Sea War Museum Jutland in Thyborøn, Denmark has made a new sensational discovery during its continued registration of shipwrecks in the North Sea and in the Skagerrak.
In April 2018, the museum has found the wreck of the German U-boat U-3523, which was sunk by depth bombs in Skagerrak by a British B24 Liberator aircraft on 6 May, 1945. The day before, the German forces in Denmark, Northwest Germany and the Netherlands had surrendered, and the U-boat was not on a war patrol, but probably on the run.
The U-3523 was of the new and highly advanced type XXI U-boats that could have revolutionized the submarine war if enough boats had been completed in due time. 118 boats were laid down, but only two entered active service, and none ever saw battle.
After the war, there were many rumors about top Nazis who fled in U-boats and brought Nazi gold to safety, and the U-3523 fed the rumors. The Type XXI was the first genuine submarine that could sail submerged for a prolonged time, and the U-3523 had a range that would have allowed it to sail non-stop all the way to South America. But nobody knows, if this was the U-boat’s destination, and nobody knows, if the U-boat had valuables or passengers aboard in addition to the 58 crew, all of whom perished.
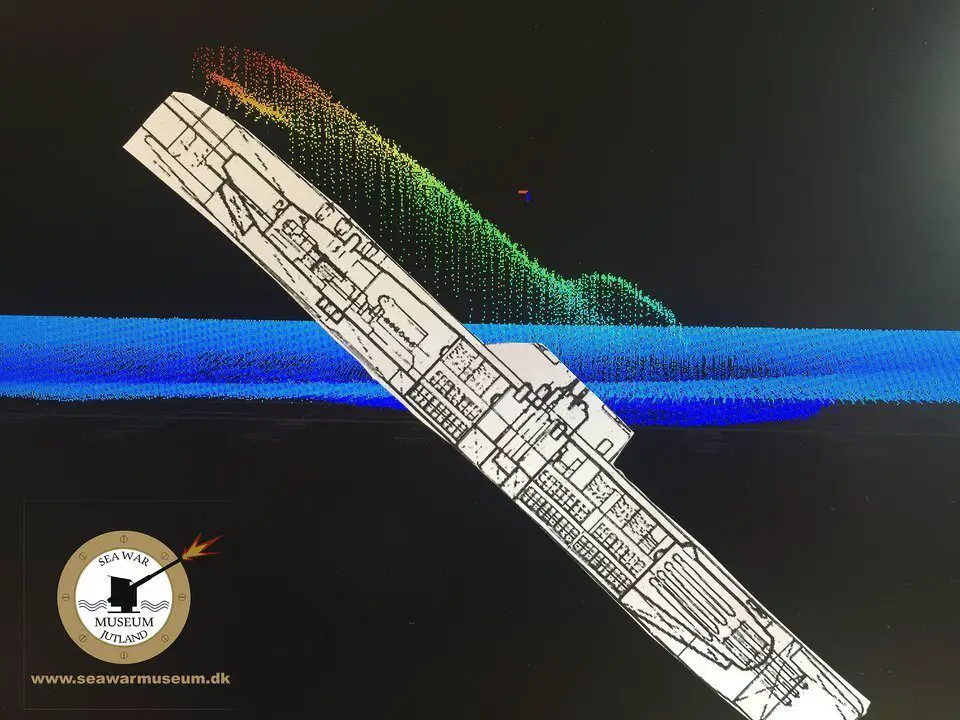
At 123 meters depth
U-3523 appeared on the screen during the museum’s scan of the seabed ten nautical miles north of Skagen, and the picture was very surprising. Most unusual the whole fore part of the U-boat lies buried in the seabed, while the stern is standing 20 meters above the bottom. The wreck lies at 123 meters of water, making it very difficult to access.
So far, it has been thought that the U-3523 was sunk in the waters northeast of Skagen, but the old position was heavily flawed. The U-3523 lies in fact about 9 nautical miles west of the position, which was reported by the British bomber at the time.
Sea War Museum Jutland in Thyborøn has so far found, registered and measured about 450 wrecks in the North Sea and in the Skagerrak. The museum has until now found the wrecks of 12 submarines, 3 of which are British and 9 are German.
After WW2 Britain, the United States, France and the Soviet Union took over a number of German Type XXI U-boats and used them for a number of years in order to profit from the German technology. In the Soviet Union, the submarine became known as the Whiskey class and was used in active service all the way up to the eighties.
Today, there is only one preserved Type XXI U-boat. It lies as a museum boat in the harbour in front of the German Maritime Museum in Bremerhaven.
Header Image Credit: Sea War Museum





