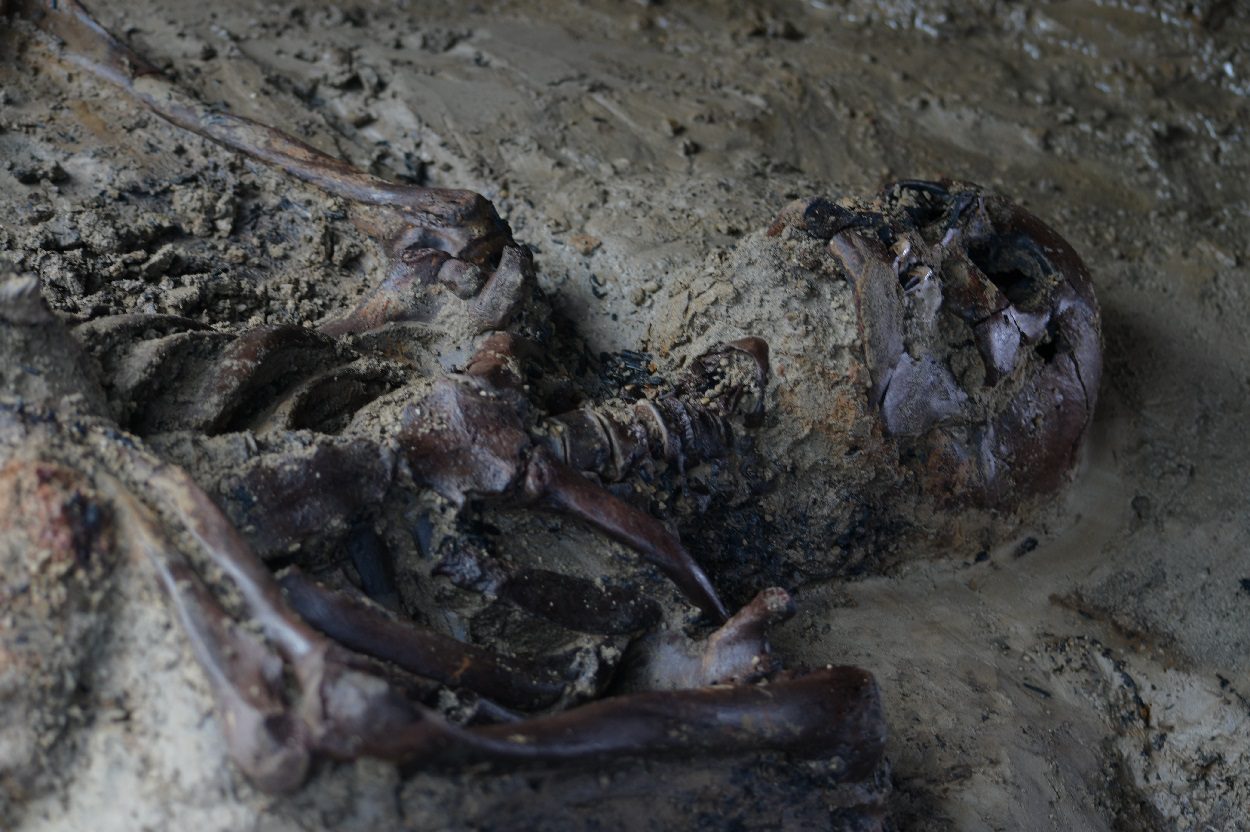
Archaeologists excavating the Roman coastal retreat of Herculaneum have unearthed the remains of a victim from the Vesuvius eruption in AD 79.
Although the town was smaller than the city of Pompeii, Herculaneum was a wealthy resort for the Roman elite, reflected in their grand and luxurious villas. During the eruption of Mount Vesuvius, the town was buried under thick layers of ash and pumice, followed by pyroclastic material that carbonised organic remains.
Based on letters by Pliny the Younger (a lawyer, author, and magistrate of Rome), Mount Vesuvius began erupting at around 1:00 pm, which scientists predict would have released a deadly cloud of super-heated tephra and gases to a height of 33 km (21 mi) – ejecting molten rock, pulverized pumice and hot ash at 1.5 million tons per second, ultimately releasing 100,000 times the thermal energy of the Hiroshima-Nagasaki bombings.
