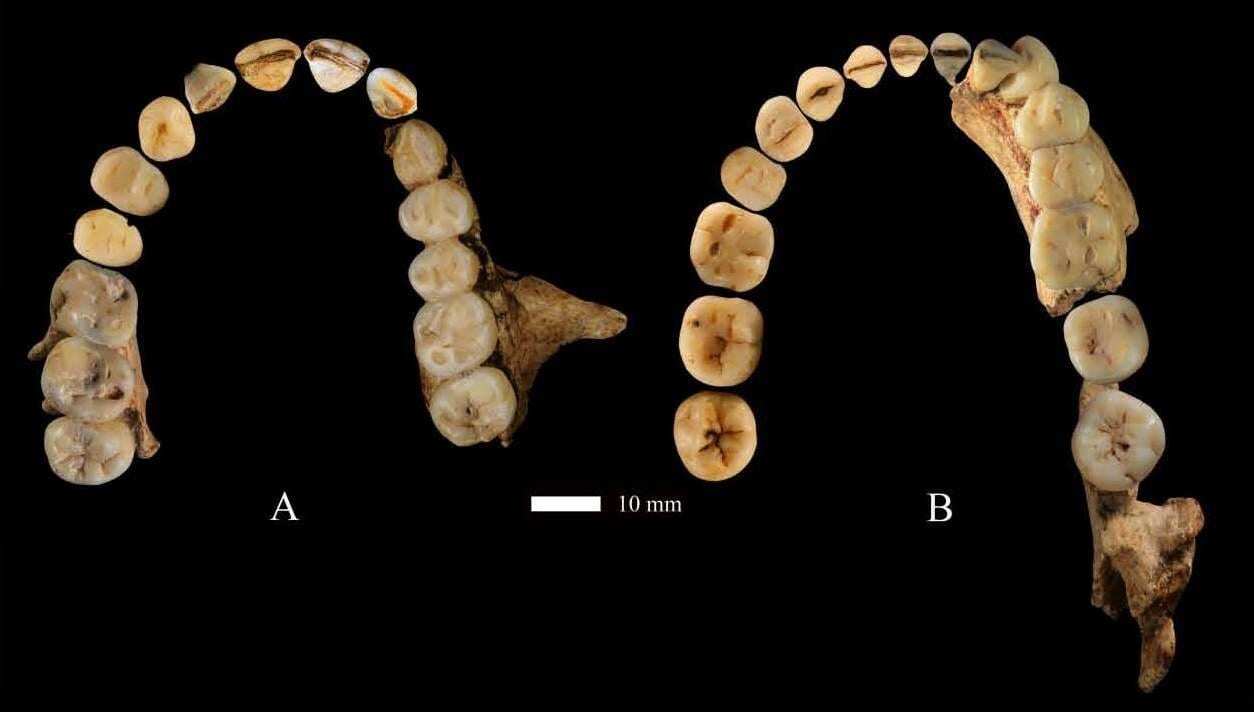
A paper published on the skeletal remains found in Dushan Cave, in Linfeng, southern China, has revealed dental characteristics which are surprising for an Upper Paleolithic population.
To find these traits, it is very often necessary to go back to the earliest representatives of the genus Homo and even to Australopithecus.
The participants in this study include María Martinón Torres and José María Bermúdez de Castro, of the Centro Nacional de Investigación sobre la Evolución Humana (CENIEH), who explain that: “It isn’t that these traits have disappeared completely from modern populations in China, but rather that their presence together in the individual known as Dushan 1 confers a certain primitive aspect on their dentition”.
There exists the possibility that Dushan 1, whose remains have been dated to between 15,280 and 12,765 years old, represents the normal variability within a little-known population in a vast territory. It would be possible to test this hypothesis with new studies of populations from the same period.
“Perhaps we find here a case of prolonged isolation of a group within a certain territory, in which primitive characteristics of the first representatives of Homo sapiens in China have been retained”, remarks Bermúdez de Castro.
Finally, interbreeding of the first Homo sapiens with resident ancestral groups is another possible explanation. The descendants of this hybridization would have survived until the end of the Pleistocene, showing in their dental apparatus the evidence of a highly particular evolutionary history.
Chinese Pleistocene
The variability among the Pleistocene humans of China is less well known than that of Africans and Europeans. Nevertheless, the balance is shifting little by little. The oldest fossils are becoming better known, and their interpretation has already been covered by the general models. It may be that the greatest problem lies in studying the more recent populations from the end of the Pleistocene, as these have held less interest for international experts.
“The skeleton of Dushan 1 makes it very possible that we will start to show more interest in this little-known epoch of the Chinese Pleistocene. We are aware that there remains much to be learned about the peculiar dynamic of the populations of our species, which moved out of Africa to colonize the whole planet”, concludes Martinón Torres.
Header Image – Upper (left) and lower (right) dentition of Dushan 1/Wei Liao