An expedition mapping submerged ancient landscapes, the first of its kind in the Black Sea, is making exciting discoveries.
An international team, involving the University of Southampton’s Centre for Maritime Archaeology and funded by the charitable organisation for marine research, the Expedition and Education Foundation (EEF), is surveying the Bulgarian waters of the Black Sea, where thousands of years ago large areas of land were inundated as the water level rose following the last Ice Age.
Professor Jon Adams, Founding Director of the University of Southampton’s Centre for Maritime Archaeology and Principle Investigator on the Black Sea Maritime Archaeology Project (Black Sea MAP) says: “We’re endeavouring to answer some hotly-debated questions about when the water level rose, how rapidly it did so and what effects it had on human populations living along this stretch of the Bulgarian coast of the Black Sea. As such, the primary focus of this project – and the scope of our funding from the EEF – is to carry out geophysical surveys to detect former land surfaces buried below the current sea bed, take core samples and characterise and date them, and create a palaeoenvironmental reconstruction of Black Sea prehistory.”

Based on board the Stril Explorer, an off-shore vessel equipped with some of the most advanced underwater survey systems in the world, the international team of researchers is surveying the sea bed using two Remotely Operated Vehicles (ROVs). One is optimised for high resolution 3D photogrammetry2 and video. The other is a revolutionary vehicle developed by the survey companies MMT and Reach Subsea. Surveyor Interceptor ‘flies’ at four times the speed of conventional ROVs and carries an entire suite of geophysical instrumentation, as well as lights, high definition cameras and a laser scanner. In the course of the project it has set new records for both depth (1,800m), sustained speed (over 6 knots), and has covered a distance of 1,250 km.
During these surveys, members of Black Sea MAP have also discovered and inspected a rare and remarkable ‘collection’ of more than 40 shipwrecks, many of which provide the first views of ship types known from historical sources, but never seen before. The wrecks, which include those from the Ottoman and Byzantine Empires, provide new data on the maritime interconnectivity of Black Sea coastal communities and manifest ways of life and seafaring that stretch back into prehistory.
Professor Adams comments: “The wrecks are a complete bonus, but a fascinating discovery, found during the course of our extensive geophysical surveys. They are astonishingly preserved due to the anoxic conditions (absence of oxygen) of the Black Sea below 150 metres.
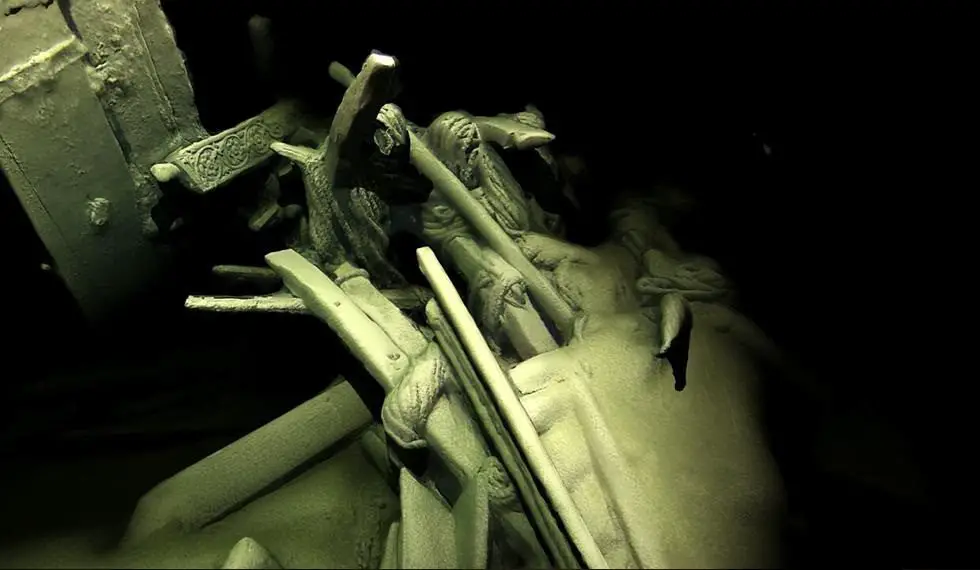
“Using the latest 3D recording technique for underwater structures, we’ve been able to capture some astonishing images without disturbing the sea bed. We are now among the very best exponents of this practice methodology and certainly no-one has achieved models of this completeness on shipwrecks at these depths.”
Professor Adams concludes: “Maritime archaeology in the deep sea has often been a contested domain, but this project, the largest of its type ever undertaken, demonstrates how effective partnerships between academia and industry can be, especially when funded by enlightened bodies such as EEF.”
The Black Sea MAP team comprises of researchers from the University of Southampton’s Centre for Maritime Archaeology (CMA), who have established a formal partnership with the Bulgarian National Institute of Archaeology with Museum and the Bulgarian Centre for Underwater Archaeology (CUA). Partner institutions include the Maritime Archaeological Research Institute at Södertörn University, Sweden; the University of Connecticut, USA; the Hellenic Centre for Marine Research, Greece; and MMT, the company whose founder Ola Oskarsson designed the Surveyor Interceptor. Core samples recovered from the Black Sea will be analysed at the British Ocean Sediment Core Research Facility at the National Oceanography Centre, Southampton.
The project operates under permits from the Bulgarian Ministry of Culture and Ministry of Foreign Affairs in strict adherence to the UNESCO Convention on the Protection of the Underwater Cultural Heritage (2001).