Previous excavations in the 1980’s of the towns shoreline discovered skeletons on the beach and in the first six so-called boat sheds. Archaeologists at the time suggested that these victims were waiting for rescue, when they were killed instantly from the heat generated by a pyroclastic flow att temperatures of around 500 °C.
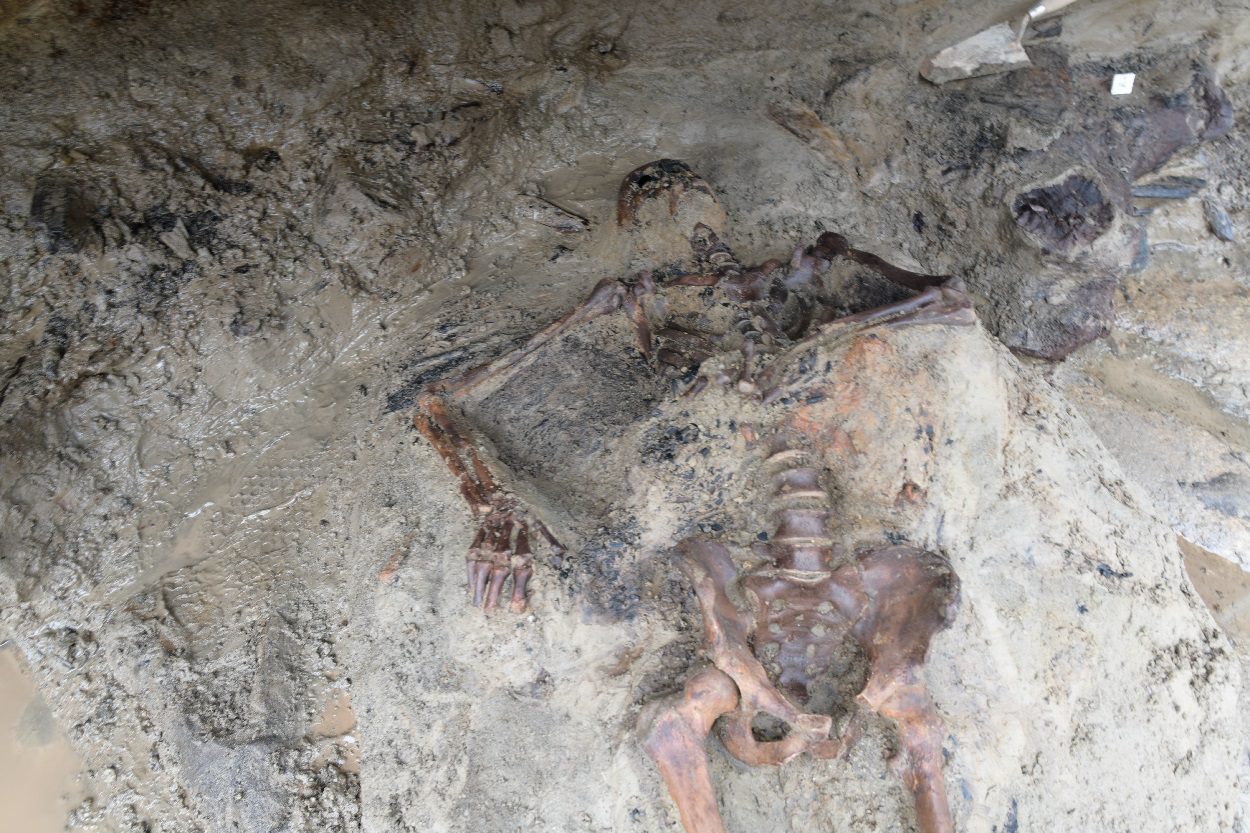

For the first time since the 1980’s excavations, archaeologists have started to explore the periphery of the town, focusing again on the beachfront where they discovered the remains of a man aged between 40-45 years of age.
Studies suggest that the victim’s body was either already on the shoreline, or was dragged by the force of the eruption and deposited with material from the town that was transported by the pyroclastic flow.
