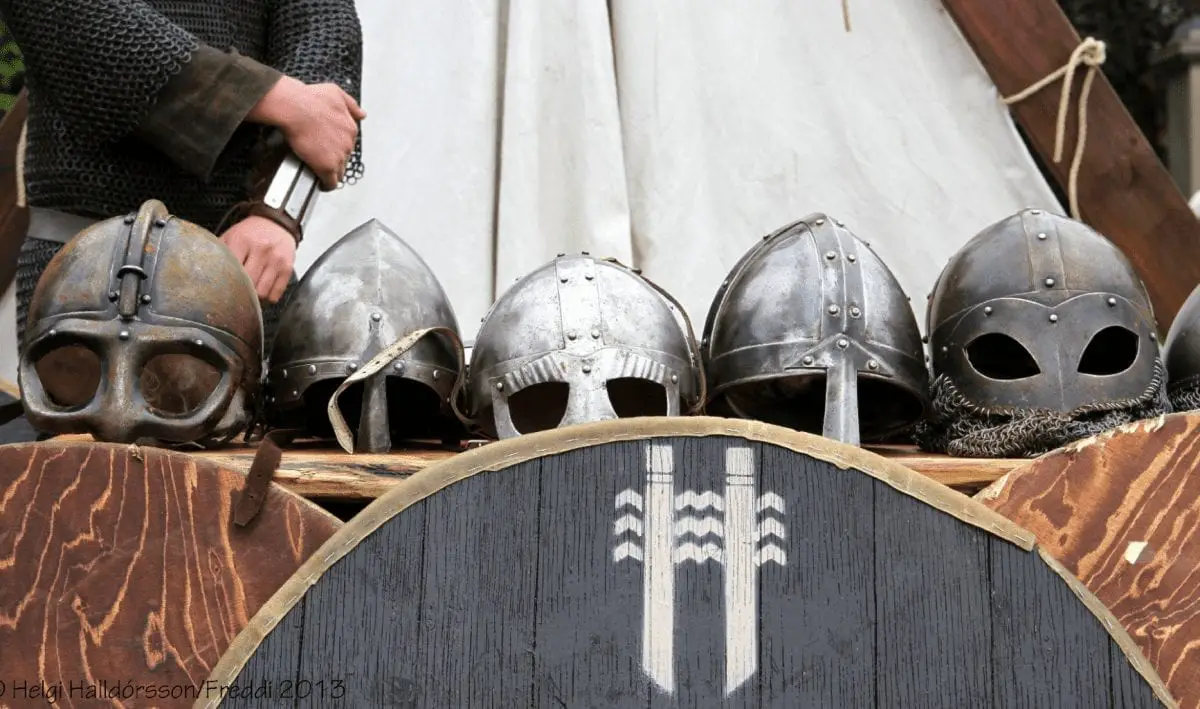
A huge camp which was home to thousands of Vikings as they prepared to conquer England in the late ninth century has been uncovered by archaeologists.
