A study published in the journal Mediterranean Archaeology and Archaeometry, suggests that Bronze Age civilisations sailed by the stars using celestial navigation techniques similar to those employed by Polynesian and Micronesian cultures.
The study by skyscape archaeologist, Alessandro Berio, has uncovered new evidence that the ancient Minoan civilisation developed significant nautical technologies to aid in the international sea trade, which is linked to the wealth and expansion of the culture throughout the Mediterranean. Due to its location, reliance on open sea navigation and international trade cycles were at the heart of Minoan culture.
The Minoans were a Bronze Age Aegean civilisation on the island of Crete, which flourished from 2600 – 1100 BC. The term “Minoan” refers to the mythical King Minos of Knossos, a figure in Greek mythology associated with Theseus, the labyrinth and the Minotaur.
The study examined the orientations of the palaces along navigational directions, where the grand rectangular central courts, oriented generally north south on the long axis, are considered the defining architectural characteristic of the Minoan palace construction.
The analysis showed that the axis of the Minoan palaces were oriented toward the rising or setting of important navigational stars, which may have helped sailors to navigate to the bustling commercial destinations in the Levant and Egypt. The orientation of these palaces symbolised Crete’s special relationship with foreign trading hubs and the control that local elites wielded over specific sea lanes.
The study suggests that the Minoans used “star paths”, or linear constellations (known in traditional Polynesian star sailing as kaveinga) to reach cities in the Mediterranean area, many of which have evidence of Minoan artefacts and frescos.
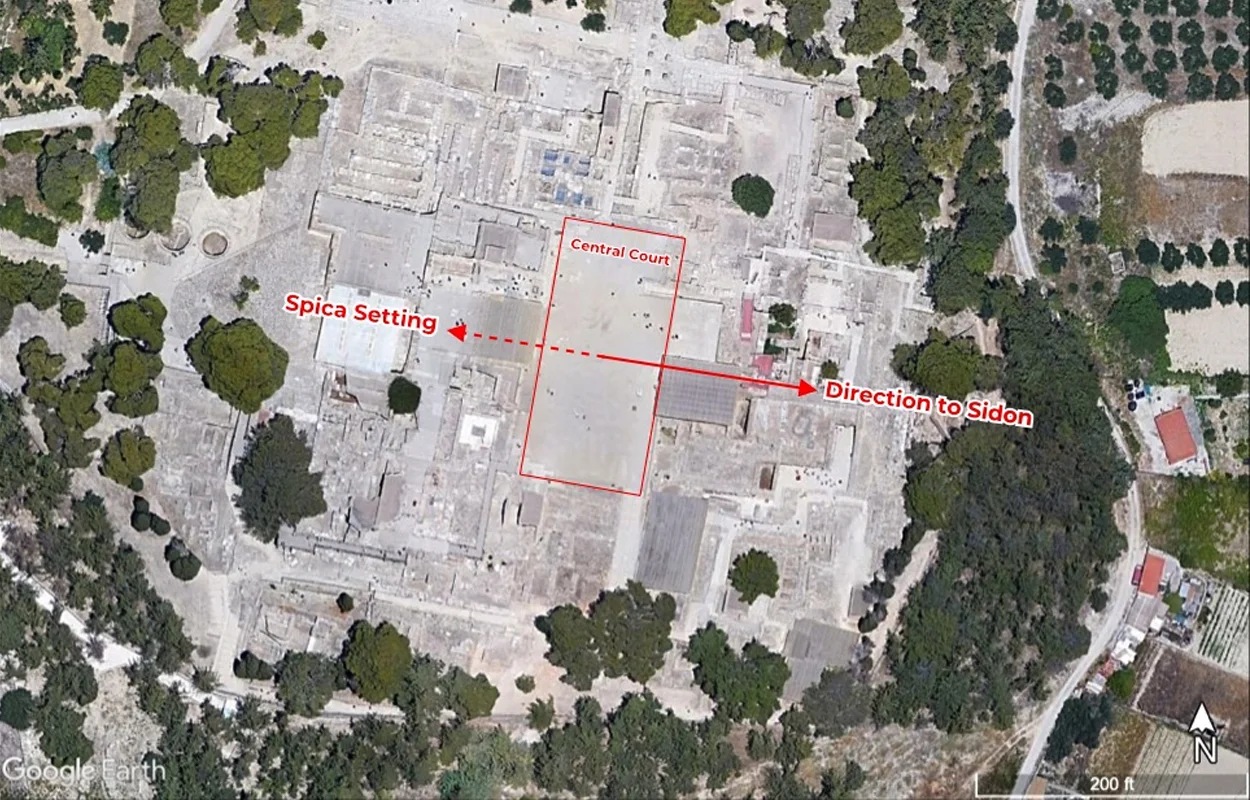
An example of a “star path” is Spica in the constellation of Virgo, which has a direct route connecting Knossos – the largest Minoan palace – to the important trading hub of Sidon (in modern Lebanon).
