The research team of the Yamagata University Institute of Nasca discovered 24 new geoglyphs in the Nasca Region of the Peruvian South Coast during the survey conducted between December 2014 and February 2015.
The geoglyphs are almost invisible on the surface and the team needed to analyze them using a three-dimensional scanner to highlight the images on the ground. As a result, the Yamagata University team was able to identify 24 geoglyphs of animals, some of which probably depict Andean native camelid, llamas.
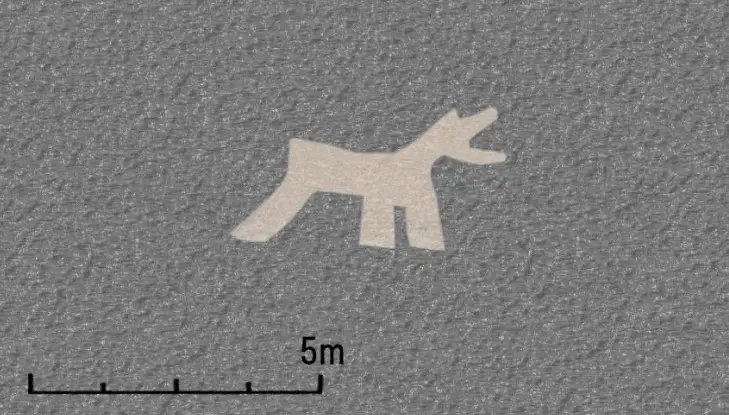
Last year, the team had discovered 17 geoglyphs of similar style in the adjacent area and thus it became clear the total of 41 animal geoglyphs are concentrated in a specific area. These geoglyphs are estimated to date back to 400 BC to 200 BC.
Prof. Masato Sakai, the head of the research team, emphasized that the geoglyphs are in danger of being destroyed by the recent expansion of urban areas and it is important to share this information with local people and government to preserve them.
Yamagata University started the study of the Nasca Geoglyphs in 2004. To advance the research and preservation of geoglyphs, the Yamagata University Institute of Nasca was founded in 2012. The agreement on the academic cooperation and preservation of the geoglyphs was signed by the Ministry of Culture of Peru and Yamagata University in April 2015.




