Researchers now know the invasion history of the tropical fire ant (Solenopsis geminata), the first ant species known to travel the globe by sea.
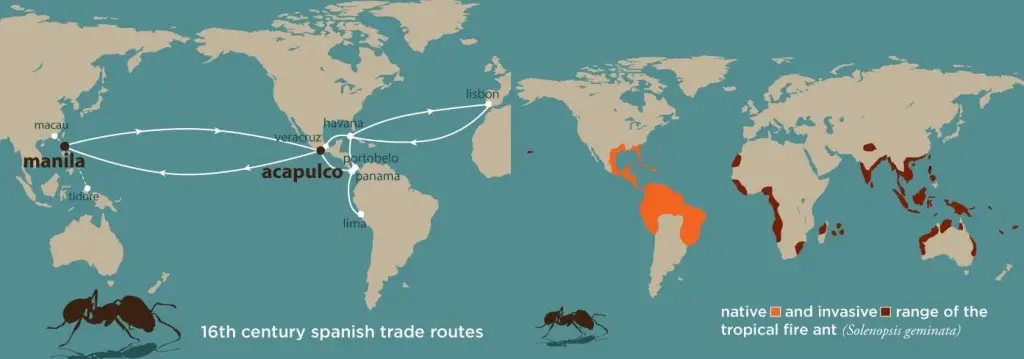
Their study, reported in the journalMolecular Ecology, reveals that 16th century Spanish galleons shuttled tropical fire ants from Acapulco, Mexico, across the Pacific to the Philippines, and from there to other parts of the world. Today, the ant species is found in virtually all tropical regions, including in Africa, the Americas, Australia, India and Southeast Asia. (See map.)
“A lot of these ships, particularly if they were going somewhere to pick up commerce, would fill their ballast with soil and then they would dump the soil out in a new port and replace it with cargo,” said University of Illinois entomology professor and animal biology department head Andrew Suarez, an author on the study. “They were unknowingly moving huge numbers of organisms in the ballast soil.”
Suarez conducted the study with U.S. Department of Agriculture research entomologistDeWayne Shoemaker, University of Vermont biology professor Sara Helms Cahan, former UVM graduate student Heather Axen (now a postdoctoral researcher at Salve Regina University), and former Illinois postdoctoral researcher Dietrich Gotzek.
“Invasive ants are a huge problem. Once they arrive, they establish really high densities in new habitats, with negative consequences for agriculture, native species and human quality of life,” Helms Cahan said. “Controlling them costs millions of dollars annually.”
The researchers analyzed the genomes of tropical fire ants from 192 locales, looking at patterns of genetic diversity. The team also analyzed the trading patterns of Spanish sailing vessels going to and from the New World in the mid-1600s.
“If you look at the records, you look at the history, you look at the old trading routes and you look at the genetics, it all paints this picture that this was one of the first global invasions, and it coincided with what could be the first global trade pattern of the Spanish,” Suarez said. “The ants from the introduced areas in the Old World are genetically most similar to ants from southwestern Mexico, suggesting that their source population came from this region.”
The researchers were able to date the ants’ invasion of the Old World to the 16th century. At this time, the Spanish had just established a regular trade route between Acapulco and Manila, Philippines, not only setting up the first trade route across the Pacific Ocean but also effectively globalizing commerce.
“Acapulco was a big stopping point for the Spanish,” Suarez said.
“From there, Spanish galleons brought silver to Manila, which served as a hub for trade with China,” the authors wrote.
The researchers hypothesized that the original ant population would have the highest level of genetic diversity and that any ants taken from that original population to a new environment would have a subset of that original variability.
And that is what they found.
“There was this very clear pattern where there was the most genetic diversity in the New World, where it’s native, and then you see these stepping stones of nested subsets of diversity as you move away from the New World into the Old World,” Suarez said. And the pattern of genetic changes over time “always overlaps the timing of when the Spanish trade was going on,” he said.
“Our research highlights the importance of historical trade routes in setting up current distributions of pest species,” said Gotzek, who conducted the genetic analyses. “It also establishes the utility of using genetic data to reveal such patterns.”
“Uncovering events that happened long ago, before the age of digital tracking codes and customs enforcement, is often a difficult task,” Helms Cahan said. “Luckily for us, however, it turns out that invasive species keep their own records of their history, encoded in their genomes.”