According to legend, Sidon is the location of Zeus’s theriomorphic transformation into a bull and subsequent abduction of the Tyrian princess Europa. The pair crossed the Mediterranean to Crete, where she gave birth to King Minos, who heralded the beginning of the Minoan civilisation.
Similar to Knossos, the central court at the Minoan trading centre of Kato Zakro’s has an orientation that aligns toward a major Minoan trade contact along traditional navigational stars, while being exactly oriented with the Etesian winds. A rhumb line toward the ancient city of Pelusium (Tel Farama), at the mouth of the Pellusiac branch of the River Nile, was at the constant azimuth, precisely aligned with the central court orientation.
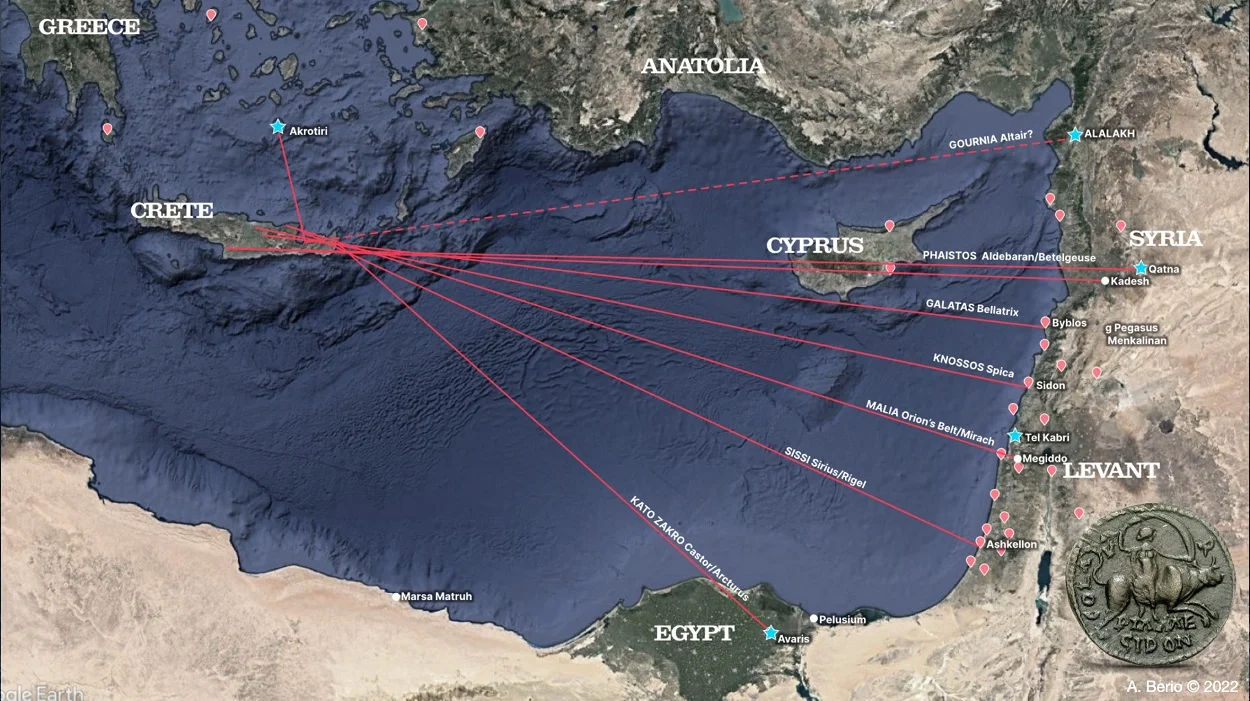
These discoveries demonstrate the sophisticated navigational abilities of the Minoans, which may have included the use of a star compass similar to those found in the Caroline islands, north of New Guinea. It also challenges the commonly-held belief about the limitations of open-sea navigation, mathematics and interregional trade in the Bronze Age.
Further research is needed to fully understand the link between specific Minoan palaces and partner cities, as well as the celestial navigation techniques used by the civilisation.
However, this study provides a fascinating glimpse into the economic and maritime heart of Minoan culture, and the powerful role celestial navigation played in the rise of this ancient civilisation.
The study concludes that the central courts of the palaces were primarily aligned toward important star paths aimed at distant coastal emporia such as Byblos and Sidon. This research has the potential to shed light on the trade networks and cultural exchanges that occurred in the ancient world and indicate the celestial navigation was being utilised a thousand years before the first historical mentions in Homer’s Odyssey.
Header Image Credit : Alessandro Berio
http://maajournal.com/Issues/2022/Vol22-3/9_Berio_22(3).pdf







