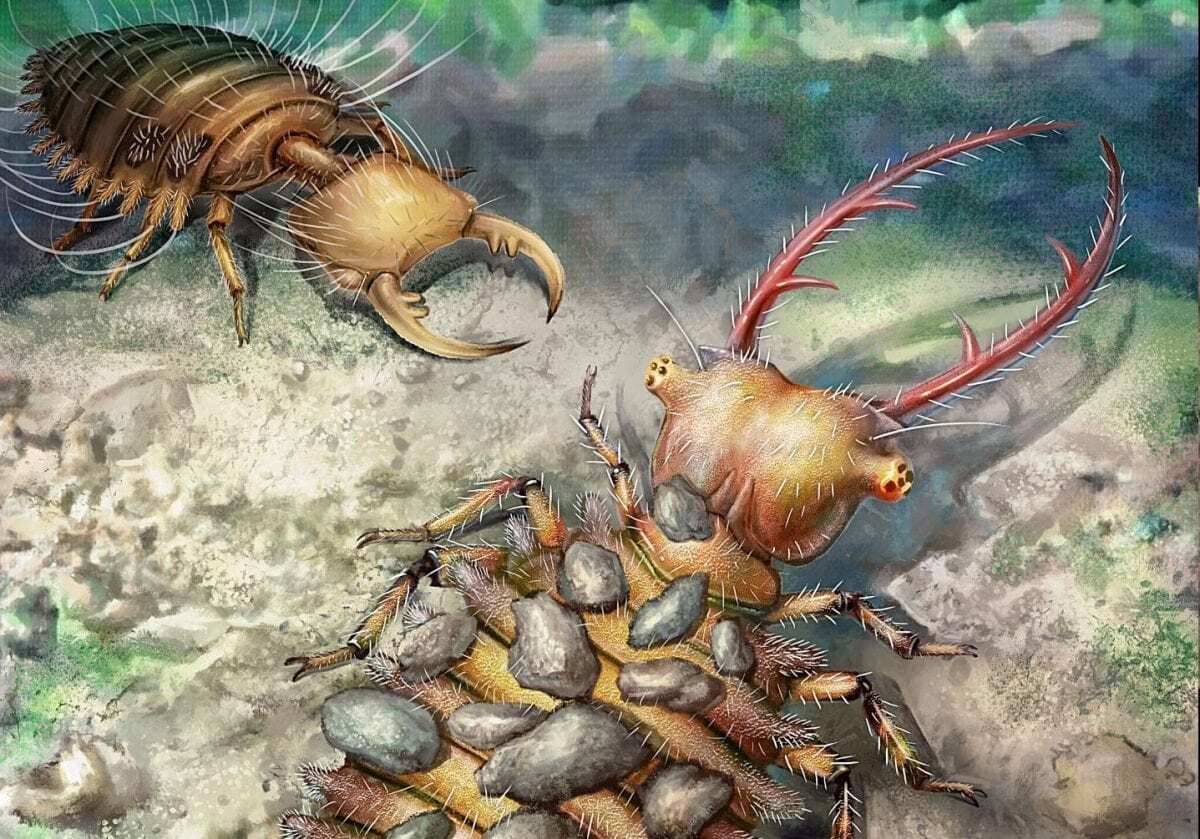
Myrmeleontiformia (antlions and their relatives) are an ancient group of lacewing insects characterized by predatory larvae with unusual morphologies and behaviours.
An international team led by Prof. WANG Bo from the Nanjing Institute of Geology and Palaeontology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (NIGPAS) and two Italian researchers found fossil Myrmeleontiformia fauna from mid-Cretaceous (approximately 100 million years ago) Burmese amber. The study was published in Nature Communications on August 22, 2018.
Their findings show that Myrmeleontiformia did not gain considerable morphological novelty during the subsequent 100 million years, and their diversity seemed to result from different combinations of a limited set of character traits in a complex trade-off.
This morphological stasis helped in reconstructing behaviors not preserved by a trace in the fossil record. Inference of these behaviors shed light on the ecological niche and lifestyle of extinct Myrmeleontiformia.
Statistical correlation analysis strongly supported a correlation between a selection of morphological traits and two hunting strategies of these ambush predators – camouflaging and fossoriality – allowing us to reconstruct habits of extinct species.
The findings suggested that fossorial specializations evolved more than once across Myrmeleontiformia from arboreal ancestors. The fossorial lifestyle of antlions was certainly one of the factors leading to their success, allowing these insects to colonize and diversify in arid habitats where they survived considerable changes in terrestrial environments during the Cretaceous lineages.
The Burmese fossils showed that debris-carrying characterized this lineage for at least 100 million years. All of these camouflaging lacewings were equipped with elongate protuberances. The strong statistical correlation between the presence of these protuberances and camouflaging behavior demonstrated that this trait is an indicator of such behavior, even when the debris covering is not directly preserved in the amber piece together with the larvae.
This research also implies that camouflaging behavior arose at least three times within Myrmeleontiformia. Camouflaging and fossoriality appear widespread across the lineage, and both behaviors allowed the predatory larvae to hide from their unsuspecting prey.
CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES HEADQUARTERS
Header Image – This is a reconstruction of two lacewing larvae. Credit : YANG Dinghua