Imagine you are about to plan and construct a building that involves several complicated geometrical shapes, but you aren’t allowed to write down any numbers or notes as you do it. For most of us, this would be impossible.
Yet, new research from Arizona State University has revealed that the ancient Southwestern Pueblo people, who had no written language or written number system, were able to do just that – and used these skills to build sophisticated architectural complexes.
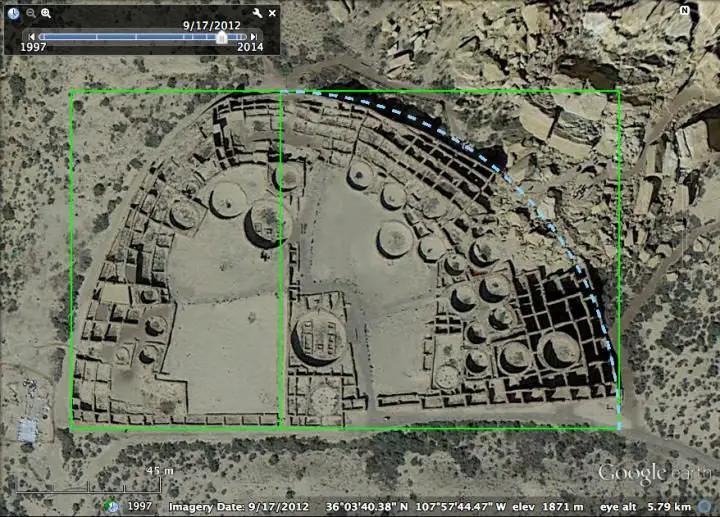
Dr. Sherry Towers, a professor with the ASU Simon A. Levin Mathematical, Computational and Modeling Sciences Center, uncovered these findings while spending several years studying the Sun Temple archaeological site in Mesa Verde National Park in Colorado, constructed around A.D. 1200.
Dr. Sherry Towers
“The site is known to have been an important focus of ceremony in the region for the ancestral Pueblo peoples, including solstice observations,” Towers says. “My original interest in the site involved looking at whether it was used for observing stars as well.”
However, as Towers delved deeper into the site’s layout and architecture, interesting patterns began to emerge.
“I noticed in my site survey that the same measurements kept popping up over and over again,” she says. “When I saw that the layout of the site’s key features also involved many geometrical shapes, I decided to take a closer look.”
The geometrical shapes used within this location would be familiar to any high school student: equilateral triangles, squares, 45-degree right triangles, Pythagorean triangles, and the “Golden rectangle,” which was well known to architects in ancient Greece and Egypt and is often used in Western art due to its pleasing proportions.
With some geometrical know-how, a straight-edge, a compass or cord, and a unit of measurement, all of the shapes are fairly easy to construct. But, unlike the ancient Greeks, Egyptians and Maya, the ancestral Pueblo people had no written language or number system to aid them when they built the site. Incredibly, their measurements were still near-perfect, with a relative error of less than one percent.
“This is what I find especially amazing,” Towers says. “The genius of the site’s architects cannot be underestimated. If you asked someone today to try to reconstruct this site and achieve the same precision that they had using just a stick and a piece of cord, it’s highly unlikely they’d be able to do it, especially if they couldn’t write anything down as they were working.”
During her research, Towers discovered that the site was laid out using a common unit of measurement just over 30 centimeters in length – equal to about one modern-day foot. She also found evidence that some of the same geometrical constructs from Sun Temple were used in at least one other ancestral Puebloan ceremonial site, Pueblo Bonito, located in New Mexico’s Chaco Culture National Historic Park.
“Further study is needed to see if that site also has the same common unit of measurement,” she says. “It’s a task that will keep us busy for some years to come.”




