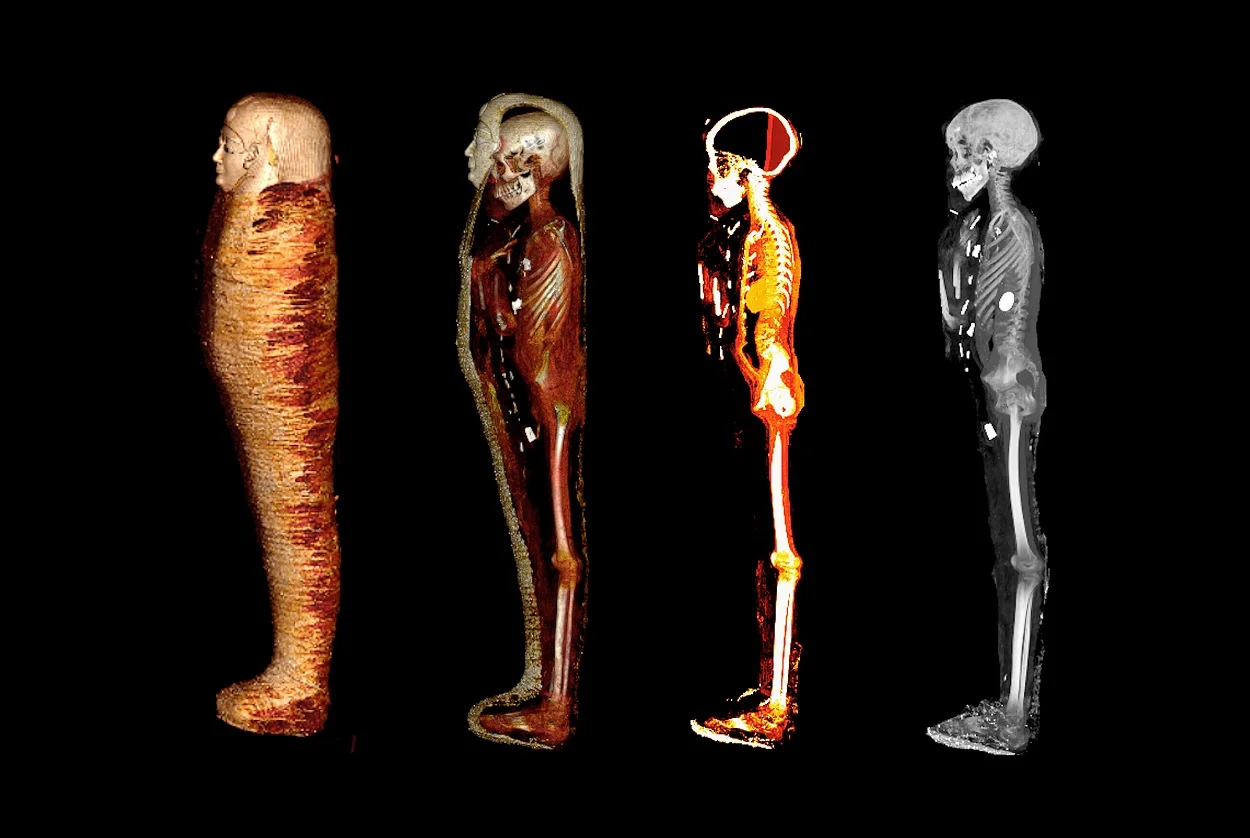
A CT scan has revealed that a 2,300-year-old Ancient Egyptian mummy has 49 amulets placed within the body.
The team used a computerised tomography (CT) to ‘digitally unwrap’ an undisturbed mummy known as “Golden Boy”.
The ’Golden boy’ mummy dates from 332 to 30 BC and was discovered by archaeologists in 1916 at Nag el-Hassay in southern Egypt. The mummy was placed in the basement of the Egyptian Museum in Cairo, where it has remained unexamined until now.
The CT scan has revealed that the mummy was laid inside two coffins: an outer coffin with a Greek inscription, and an inner wooden sarcophagus. Apart from the heart, the viscera had been removed through an incision, while the brain had been removed through the nose and replaced with resin.
