Neutron radiation caused by 33 A.D. earthquake could have led to “wrong” 1988 radiocarbon dating of Shroud, suggest researchers.
An earthquake in Old Jerusalem might be behind the famous image of the Shroud of Turin, says a group of researchers led by Alberto Carpinteri of the Politecnico di Torino in Italy in an article published in Springer’s journal Meccanica. They believe that neutron radiation caused by an earthquake could have induced the image of a crucified man – which many people believe to be that of Jesus – onto the length of linen cloth, and caused carbon-14 dating done on it in 1988 to be wrong.
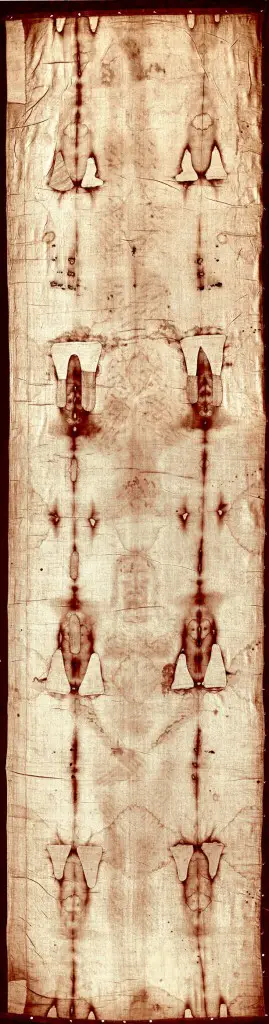
The Shroud has attracted widespread interest ever since Secondo Pia took the first photograph of it in 1898: about whether it is Jesus’ purported burial cloth, how old it might be, and how the image was created. According to radiocarbon dating done in 1988, the cloth was only 728 years old at the time.
Other researchers have since suggested that the shroud is much older and that the dating process was incorrect because of neutron radiation – a process which is the result of nuclear fusion or nuclear fission during which free neutrons are released from atoms – and its interaction with the nuclei of other atoms to form new carbon isotopes.
However, no plausible physical reason has yet been proposed to explain the origin of this neutron radiation. Now Carpinteri’s team, through mechanical and chemical experimentation, hypothesizes that high-frequency pressure waves generated in the Earth’s crust during earthquakes are the source of such neutron emissions.
This is based on their research into piezonuclear fission reactions, which are triggered when very brittle rock specimens are crushed under a press machine. In the process, neutrons are produced without gamma emissions. Analogously, the researchers theorize further that neutron flux increments, in correspondence to seismic activity, should be a result of the same reactions.
The researchers therefore believe that neutron emission from a historical earthquake in 33 A.D. in Old Jerusalem, which measured 8.2 on the Richter Scale, could have been strong enough to cause neutron imaging through its interaction with nitrogen nuclei.
On the one hand, this could have created the distinctive image on the Shroud through radiation imagery, while on the other, it could have increased the level of carbon-14 isotopes found on the linen fibres that could have confused the 1988 radiocarbon dating tests.
“We believe it is possible that neutron emissions by earthquakes could have induced the image formation on the Shroud’s linen fibres, through thermal neutron capture on nitrogen nuclei, and could also have caused a wrong radiocarbon dating,” hypothesizes Carpinteri.
Contributing Source : Springer Science