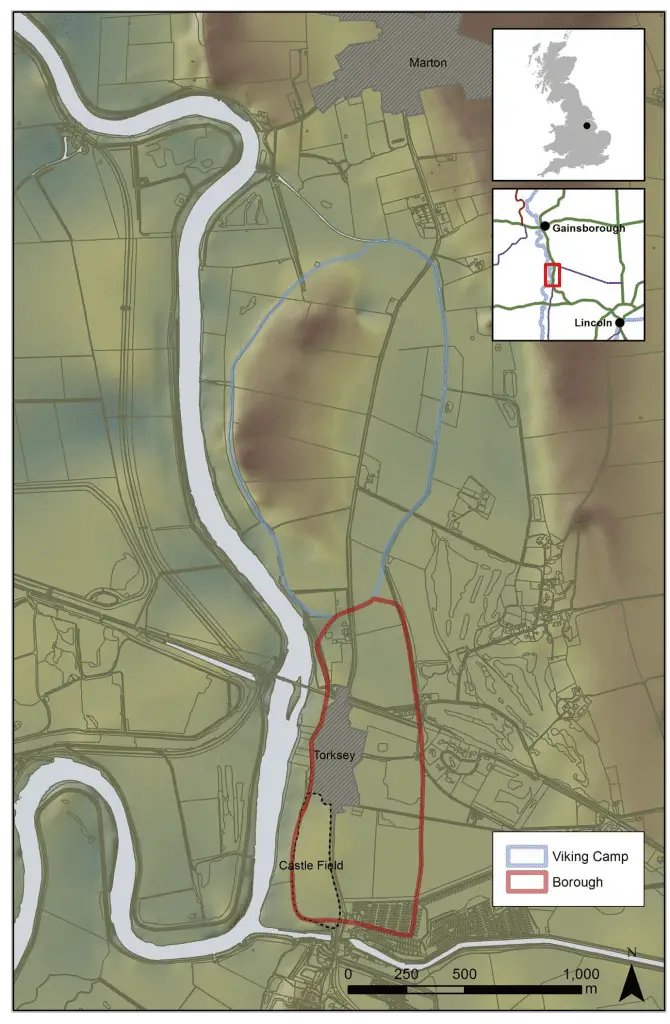
Established in Torksey, on the banks of the River Trent in Lincolnshire, the camp was used as the Vikings’ defensive and strategic position during the winter months.
The research, conducted by archaeologists at the Universities of Sheffield and York, has revealed how the camp was used by thousands of Viking warriors, women and children who lived there temporarily in tented accommodation.
They also used the site as a base to repair ships, melt down stolen loot, manufacture, trade and play games.
Professor Dawn Hadley, who led the research from the University of Sheffield’s Department of Archaeology said: “The Vikings’ camp at Torksey was much more than just a handful of hardy warriors – this was a huge base, larger than most contemporary towns, complete with traders, families, feasting, and entertainment.
“From what has been found at the site, we know they were repairing their boats there and melting down looted gold and silver to make ingots – or bars of metal they used to trade.
“Metal detectorists have also found more than 300 lead game pieces, suggesting the Vikings, including, women and children, were spending a lot of time playing games to pass the time, waiting for spring and the start of their next offensive.”
The findings have now been used to create a virtual reality experience giving users an opportunity to experience what life was like in a Viking army camp.
The virtual reality experience has been developed by researchers at the University of York and is part of an exhibition at the Yorkshire Museum that opens on Friday (19 May 2017).
All the scenes featured in the virtual reality experience are based on real objects found by archaeologists and metal detectorists at Torksey.
Professor Julian Richards, from the Department of Archaeology at the University of York, said: “These extraordinary images offer a fascinating snap shot of life at a time of great upheaval in Britain.
“The Vikings had previously often raided exposed coastal monasteries and returned to Scandinavia in winter, but in the later ninth century they came in larger numbers, and decided to stay. This sent a very clear message that they now planned not only to loot and raid – but to control and conquer.”
Dr Gareth Beale from York’s Digital Creativity Labs added: “The new research by the Universities of Sheffield and York has been used to create the most realistic images of the camp to date, based on real findings. These images are also believed to be the most realistic Virtual Reality ever created anywhere of the Viking world.”
The exact location and scale of the camp in Lincolnshire has been debated for many years, but now the research by Sheffield and York is beginning to reveal the true extent of the camp. It is now thought to be at least 55 hectares in size, bigger than many towns and cities of the time, including York.
There have also been more than a thousand finds by metal detectorists and archaeologists, including over 300 coins. They include more than 100 Arabic silver coins which would have come to the area through established Viking trade routes.
More than 50 pieces of chopped up silver, including brooch fragments and ingots have been found along with rare hackgold. Evidence has been found that these items were being processed at the camp – chopped up to be melted down. Other finds include the 300 gaming pieces, iron tools, spindle whorls, needles and fishing weights.
Using landscape analysis, the research has been able to reveal the topography of the camp. With the River Trent to the west and surrounding land prone to flooding to this day, its strength as a defensive position becomes clear.
The research at Torskey has been made available as an Open Access publication and can be downloaded here







