Maxilla of Canis chihliensis (IVPP V 18333.1), A. dorsal view; B. lateral view; C. ventral view. (Image by TONG Haowen)
Remains of fossil canids are not rare in China, but they have not been systematically studied.
Previous studies based on dental characters caused considerable confusion on taxonomic classification. In a paper published in the latest issue of Vertebrata PalAsiatica 2012(4), paleontologists from Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology (IVPP), Chinese Academy of Sciences and Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County, reported new materials of a fossil wolf, Canis Chihliensis, from the newly discovered Shanshenmiaozui Locality in the Nihewan Basin, North China.
The new finding helps better understand the morphological characters of Canis chihliensis, showing that this species is much closer to Canis than to Xenocyon or Cuon.
The Shanshenmiaozui locality lies near the hill of Xiaochangliang, a famous Paleolithic Site in the Nihewan Basin. Based on the horizon correlation in the field, the fossil-bearing sand-silt bed at the new locality can be correlated with the cultural layer at Xiaochangliang site whose paleomagnetic age is about 1.36 million years ago.
The new finding includes broken crania, premaxillae, maxillae, mandibles and postcranial skeleton with most of the elements preserved, and represents the most extensive and informative sample of early fossil Canis ever recovered in China.
Considering its large size, long symphyseal suture, robust canines, large M2 and m2 relative to the M1 and m1 respectively, and well-developed hypocone and lingual cingulum on the M1−2, as well as the presence of an m3, the canid materials from the Shanshenmiaozui locality are assigned to the genus Canis. According to the paper, researchers identified these remains as the species Canis chihliensis based on morphological and metric characters, including large size, robust I3, elongated P4 with anterior notch and well-developed protocone, M1 strongly mesiodistally compressed and with broad cingular hypocone, m1 with metaconid and entoconid (however small), M2 and m2 large relative to M1 and m1 respectively, and m2 with broad talonid.
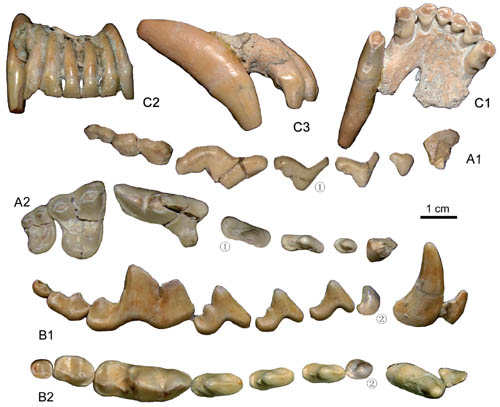
However, the first lower molars from Shanshenmiaozui are quite variable in the development of their lingual cuspids. “This study shows that it is not easy to distinguish Canis chihliensis from Xenocyon dubius (=Cuon dubius) based exclusively on characters of the first lower molar, and the taxonomic status of the latter species is still open to question.




