A study published in Scientific Reports-Nature puts forward a new explanation for the Martian megafloods: enormous discharges of subterranean water that dug out the biggest flood channels in the solar system over 3000 million years ago.
For many years it was thought that these megafloods were caused by the release of a deep global hydrosphere in the Martian subsoil. However, the research conducted by J. P. Alexis Rodríguez of the Planetary Science Institute (PSI–USA), with the participation of Rogelio Linares and Mario Zarroca of the Department of Geology of the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (UAB), has revealed that their origin could have been vast quantities of sediment and ice deposited 450 million years before the floods.

The findings from this project, which was partially supported by NASA funding for the PSI under its Planetary Geology and Geophysics Program, were published recently as a Scientific Report (Nature Publishing Group) with the title “Martian outflow channels: How did their source aquifers form, and why did they drain so quickly?”.
The article, co-authored by the UAB Geology Department members mentioned above, describes how the sediments carried by rivers and glaciers filled up enormous canyons below an ancient ocean located in the Northern Lowlands, and how it was the release of the water trapped in these buried sediments that caused the megafloods, whose effects we can observe in the present.
The canyons filled up, the ocean disappeared and the planet surface remained frozen for around 450 million years. Subsequently, 3200 million years ago, the heat from lava beneath the canyons thawed the ice trapped in the sediments and enormous rivers of subterranean water spread over hundreds of kilometres, before eventually bursting out on to the now-dry surface and causing the megafloods.
In the words of the Geology Department researchers, “Our research suggests that, given that the process was regional rather than global, there could still be large reservoirs of subterranean water trapped under the surface of Mars, in the areas around the old northern ocean, or in other parts of the planet where seas and lakes formed at the same time”. “Traces of ancient environments capable of sustaining life forms similar to those on Earth could have been preserved in sub-surface materials that are now exposed”, claim R. Linares and M. Zarroca. “The results obtained could have clear implications both for exobiological research and for future human activity on Mars”.
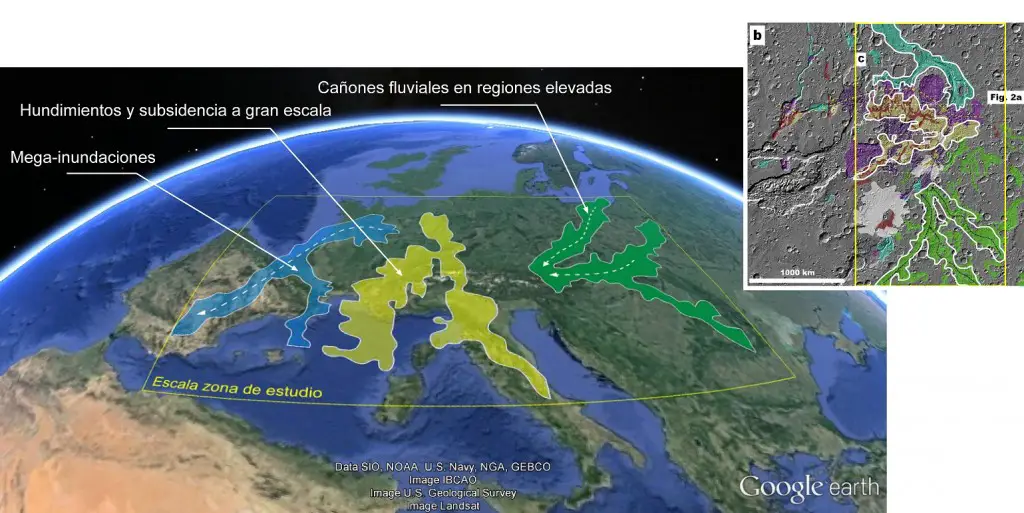
To illustrate the scale of the Martian megafloods, the UAB researchers have estimated the effect they would have on Europe, quantifying it as around 2,500,000 km2.
Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona