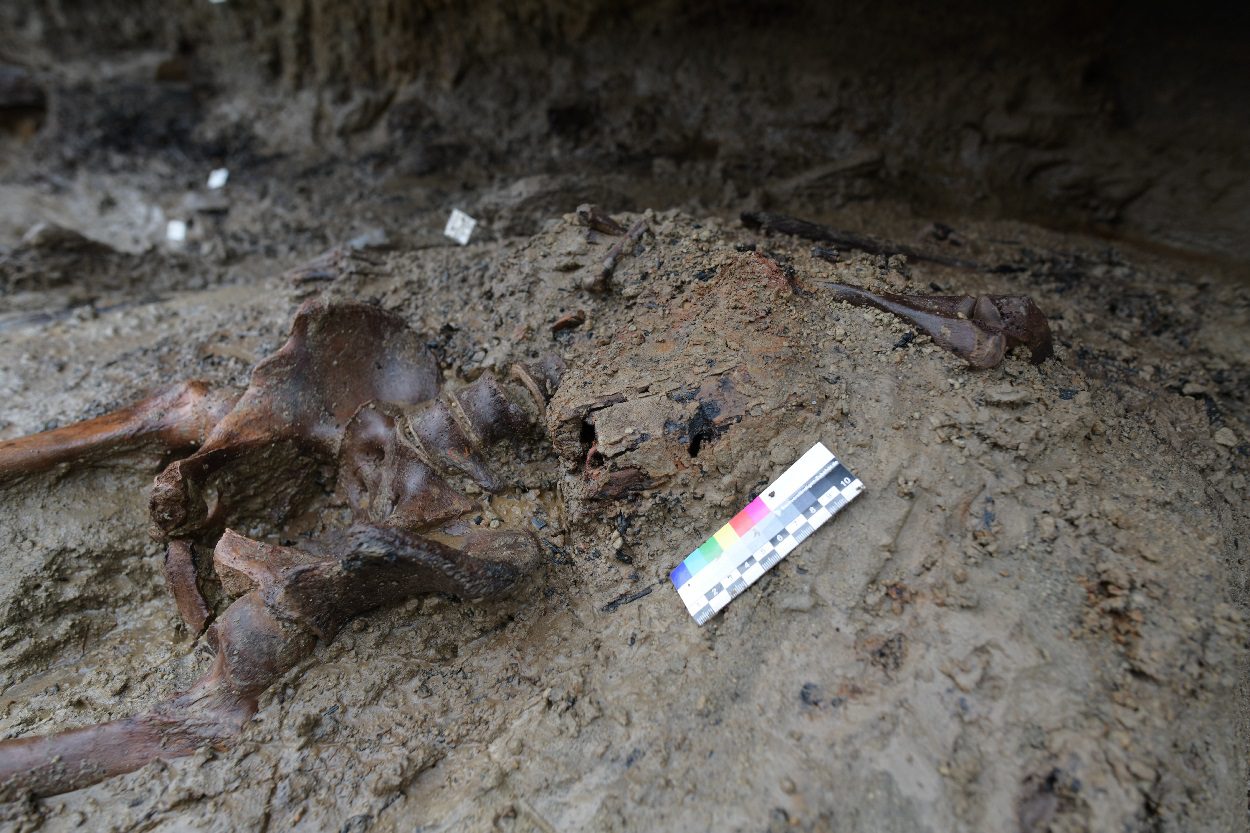
The body shows indications of numerous fractures, whilst the high temperatures caused the immediate evaporation of the tissues and internal organs, leaving only the skeleton imprisoned in a mass of ash, gas and entrained debris. Alongside the skeleton was a cloth shoulder bag, where an analysis has identified various materials: a wooden box containing objects in metal, pieces of cloth and probable traces of gold finish.

The Manager of the Herculaneum Conservation Project Jane Thompson said: “The Packard Humanities Institute in recent years has concentrated its energies precisely on the boundaries of the site because, as in the case of the ancient beach, the explorations had been partial and had left unresolved and critical conditions.”
“This is a modern excavation,” says Francesco Sirano, the director of the archaeological park, describing it as “a multidisciplinary open-air laboratory” in which each phase of work is systematically documented and surveyed to give a snapshot of the tragedy that unfolded on the beach.
Archaeological Park of Herculaneum
Header Image Credit : Archaeological Park of Herculaneum