During the Middle Ages, nearly everyone in Europe was exposed to the disfiguring, painful and ostracizing disease of leprosy. But did contracting the disease necessarily increase a person’s chances of dying?
“You’d think it would be a shut case,” says ASU-SFI Center Postdoctoral Fellow Mike Price, an author on a new paper in the American Journal of Physical Anthropology. “But interpreting archaeological data is tricky. Archaeologists must study the bones of people who have died, and dead people are not representative of the living.
It’s like making conclusions about modern, healthy people by observing sick people in hospitals.” The paper lays out a model that offers a way to explore both morbidity — contracting a disease — and mortality — dying from it — through a unique data set of bones recovered from a rural monastery in Denmark.
“Our paper does say, yes, if you have leprosy, you will die sooner. But there are subtleties,” says Price. Sex and social status also likely played roles in a person’s risk of death from leprosy.
Leprosy first presents outwardly as boils on the skin. As it progresses, it can form lesions on the bones, allowing for paleopathological study of the disease.
“There’s a paradoxical component to looking at skeletons,” says Penn State bioarcheologist Saige Kelmelis, lead author, who analyzed the skeletons. Say you have bones of two people who were born in the same year. One died at age 25, and their bones are pristine while the other, who died at age 50, has lesions all over their skeleton.
Which person was healthier? “This model takes into account how we calculate age of death and errors in that, and lesion data, to get a picture of someone’s risk of death. Then we can say something tangible about what the living population would have been like.”
Today, leprosy shows up in different populations in different ways. It’s very rare in the US, but is still an enormous problem in other parts of the world, and people in lower socio-economic statuses are at greater risk says Kelmelis. “Knowing the current state of the disease, we wondered if we could see similar patterns in the past.”
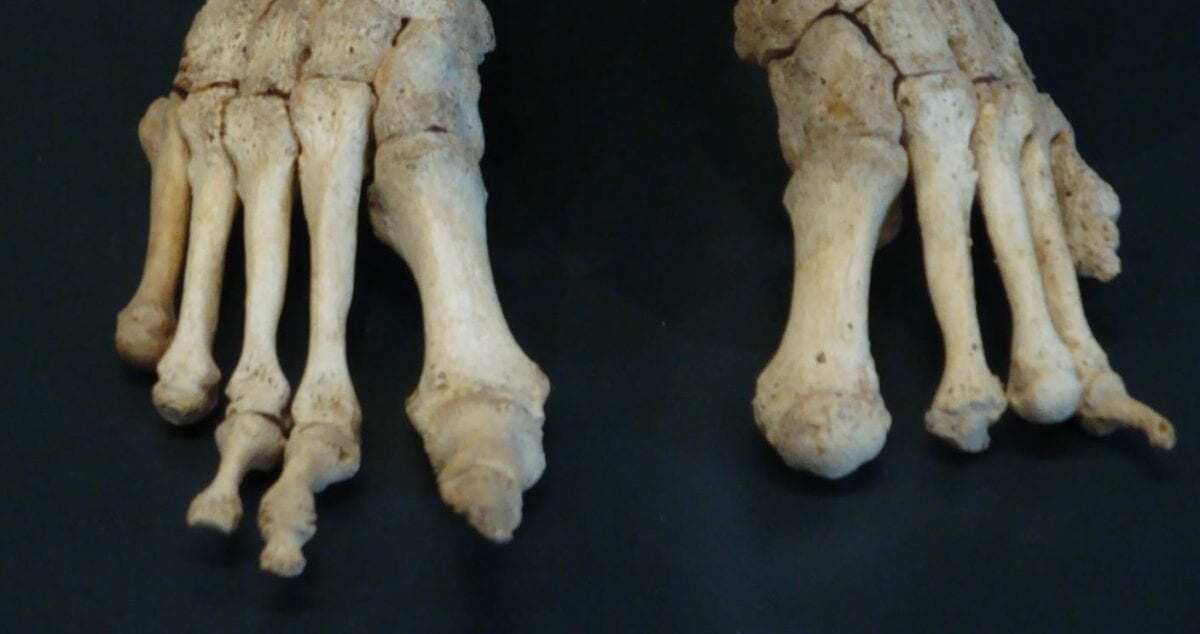
Header Image – These are feet bones, severely affected by leprosy, from the Om Kloster museum in northern Jutland Denmark. CREDIT Saige Kelmelis