A study published in the journal Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences reveals new manufacturing techniques on how craftsmen in Denmark recycled glass from Roman glass mosaics during the 8th century AD.
Glass became a scarce commodity during the Early Medieval Period, with mosaics in abandoned Roman and Byzantine structures often looted for the coloured glass cubes called tesserae. A trading network transported them north to emporia towns such as Ribe in Denmark, where they were melted down in large vessels and shaped into decorative beads.
Until now, archaeologists have assumed that the beadmakers used the opaque white tesserae as raw materials for the production of white, opaque beads. However, a new study of an early beadmaking worship in Ribe by Aarhus University has revealed that the chemical composition of white Viking beads was produced by crushing gold-gilded transparent tesserae which was then re-melted at low temperatures.
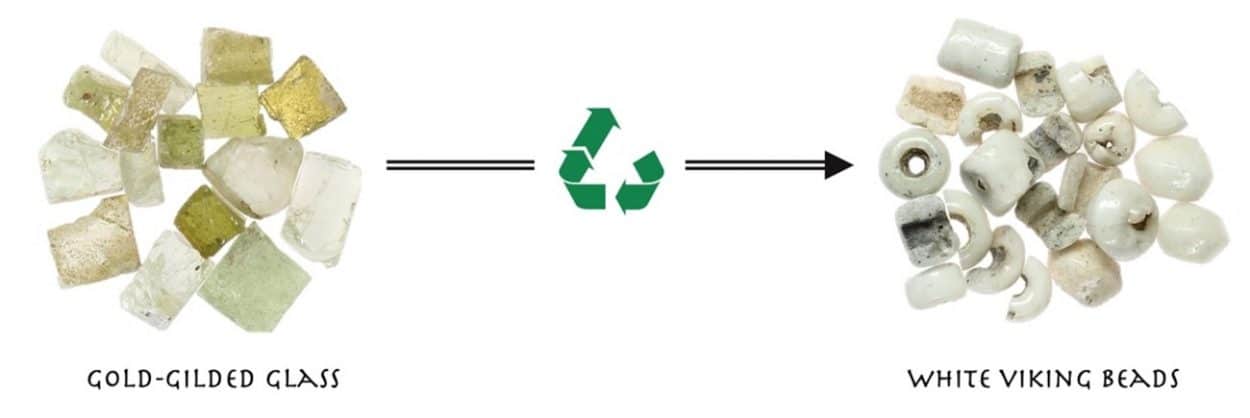
The melted glass would then be stirred to trap air in the form of bubbles, and then wrapped around an iron mandrel to form the beads. The thin sheets of gold on the tesserae were removed prior to the re-melting process, however, the study shows that some gold still inevitably ended up in the melting pot. This process is indicated by the tiny drops of gold in the white beads, the many air holes (which is why the beads are opaque), as well no chemical colour tracers present.
Traces of gold was also found in the blue beads from the same workshop. Here the chemistry shows that the glassmaker’s recipe consisted of a mixture of the blue and golden mosaic stones.
Mixing them was necessary because the Roman blue mosaic stones contained high concentrations of chemical substances which made them opaque – and therefore ideal for mosaics, but not for blue beads. By thus diluting the chemical substances, the result was the deep blue, transparent glass that we know from Viking Age beads.
Claus Feveile, from the Museum of Southwest Jutland said: “These exciting results clearly show the potential of elucidating new facts about the Vikings. By combining our high-resolution excavations with such chemical analyses I predict many more revelations in the near future.”
https://doi.org/10.1007/s12520-022-01646-8
Header Image Credit : Shutterstock (Copyright)