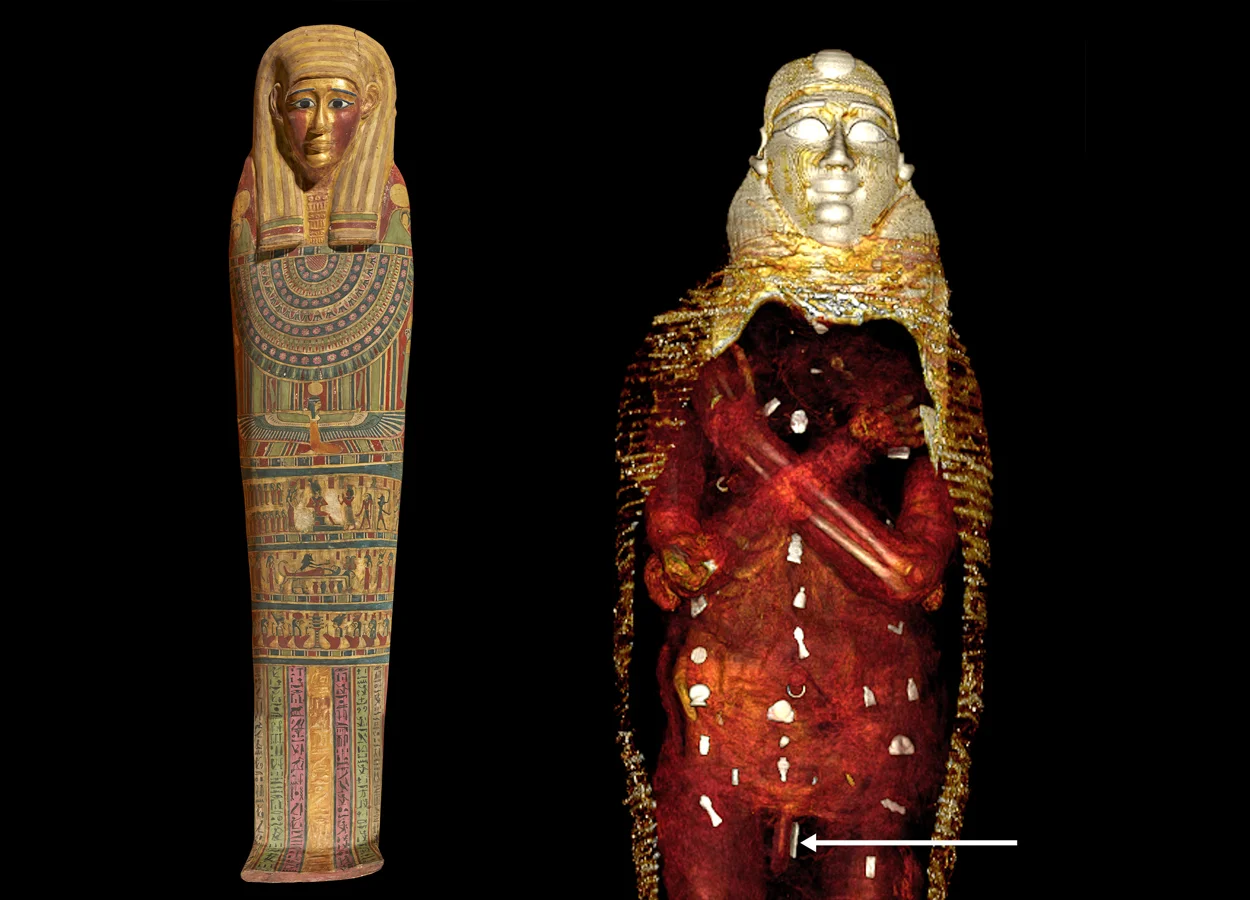

Within, a gilded head mask was placed on the head, while a pair of sandals was placed on the feet and was garlanded with ferns. “The sandals were probably meant to enable the boy to walk out of the coffin. According to the ancient Egyptians’ ritual Book of The Dead, the deceased had to wear white sandals to be pious and clean before reciting its verses,” said Dr Sahar Saleem at the Faculty of Medicine of Cairo University, Egypt.
’Golden boy’ was sent on his way to the afterlife with 48 amulets of 21 types to promote his bodily resurrection. The amulets have been placed in three columns between the folds of the wrappings and inside the mummy’s body cavity.
These include the Eye of Horus, the scarab, the akhet amulet of the horizon, the placenta, the Knot of Isis, and others. Many were made of gold, while some were made of semiprecious stones, fired clay, or faience.
A golden tongue leaf was also placed inside the mouth to ensure that ’Golden boy’ could speak in the afterlife, while a two-finger amulet was placed beside his penis to protect the embalming incision.
The CT scans have also shown that ’Golden boy’ was 128 cm tall, not circumcised, and without any known cause of death other than natural causes. From the degree of bone fusion and the non-erupted wisdom teeth, the authors estimate that the boy was between 14 and 15 years old.
Header Image Credit : SN SALEEM