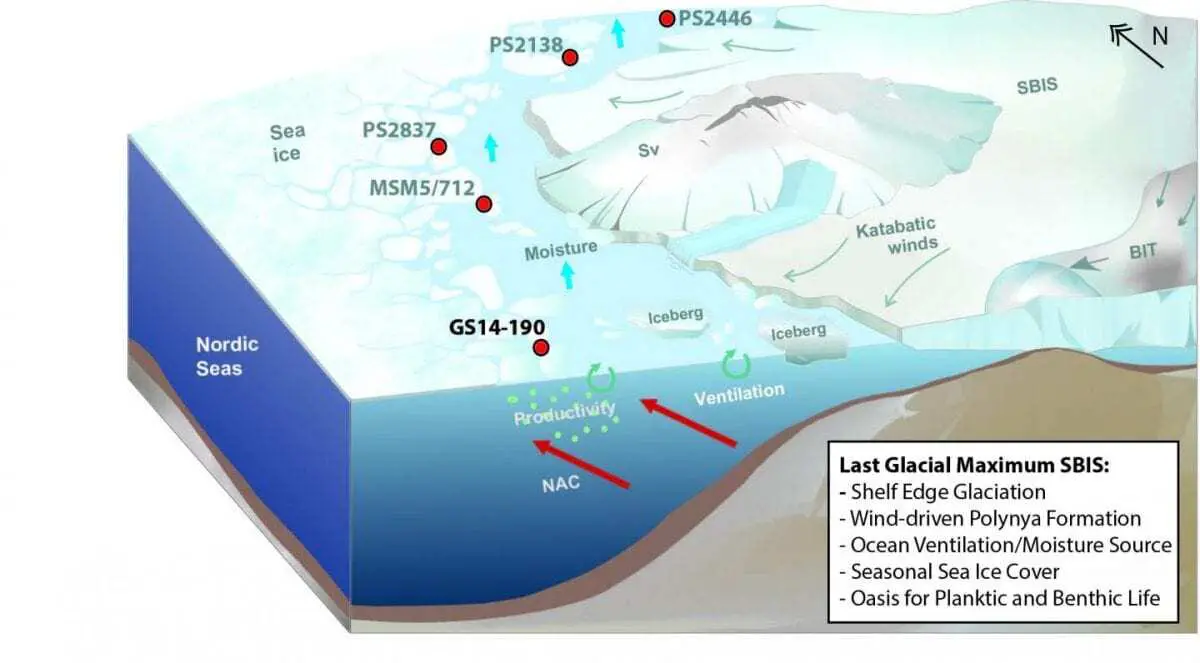
The new findings, which were published recently in Nature Communications, also reveal that the polynya was sustained for at least 5000 years, when the surroundings were largely covered by ice, and global ocean circulation was at a minimum.
Common today in Antarctica and Greenland
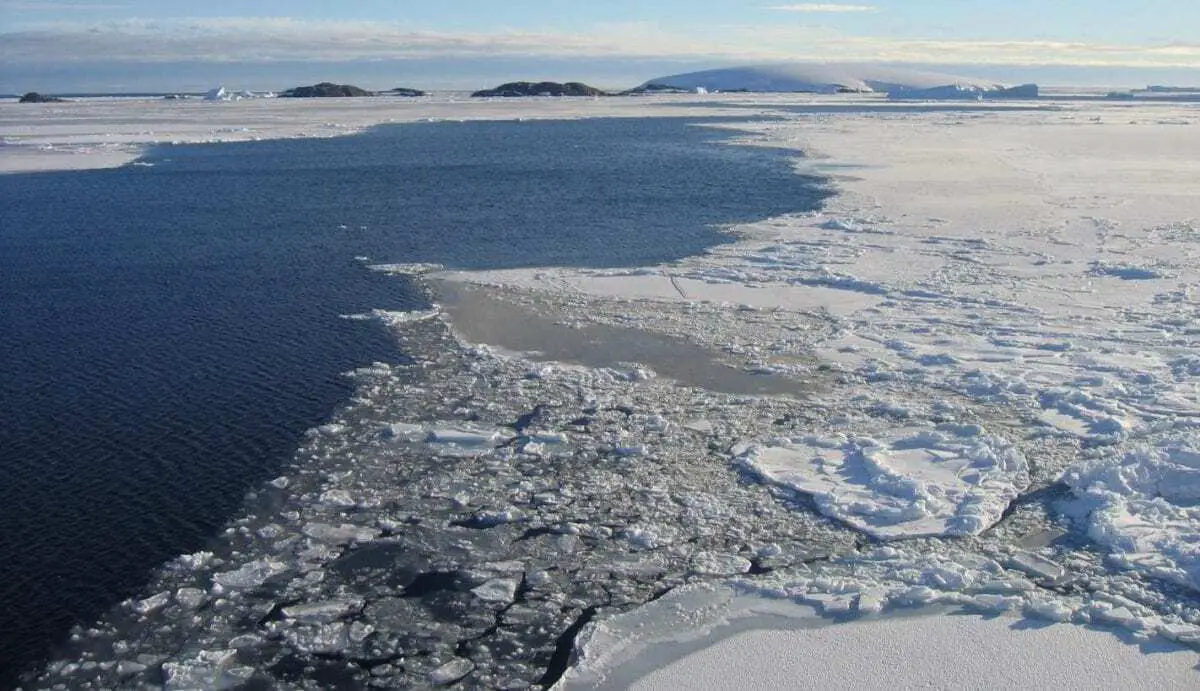
Today, polynyas are common around Antarctica and Greenland. They form through a combination of offshore winds blowing from nearby ice sheets and warm water rising from the deep ocean. In areas of extreme cold and little access to food, polynyas provide an oasis for marine mammals to survive and they are also critical for global ocean circulation.
“Polynyas in the polar regions are common nowadays, but it’s difficult to confirm their existence in the past. However, by finding chemical fossils of algae that live in the open ocean and in sea ice, we have shown that polynyas must have existed during the last Ice Age” says co-author Simon Belt, professor of chemistry at Plymouth University.
During a subsequent period of abrupt climate change around 17,500 years ago, cold freshwater from the melting ice caps caused entire northern oceans to be covered by thick sea ice and the polynya disappeared. This resulted in a dramatic decline in marine life. It took up to 2000 years for the life to recover.
The research is of international importance since it shows the vulnerability of marine ecosystems in the northern oceans to periods of rapid climate change, as well as their adaptability to various extreme climate states.
CAGE – CENTER FOR ARCTIC GAS HYDRATE, CLIMATE AND ENVIRONMENT
Header Image – Sea ice marginal zone in front of West Antarctic ice sheet. Polynias, ice free corridors between the sea ice and land based ice sheets, are common in Antarctica today. Credit : Photo: M. Forwick





